“Neural light field 3D printing” by Zheng, Babaei, Wetzstein, Seidel, Zwicker, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Neural light field 3D printing
Session/Category Title: Fabrication: Carving, Dicing, and Printing
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
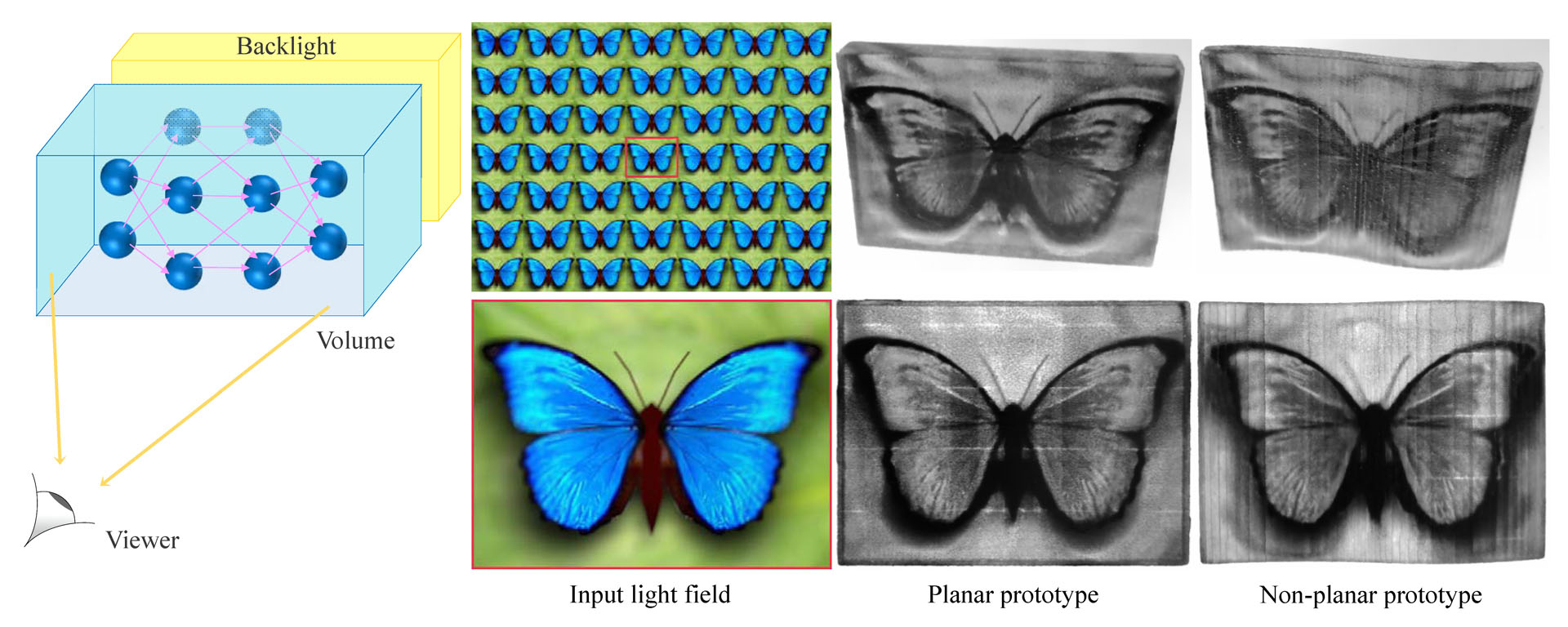
Modern 3D printers are capable of printing large-size light-field displays at high-resolutions. However, optimizing such displays in full 3D volume for a given light-field imagery is still a challenging task. Existing light field displays optimize over relatively small resolutions using a few co-planar layers in a 2.5D fashion to keep the problem tractable. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end optimization approach that encodes input light field imagery as a continuous-space implicit representation in a neural network. This allows fabricating high-resolution, attenuation-based volumetric displays that exhibit the target light fields. In addition, we incorporate the physical constraints of the material to the optimization such that the result can be printed in practice. Our simulation experiments demonstrate that our approach brings significant visual quality improvement compared to the multilayer and uniform grid-based approaches. We validate our simulations with fabricated prototypes and demonstrate that our pipeline is flexible enough to allow fabrications of both planar and non-planar displays.
