“A moving least square reproducing kernel particle method for unified multiphase continuum simulation” by Chen, Li, Cao, Jiang and Hu
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- A moving least square reproducing kernel particle method for unified multiphase continuum simulation
Session/Category Title:
- Animation: Fluids - Phenomenon
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
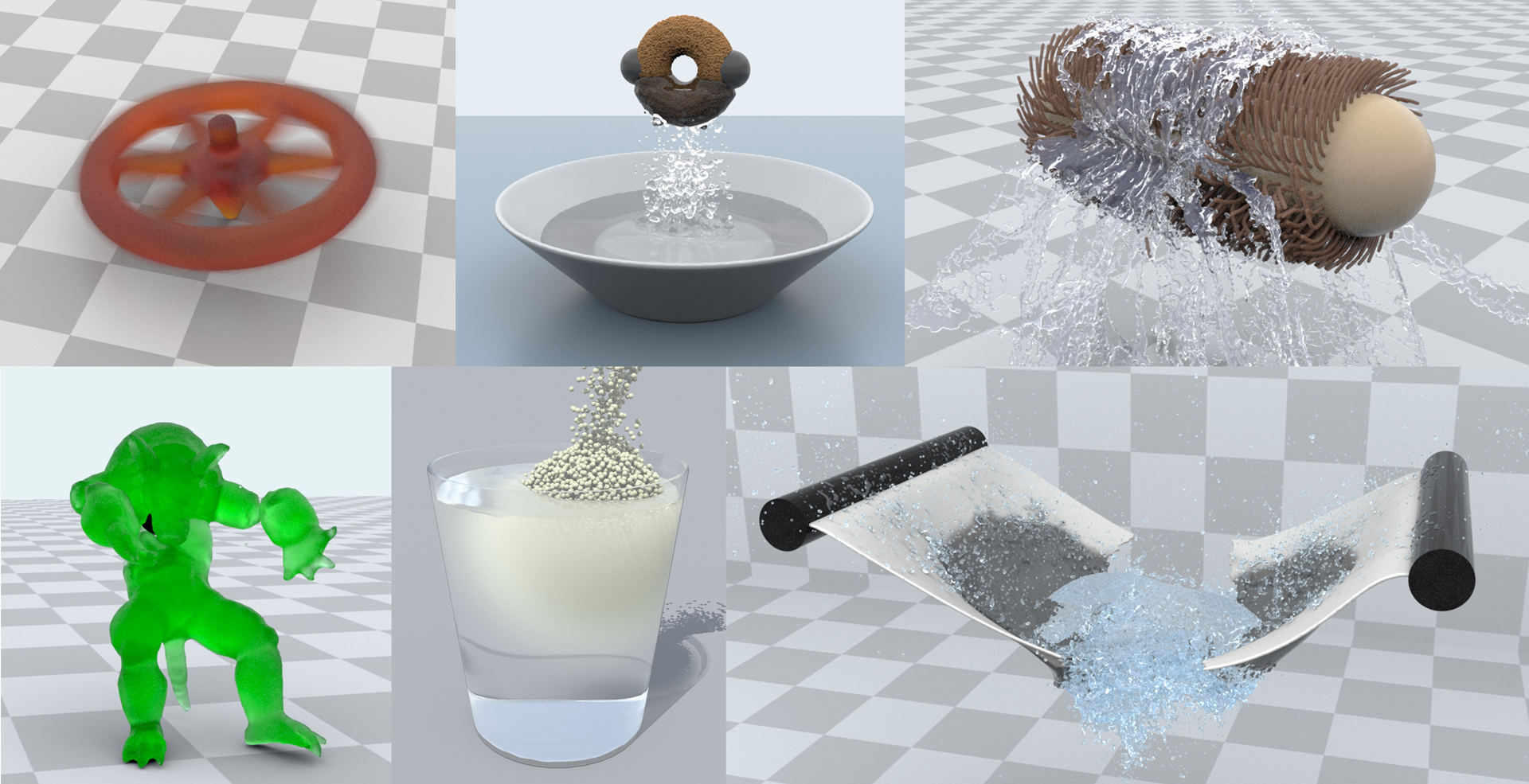
In physically based-based animation, pure particle methods are popular due to their simple data structure, easy implementation, and convenient parallelization. As a pure particle-based method and using Galerkin discretization, the Moving Least Square Reproducing Kernel Method (MLSRK) was developed in engineering computation as a general numerical tool for solving PDEs. The basic idea of Moving Least Square (MLS) has also been used in computer graphics to estimate deformation gradient for deformable solids. Based on these previous studies, we propose a multiphase MLSRK framework that animates complex and coupled fluids and solids in a unified manner. Specifically, we use the Cauchy momentum equation and phase field model to uniformly capture the momentum balance and phase evolution/interaction in a multiphase system, and systematically formulate the MLSRK discretization to support general multiphase constitutive models. A series of animation examples are presented to demonstrate the performance of our new multiphase MLSRK framework, including hyperelastic, elastoplastic, viscous, fracturing and multiphase coupling behaviours etc.
