“MakeltTalk: speaker-aware talking-head animation” by Zhou, Han, Shechtman, Echevarria, Kalogerakis, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- MakeltTalk: speaker-aware talking-head animation
Session/Category Title: Hands and Faces
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
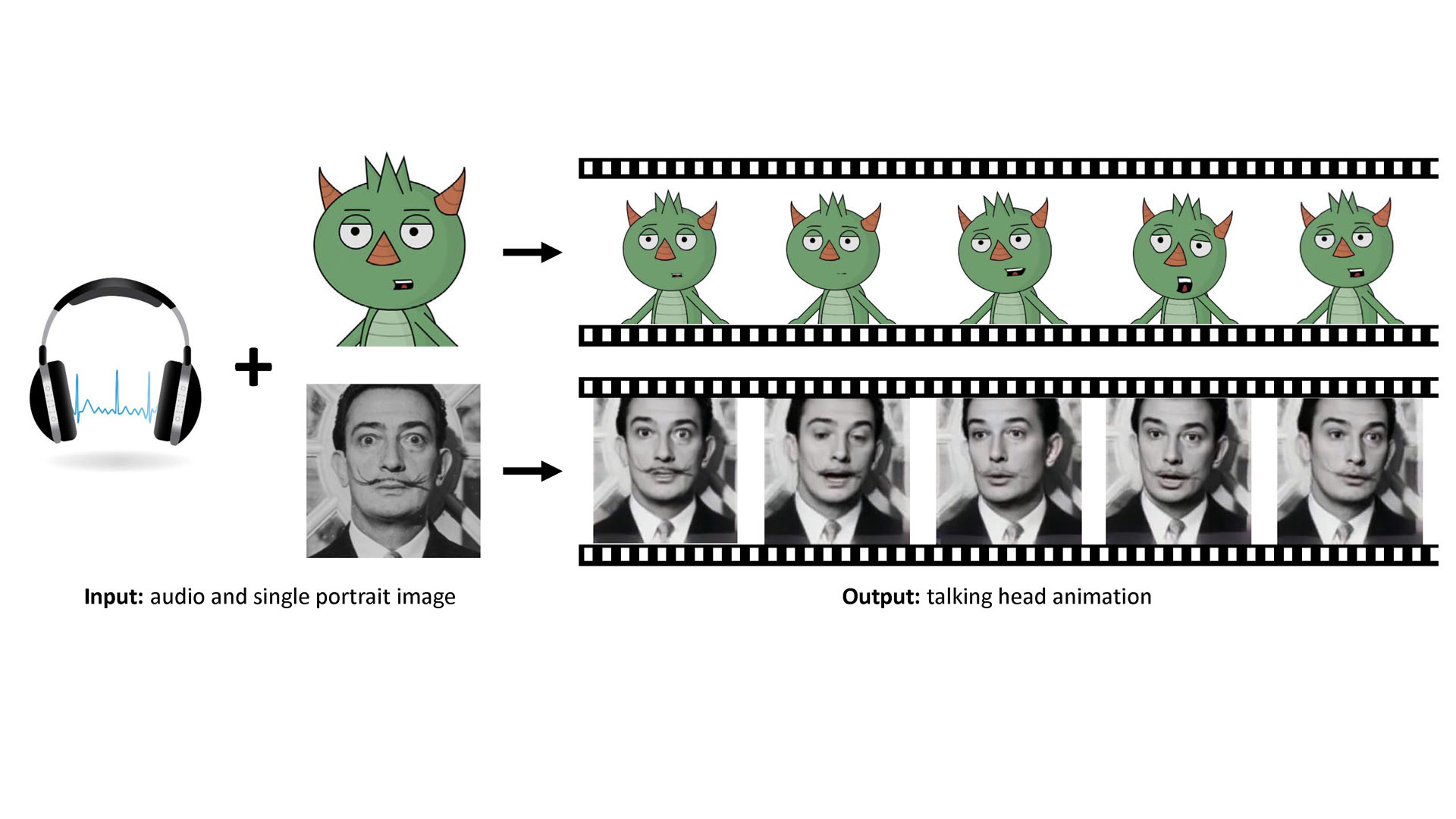
We present a method that generates expressive talking-head videos from a single facial image with audio as the only input. In contrast to previous attempts to learn direct mappings from audio to raw pixels for creating talking faces, our method first disentangles the content and speaker information in the input audio signal. The audio content robustly controls the motion of lips and nearby facial regions, while the speaker information determines the specifics of facial expressions and the rest of the talking-head dynamics. Another key component of our method is the prediction of facial landmarks reflecting the speaker-aware dynamics. Based on this intermediate representation, our method works with many portrait images in a single unified framework, including artistic paintings, sketches, 2D cartoon characters, Japanese mangas, and stylized caricatures. In addition, our method generalizes well for faces and characters that were not observed during training. We present extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluation of our method, in addition to user studies, demonstrating generated talking-heads of significantly higher quality compared to prior state-of-the-art methods.