References:
1. Martín Abadi, Ashish Agarwal, Paul Barham, Eugene Brevdo, and et al. 2015. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. https://www.tensorflow.org/ Software available from tensorflow.org.Google Scholar
2. Vahid Babaei, Kiril Vidimče, Michael Foshey, Alexandre Kaspar, Piotr Didyk, and Wojciech Matusik. 2017. Color Contoning for 3D Printing. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (July 2017), 124:1–124:15. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Ilya Baran, Philipp Keller, Derek Bradley, Stelian Coros, Wojciech Jarosz, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Markus Gross. 2012. Manufacturing layered attenuators for multiple prescribed shadow images. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 31. Wiley Online Library, 603–610.Google Scholar
4. Peter C Barnum, Srinivasa G Narasimhan, and Takeo Kanade. 2010. A multi-layered display with water drops. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2010 papers. 1–7.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Yoshua Bengio, Aaron Courville, and Pascal Vincent. 2012. Representation Learning: A Review and New Perspectives. arXiv:1206.5538 [cs.LG]Google Scholar
6. BG Blundell, AJ Schwarz, and DK Horrell. 1993. Volumetric threedimensional display systems: their past present and future. Engineering Science & Education Journal 2, 5 (1993), 196–200.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Barry G Blundell, Adam J Schwarz, and Damon K Horrell. 1994. Cathode ray sphere: a prototype system to display volumetric three-dimensional images. Optical Engineering 33, 1 (1994), 180–187.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Alan Brunton, Can Ates Arikan, and Philipp Urban. 2015. Pushing the Limits of 3D Color Printing: Error Diffusion with Translucent Materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 1 (Dec. 2015), 4:1–4:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Thomas F Coleman and Yuying Li. 1996. A reflective Newton method for minimizing a quadratic function subject to bounds on some of the variables. SIAM Journal on Optimization 6, 4 (1996), 1040–1058.Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Oliver S Cossairt, Joshua Napoli, Samuel L Hill, Rick K Dorval, and Gregg E Favalora. 2007. Occlusion-capable multiview volumetric three-dimensional display. Applied optics 46, 8 (2007), 1244–1250.Google Scholar
11. Robert A Drebin, Loren Carpenter, and Pat Hanrahan. 1988. Volume rendering. ACM Siggraph Computer Graphics 22, 4 (1988), 65–74.Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Oskar Elek, Denis Sumin, Ran Zhang, Tim Weyrich, Karol Myszkowski, Bernd Bickel, Alexander Wilkie, and Jaroslav Křivánek. 2017. Scattering-aware Texture Reproduction for 3D Printing. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6, Article 241 (Nov. 2017), 15 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Gregg E Favalora. 2005. Volumetric 3D displays and application infrastructure. Computer 38, 8 (2005), 37–44.Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Ioannis Gkioulekas, Shuang Zhao, Kavita Bala, Todd Zickler, and Anat Levin. 2013. Inverse volume rendering with material dictionaries. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 6 (2013), 1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Xavier Glorot and Yoshua Bengio. 2010. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics. 249–256.Google Scholar
16. Steven J Gortler, Radek Grzeszczuk, Richard Szeliski, and Michael F Cohen. 1996. The lumigraph. In Proceedings of the 23rd annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 43–54.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Hironobu Gotoda. 2010. A multilayer liquid crystal display for autostereoscopic 3D viewing. In Stereoscopic Displays and Applications XXI, Vol. 7524. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 75240P.Google ScholarCross Ref
18. K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun. 2016. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 770–778.Google Scholar