References:
1. Bart Adams, Mark Pauly, Richard Keiser, and Leonidas J Guibas. 2007. Adaptively sampled particle fluids. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 26. Acm, 48.Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Nadir Akinci, Markus Ihmsen, Gizem Akinci, Barbara Solenthaler, and Matthias Teschner. 2012. Versatile rigid-fluid coupling for incompressible SPH. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4 (2012), 62.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Iván Alduán and Miguel A. Otaduy. 2011. SPH granular flow with friction and cohesion. In Proceedings of the 2011 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA ’11). Association for Computing Machinery, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 25–32. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Y. Bazilevs, G. Moutsanidis, J. Bueno, K. Kamran, D. Kamensky, M. C. Hillman, H. Gomez, and J. S. Chen. 2017. A new formulation for air-blast fluid-structure interaction using an immersed approach: part II—coupling of IGA and meshfree discretizations. Computational Mechanics 60, 1 (July 2017), 101–116. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Markus Becker, Markus Ihmsen, and Matthias Teschner. 2009. Corotated SPH for deformable solids. In Proceedings of the Fifth Eurographics conference on Natural Phenomena (NPH’09). Eurographics Association, Munich, Germany, 27–34.Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Markus Becker and Matthias Teschner. 2007. Weakly compressible SPH for free surface flows. In Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. Eurographics Association, 209–217.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Jan Bender and Dan Koschier. 2015. Divergence-free smoothed particle hydrodynamics. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on computer animation. ACM, 147–155.Google ScholarDigital Library
8. J. Bonet and T. S. L. Lok. 1999. Variational and momentum preservation aspects of Smooth Particle Hydrodynamic formulations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 180, 1 (Nov. 1999), 97–115. Google ScholarCross Ref
9. Jiun-Shyan Chen, Chunhui Pan, Cheng-Tang Wu, and Wing Kam Liu. 1996. Reproducing kernel particle methods for large deformation analysis of non-linear structures. Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering 139, 1–4 (1996), 195–227.Google Scholar
10. Jiun-Shyan Chen, Cheng-Tang Wu, Sangpil Yoon, and Yang You. 2001. A stabilized conforming nodal integration for Galerkin mesh-free methods. International journal for numerical methods in engineering 50, 2 (2001), 435–466.Google ScholarCross Ref
11. Mengyuan Ding, Xuchen Han, Stephanie Wang, Theodore F Gast, and Joseph M Teran. 2019. A thermomechanical material point method for baking and cooking. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6 (2019), 192.Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Yun Raymond Fei, Christopher Batty, Eitan Grinspun, and Changxi Zheng. 2018. A multi-scale model for simulating liquid-fabric interactions. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 51.Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Yun (Raymond) Fei, Christopher Batty, Eitan Grinspun, and Changxi Zheng. 2019. A Multi-Scale Model for Coupling Strands with Shear-Dependent Liquid. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 6, Article 190 (Nov. 2019), 20 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Yun Raymond Fei, Henrique Teles Maia, Christopher Batty, Changxi Zheng, and Eitan Grinspun. 2017. A multi-scale model for simulating liquid-hair interactions. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 56.Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Chuyuan Fu, Qi Guo, Theodore Gast, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Joseph Teran. 2017. A polynomial particle-in-cell method. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 6 (2017), 222.Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Ming Gao, Andre Pradhana, Xuchen Han, Qi Guo, Grant Kot, Eftychios Sifakis, and Chenfanfu Jiang. 2018a. Animating fluid sediment mixture in particle-laden flows. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 149.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Ming Gao, Andre Pradhana Tampubolon, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2017. An adaptive generalized interpolation material point method for simulating elastoplastic materials. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 6 (2017), 223.Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Ming Gao, Xinlei Wang, Kui Wu, Andre Pradhana, Eftychios Sifakis, Cem Yuksel, and Chenfanfu Jiang. 2018b. Gpu optimization of material point methods. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2018 Technical Papers. ACM, 254.Google Scholar