References:
1. Shruti Agarwal, Hany Farid, Yuming Gu, Mingming He, Koki Nagano, and Hao Li. 2019. Protecting World Leaders Against Deep Fakes. In Proc. CVPRW.Google Scholar
2. Hadar Averbuch-Elor, Daniel Cohen-Or, Johannes Kopf, and Michael F Cohen. 2017. Bringing portraits to life. ACM Trans. Graphics (2017).Google Scholar
3. Thabo Beeler and Derek Bradley. 2014. Rigid stabilization of facial expressions. ACM Trans. Graphics (2014).Google Scholar
4. Matthew Brand. 1999. Voice puppetry. In Proc. SIGGRAPH.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Adrian Bulat and Georgios Tzimiropoulos. 2017. How far are we from solving the 2d & 3d face alignment problem? (and a dataset of 230,000 3d facial landmarks). In Proc. ICCV.Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Lele Chen, Zhiheng Li, Ross K Maddox, Zhiyao Duan, and Chenliang Xu. 2018. Lip movements generation at a glance. In Proc. ECCV.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Lele Chen, Ross K Maddox, Zhiyao Duan, and Chenliang Xu. 2019. Hierarchical cross-modal talking face generation with dynamic pixel-wise loss. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Joon Son Chung, Amir Jamaludin, and Andrew Zisserman. 2017. You said that?. In Proc. BMVC.Google Scholar
9. Joon Son Chung, Arsha Nagrani, and Andrew Zisserman. 2018. VoxCeleb2: Deep Speaker Recognition. In Proc. INTERSPEECH.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. Daniel Cudeiro, Timo Bolkart, Cassidy Laidlaw, Anurag Ranjan, and Michael J Black. 2019. Capture, Learning, and Synthesis of 3D Speaking Styles. In Proc. CVPR.Google Scholar
11. Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee, and Kristina Toutanova. 2018. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv:1810.04805 (2018).Google Scholar
12. Pif Edwards, Chris Landreth, Eugene Fiume, and Karan Singh. 2016. JALI: an animator-centric viseme model for expressive lip synchronization. ACM Trans. Graphics (2016).Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Paul Ekman and Wallace V Friesen. 1978. Facial action coding system: a technique for the measurement of facial movement. (1978).Google Scholar
14. Sefik Emre Eskimez, Ross K Maddox, Chenliang Xu, and Zhiyao Duan. 2018. Generating talking face landmarks from speech. In Proc. LVA/ICA.Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Sefik Emre Eskimez, Ross K Maddox, Chenliang Xu, and Zhiyao Duan. 2019. Noise-Resilient Training Method for Face Landmark Generation From Speech. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, and Language Processing (2019).Google Scholar
16. Patrick Esser, Ekaterina Sutter, and Björn Ommer. 2018. A variational u-net for conditional appearance and shape generation. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarCross Ref
17. Gary Faigin. 2012. The artist’s complete guide to facial expression. Watson-Guptill.Google Scholar
18. Jakub Fišer, Ondřej Jamriška, David Simons, Eli Shechtman, Jingwan Lu, Paul Asente, Michal Lukáč, and Daniel Sýkora. 2017. Example-Based Synthesis of Stylized Facial Animations. ACM Trans. Graphics (2017).Google Scholar
19. Chuang Gan, Deng Huang, Peihao Chen, Joshua B Tenenbaum, and Antonio Torralba. 2020a. Foley Music: Learning to Generate Music from Videos. ECCV (2020).Google Scholar
20. Chuang Gan, Deng Huang, Hang Zhao, Joshua B Tenenbaum, and Antonio Torralba. 2020b. Music Gesture for Visual Sound Separation. In CVPR. 10478–10487.Google Scholar