19. Michael Holroyd, Ilya Baran, Jason Lawrence, and Wojciech Matusik. 2011. Computing and fabricating multilayer models. In Proceedings of the 2011 SIGGRAPH Asia Conference. 1–8.Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Youngjin Jo, Seungjae Lee, Dongheon Yoo, Suyeon Choi, Dongyeon Kim, and Byoungho Lee. 2019. Tomographic projector: large scale volumetric display with uniform viewing experiences. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6 (2019), 1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Andrew Jones, Ian McDowall, Hideshi Yamada, Mark Bolas, and Paul Debevec. 2007. Rendering for an interactive 360 light field display. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 papers. 40-es.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Simon Kallweit, Thomas Müller, Brian Mcwilliams, Markus Gross, and Jan Novák. 2017. Deep Scattering: Rendering Atmospheric Clouds with Radiance-Predicting Neural Networks. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6, Article 231 (Nov. 2017), 11 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Diederik P Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2014. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014).Google Scholar
24. Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. 2012. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In NIPS.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Douglas Lanman, Matthew Hirsch, Yunhee Kim, and Ramesh Raskar. 2010. Content-adaptive parallax barriers: optimizing dual-layer 3D displays using low-rank light field factorization. In ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2010 papers. 1–10.Google Scholar
26. Douglas Lanman, Gordon Wetzstein, Matthew Hirsch, Wolfgang Heidrich, and Ramesh Raskar. 2011. Polarization fields: dynamic light field display using multi-layer LCDs. In Proceedings of the 2011 SIGGRAPH Asia Conference. 1–10.Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Yann LeCun, Y. Bengio, and Geoffrey Hinton. 2015. Deep Learning. Nature 521 (05 2015), 436–44. Google ScholarCross Ref
28. Marc Levoy and Pat Hanrahan. 1996. Light field rendering. In Proceedings of the 23rd annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 31–42.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Lingjie Liu, Jiatao Gu, Kyaw Zaw Lin, Tat-Seng Chua, and Christian Theobalt. 2020. Neural Sparse Voxel Fields. arXiv:2007.11571Google Scholar
30. Stephen Lombardi, Tomas Simon, Jason Saragih, Gabriel Schwartz, Andreas Lehrmann, and Yaser Sheikh. 2019. Neural Volumes: Learning Dynamic Renderable Volumes from Images. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4, Article 65 (July 2019), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. A Loukianitsa and Andrey N Putilin. 2002. Stereodisplay with neural network image processing. In Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems IX, Vol. 4660. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 207–211.Google ScholarCross Ref
32. Hiroyuki Maeda, Kazuhiko Hirose, Jun Yamashita, Koichi Hirota, and Michitaka Hirose. 2003. All-around display for video avatar in real world. In The Second IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, 2003. Proceedings. IEEE, 288–289.Google ScholarCross Ref
33. Stéphane Mallat. 1999. A wavelet tour of signal processing. Elsevier.Google Scholar
34. Kshitij Marwah, Gordon Wetzstein, Yosuke Bando, and Ramesh Raskar. 2013. Compressive light field photography using overcomplete dictionaries and optimized projections. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4 (2013), 1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Ben Mildenhall, Pratul P. Srinivasan, Rodrigo Ortiz-Cayon, Nima Khademi Kalantari, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Ren Ng, and Abhishek Kar. 2019. Local Light Field Fusion: Practical View Synthesis with Prescriptive Sampling Guidelines. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4, Article 29 (July 2019), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Ben Mildenhall, Pratul P. Srinivasan, Matthew Tancik, Jonathan T. Barron, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Ren Ng. 2020. NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis. arXiv:2003.08934 [cs.CV]Google Scholar