19. Dan Gerszewski, Haimasree Bhattacharya, and Adam W. Bargteil. 2009. A point-based method for animating elastoplastic solids. In Proceedings of the 2009 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA ’09). Association for Computing Machinery, New Orleans, Louisiana, 133–138. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. R. A. Gingold and J. J. Monaghan. 1977. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: theory and application to non-spherical stars. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 181, 3 (Dec. 1977), 375–389. Publisher: Oxford Academic. Google ScholarCross Ref
21. Christoph Gissler, Andreas Henne, Stefan Band, Andreas Peer, and Matthias Teschner. 2020. An Implicit Compressible SPH Solver for Snow Simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 39, 4 (2020).Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Christoph Gissler, Andreas Peer, Stefan Band, Jan Bender, and Matthias Teschner. 2019. Interlinked SPH pressure solvers for strong fluid-rigid coupling. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 1 (2019), 5.Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Pai Chen Guan, Jiun-Shyan Chen, Y Wu, H Teng, J Gaidos, K Hofstetter, and M Alsaleh. 2009. Semi-Lagrangian reproducing kernel formulation and application to modeling earth moving operations. Mechanics of Materials 41, 6 (2009), 670–683.Google ScholarCross Ref
24. Qi Guo, Xuchen Han, Chuyuan Fu, Theodore Gast, Rasmus Tamstorf, and Joseph Teran. 2018. A material point method for thin shells with frictional contact. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 147.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Yuanming Hu, Yu Fang, Ziheng Ge, Ziyin Qu, Yixin Zhu, Andre Pradhana, and Chenfanfu Jiang. 2018. A moving least squares material point method with displacement discontinuity and two-way rigid body coupling. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 150.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Yuanming Hu, Tzu-Mao Li, Luke Anderson, Jonathan Ragan-Kelley, and Frédo Durand. 2019. Taichi: a language for high-performance computation on spatially sparse data structures. ACM Transactions on Graphics 38, 6 (Nov. 2019), 201:1–201:16. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Markus Ihmsen, Jens Cornelis, Barbara Solenthaler, Christopher Horvath, and Matthias Teschner. 2013. Implicit incompressible SPH. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 20, 3 (2013), 426–435.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Chenfanfu Jiang, Theodore Gast, and Joseph Teran. 2017. Anisotropic elastoplasticity for cloth, knit and hair frictional contact. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 152.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Chenfanfu Jiang, Craig Schroeder, Andrew Selle, Joseph Teran, and Alexey Stomakhin. 2015. The affine particle-in-cell method. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 51.Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Chenfanfu Jiang, Craig Schroeder, Joseph Teran, Alexey Stomakhin, and Andrew Selle. 2016. The material point method for simulating continuum materials. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2016 Courses (SIGGRAPH ’16). Association for Computing Machinery, Anaheim, California, 1–52. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Ben Jones, Stephen Ward, Ashok Jallepalli, Joseph Perenia, and Adam W. Bargteil. 2014. Deformation embedding for point-based elastoplastic simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 33, 2 (April 2014), 21:1–21:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. R. Keiser, B. Adams, D. Gasser, P. Bazzi, P. Dutre, and M. Gross. 2005. A unified Lagrangian approach to solid-fluid animation. In Proceedings Eurographics/IEEE VGTC Symposium Point-Based Graphics, 2005. 125–148. ISSN: 1511–7813. Google ScholarCross Ref