21. Pablo Garrido, Levi Valgaerts, Hamid Sarmadi, Ingmar Steiner, Kiran Varanasi, Patrick Perez, and Christian Theobalt. 2015. Vdub: Modifying face video of actors for plausible visual alignment to a dubbed audio track. In Computer graphics forum.Google Scholar
22. Shiry Ginosar, Amir Bar, Gefen Kohavi, Caroline Chan, Andrew Owens, and Jitendra Malik. 2019. Learning Individual Styles of Conversational Gesture. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarCross Ref
23. Alex Graves and Navdeep Jaitly. 2014. Towards end-to-end speech recognition with recurrent neural networks. In Proc. ICML.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. David Greenwood, Iain Matthews, and Stephen Laycock. 2018. Joint learning of facial expression and head pose from speech. Interspeech.Google Scholar
25. Xintong Han, Zuxuan Wu, Weilin Huang, Matthew R Scott, and Larry S Davis. 2019. FiNet: Compatible and Diverse Fashion Image Inpainting. In Proc. ICCV.Google ScholarCross Ref
26. Phillip Isola, Jun-Yan Zhu, Tinghui Zhou, and Alexei A Efros. 2017. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Justin Johnson, Alexandre Alahi, and Li Fei-Fei. 2016. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In Proc. ECCV.Google ScholarCross Ref
28. Tero Karras, Timo Aila, Samuli Laine, Antti Herva, and Jaakko Lehtinen. 2017. Audio-driven facial animation by joint end-to-end learning of pose and emotion. ACM Trans. Graphics (2017).Google Scholar
29. Hyeongwoo Kim, Mohamed Elgharib, Michael Zollhöfer, Hans-Peter Seidel, Thabo Beeler, Christian Richardt, and Christian Theobalt. 2019. Neural style-preserving visual dubbing. ACM Trans. Graphics (2019).Google Scholar
30. Yilong Liu, Feng Xu, Jinxiang Chai, Xin Tong, Lijuan Wang, and Qiang Huo. 2015. Video-audio driven real-time facial animation. ACM Trans. Graphics (2015).Google Scholar
31. Laurens van der Maaten and Geoffrey Hinton. 2008. Visualizing data using t-SNE. JMLR (2008).Google Scholar
32. Xudong Mao, Qing Li, Haoran Xie, Raymond YK Lau, Zhen Wang, and Stephen Paul Smolley. 2017. Least squares generative adversarial networks. In Proc. ICCV.Google ScholarCross Ref
33. Harry McGurk and John MacDonald. 1976. Hearing lips and seeing voices. Nature (1976).Google Scholar
34. Notevibes. 2020. Text to Speech converter. https://notevibes.com/.Google Scholar
35. Hai Xuan Pham, Yuting Wang, and Vladimir Pavlovic. 2018. End-to-end learning for 3d facial animation from speech. In Proc. ICMI.Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Albert Pumarola, Antonio Agudo, Aleix M Martinez, Alberto Sanfeliu, and Francesc Moreno-Noguer. 2018. Ganimation: Anatomically-aware facial animation from a single image. In Proc. ECCV.Google ScholarCross Ref
37. Kaizhi Qian, Yang Zhang, Shiyu Chang, Xuesong Yang, and Mark Hasegawa-Johnson. 2019. AUTOVC: Zero-Shot Voice Style Transfer with Only Autoencoder Loss. In Proc. ICML. 5210–5219.Google Scholar
38. Olaf Ronneberger, Philipp Fischer, and Thomas Brox. 2015. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proc. MICCAI.Google ScholarCross Ref
39. Aleksandr Segal, Dirk Haehnel, and Sebastian Thrun. 2009. Generalized-icp., In Proc. Robotics: science and systems.Google ScholarCross Ref
40. Soumyadip Sengupta, Vivek Jayaram, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz, and Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman. 2020. Background Matting: The World is Your Green Screen. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarCross Ref
41. Takaaki Shiratori, Atsushi Nakazawa, and Katsushi Ikeuchi. 2006. Dancing-to-music character animation. In Computer Graphics Forum.Google Scholar