37. Niloy J Mitra and Mark Pauly. 2009. Shadow art. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 28, 5 (2009), 1–7.Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Shree K Nayar and Vijay N Anand. 2007. 3D display using passive optical scatterers. Computer 40, 7 (2007), 54–63.Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Ren Ng, Marc Levoy, Mathieu Brédif, Gene Duval, Mark Horowitz, Pat Hanrahan, et al. 2005. Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera. Computer Science Technical Report CSTR 2, 11 (2005), 1–11.Google Scholar
40. Victor Ostromoukhov. 2001. A simple and efficient error-diffusion algorithm. In Proceedings of the 28th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 567–572.Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Matt Pharr, Wenzel Jakob, and Greg Humphreys. 2016. Physically Based Rendering: From Theory to Implementation (3 ed.). Morgan Kaufmann.Google Scholar
42. Nasim Rahaman, Aristide Baratin, Devansh Arpit, Felix Draxler, Min Lin, Fred A. Hamprecht, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville. 2018. On the Spectral Bias of Neural Networks. arXiv:1806.08734Google Scholar
43. Artin Saberpour, Roger D Hersch, Jiajing Fang, Rhaleb Zayer, Hans-Peter Seidel, and Vahid Babaei. 2020. Fabrication of moiré on curved surfaces. Optics Express 28, 13 (2020), 19413–19427.Google ScholarCross Ref
44. Liang Shi, Vahid Babaei, Changil Kim, Michael Foshey, Yuanming Hu, Pitchaya Sitthi-Amorn, Szymon Rusinkiewicz, and Wojciech Matusik. 2018. Deep multispectral painting reproduction via multi-layer, custom-ink printing. ACM Transactions on Graphics 37, 6 (Dec. 2018), 271:1–271:15. Google ScholarDigital Library
45. Vincent Sitzmann, Michael Zollhöfer, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2019. Scene representation networks: Continuous 3d-structure-aware neural scene representations. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 1121–1132.Google Scholar
46. Pratul P. Srinivasan, Ben Mildenhall, Matthew Tancik, Jonathan T. Barron, Richard Tucker, and Noah Snavely. 2020. Lighthouse: Predicting Lighting Volumes for Spatially-Coherent Illumination. In CVPR.Google Scholar
47. Stratasys. 2020. Stratasys ultimate full-color multi-material 3D printer. https://www.stratasys.com/3d-printers/j8-series. [Online; Accessed 15-05-2020].Google Scholar
48. Denis Sumin, Tobias Rittig, Vahid Babaei, Thomas Nindel, Alexander Wilkie, Piotr Didyk, Bernd Bickel, Jaroslav Křivánek, Karol Myszkowski, and Tim Weyrich. 2019. Geometry-Aware Scattering Compensation for 3D Printing. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4, Article 111 (July 2019), 14 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
49. Matthew Tancik, Pratul P Srinivasan, Ben Mildenhall, Sara Fridovich-Keil, Nithin Raghavan, Utkarsh Singhal, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Jonathan T Barron, and Ren Ng. 2020. Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.10739 (2020).Google Scholar
50. James Tompkin, Simon Heinzle, Jan Kautz, and Wojciech Matusik. 2013. Content-adaptive lenticular prints. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4 (2013), 1–10.Google ScholarDigital Library
51. Zhou Wang, Alan C Bovik, Hamid R Sheikh, and Eero P Simoncelli. 2004. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE transactions on image processing 13, 4 (2004), 600–612.Google ScholarDigital Library
52. Gordon Wetzstein, Douglas Lanman, Wolfgang Heidrich, and Ramesh Raskar. 2011. Layered 3D: tomographic image synthesis for attenuation-based light field and high dynamic range displays. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2011 papers. 1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
53. Gordon Wetzstein, Douglas Lanman, Matthew Hirsch, and Ramesh Raskar. 2012. Tensor displays: compressive light field synthesis using multilayer displays with directional backlighting. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4 (2012), 1–11.Google ScholarDigital Library
54. Tomohiro Yendo, Naoki Kawakami, and Susumu Tachi. 2005. Seelinder: the cylindrical lightfield display. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Emerging technologies. 16-es.Google ScholarDigital Library