42. Aliaksandr Siarohin, Stéphane Lathuilière, Sergey Tulyakov, Elisa Ricci, and Nicu Sebe. 2019. First Order Motion Model for Image Animation. In Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS).Google Scholar
43. Karen Simonyan and Andrew Zisserman. 2014. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proc. ICLR.Google Scholar
44. Yang Song, Jingwen Zhu, Dawei Li, Andy Wang, and Hairong Qi. 2019. Talking Face Generation by Conditional Recurrent Adversarial Network. In Proc. IJCAI.Google ScholarCross Ref
45. Olga Sorkine. 2006. Differential representations for mesh processing. In Computer Graphics Forum.Google Scholar
46. Yannis Stylianou. 2009. Voice transformation: a survey. In Proc. ICASSP.Google ScholarDigital Library
47. Supasorn Suwajanakorn, Steven M Seitz, and Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman. 2017. Synthesizing obama: learning lip sync from audio. ACM Trans. Graphics (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
48. Sarah Taylor, Taehwan Kim, Yisong Yue, Moshe Mahler, James Krahe, Anastasio Garcia Rodriguez, Jessica Hodgins, and Iain Matthews. 2017. A deep learning approach for generalized speech animation. ACM Trans. Graphics (2017).Google Scholar
49. Justus Thies, Mohamed Elgharib, Ayush Tewari, Christian Theobalt, and Matthias Nießner. 2020. Neural Voice Puppetry: Audio-driven Facial Reenactment. In Proc. CVPR, to appear.Google ScholarCross Ref
50. Justus Thies, Michael Zollhofer, Marc Stamminger, Christian Theobalt, and Matthias Nießner. 2016. Face2face: Real-time face capture and reenactment of rgb videos. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarDigital Library
51. Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. Attention is all you need. In Proc. NeurIPS.Google Scholar
52. Christophe Veaux, Junichi Yamagishi, Kirsten MacDonald, et al. 2016. Superseded-cstr vctk corpus: English multi-speaker corpus for cstr voice cloning toolkit. (2016).Google Scholar
53. Konstantinos Vougioukas, Stavros Petridis, and Maja Pantic. 2019. Realistic Speech-Driven Facial Animation with GANs. IJCV (2019).Google Scholar
54. Marilyn A Walker, Janet E Cahn, and Stephen J Whittaker. 1997. Improvising linguistic style: Social and affective bases for agent personality. In Proc. IAA.Google Scholar
55. Li Wan, Quan Wang, Alan Papir, and Ignacio Lopez Moreno. 2018. Generalized end-to-end loss for speaker verification. In Proc. ICASSP.Google ScholarCross Ref
56. Chung-Yi Weng, Brian Curless, and Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman. 2019. Photo wake-up: 3d character animation from a single photo. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarCross Ref
57. Jordan Yaniv, Yael Newman, and Ariel Shamir. 2019. The face of art: landmark detection and geometric style in portraits. ACM Trans. Graphics (2019).Google ScholarDigital Library
58. Egor Zakharov, Aliaksandra Shysheya, Egor Burkov, and Victor Lempitsky. 2019. Few-Shot Adversarial Learning of Realistic Neural Talking Head Models. In Proc. ICCV.Google ScholarCross Ref
59. Hang Zhou, Yu Liu, Ziwei Liu, Ping Luo, and Xiaogang Wang. 2019. Talking face generation by adversarially disentangled audio-visual representation. In Proc. AAAI.Google ScholarDigital Library
60. Yang Zhou, Zhan Xu, Chris Landreth, Evangelos Kalogerakis, Subhransu Maji, and Karan Singh. 2018. Visemenet: Audio-driven animator-centric speech animation. ACM Trans. Graphics (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library