33. Gergely Klár, Theodore Gast, Andre Pradhana, Chuyuan Fu, Craig Schroeder, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Joseph Teran. 2016. Drucker-prager elastoplasticity for sand animation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 4 (2016), 103.Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Wing K Liu, Shaofan Li, and Ted Belytschko. 1997. Moving least-square reproducing kernel methods (I) methodology and convergence. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 143, 1–2 (1 1 1997), 113–154. Google ScholarCross Ref
35. Wing Kam Liu, Sukky Jun, and Yi Fei Zhang. 1995. Reproducing kernel particle methods. International journal for numerical methods in fluids 20, 8–9 (1995), 1081–1106.Google ScholarCross Ref
36. Vlado A Lubarda. 2004. Constitutive theories based on the multiplicative decomposition of deformation gradient: Thermoelasticity, elastoplasticity, and biomechanics. Applied Mechanics Reviews 57, 2 (2004), 95–108. : https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/appliedmechanicsreviews/article-pdf/57/2/95/5440572/95_1.pdf. Google ScholarCross Ref
37. Miles Macklin and Matthias Müller. 2013. Position based fluids. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4 (2013), 104.Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Miles Macklin, Matthias Müller, Nuttapong Chentanez, and Tae-Yong Kim. 2014. Unified particle physics for real-time applications. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 4 (2014), 153.Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Sebastian Martin, Peter Kaufmann, Mario Botsch, Eitan Grinspun, and Markus Gross. 2010. Unified simulation of elastic rods, shells, and solids. ACM Transactions on Graphics 29, 4 (July 2010), 39:1–39:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Matthias Müller, Bruno Heidelberger, Matthias Teschner, and Markus Gross. 2005. Meshless deformations based on shape matching. ACM Transactions on Graphics 24, 3 (July 2005), 471–478. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Joe J Monaghan. 1992. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Annual review of astronomy and astrophysics 30, 1 (1992), 543–574.Google Scholar
42. Georgios Moutsanidis, David Kamensky, J. S. Chen, and Yuri Bazilevs. 2018. Hyperbolic phase field modeling of brittle fracture: Part II—immersed IGA-RKPM coupling for air-blast-structure interaction. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 121 (Dec. 2018), 114–132. Google ScholarCross Ref
43. Matthias Müller, David Charypar, and Markus Gross. 2003. Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications. In Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. Eurographics Association, 154–159.Google ScholarDigital Library
44. Matthias Müller, Richard Keiser, Andrew Nealen, Mark Pauly, Markus Gross, and Marc Alexa. 2004. Point based animation of elastic, plastic and melting objects. In Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. Eurographics Association, 141–151.Google ScholarDigital Library
45. Ken Museth. 2013. VDB: High-resolution sparse volumes with dynamic topology. ACM Transactions on Graphics 32, 3 (July 2013), 27:1–27:22. Google ScholarDigital Library
46. Mark Pauly, Richard Keiser, Bart Adams, Philip Dutré, Markus Gross, and Leonidas J. Guibas. 2005. Meshless animation of fracturing solids. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers (SIGGRAPH ’05). Association for Computing Machinery, Los Angeles, California, 957–964. Google ScholarDigital Library
47. Andreas Peer, Christoph Gissler, Stefan Band, and Matthias Teschner. 2018. An implicit SPH formulation for incompressible linearly elastic solids. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. Wiley Online Library, 135–148.Google Scholar
48. Andreas Peer, Markus Ihmsen, Jens Cornelis, and Matthias Teschner. 2015. An implicit viscosity formulation for SPH fluids. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 114.Google ScholarDigital Library
49. Andreas Peer and Matthias Teschner. 2016. Prescribed velocity gradients for highly viscous SPH fluids with vorticity diffusion. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 23, 12 (2016), 2656–2662.Google Scholar
50. Stefan Reinhardt, Tim Krake, Bernhard Eberhardt, and Daniel Weiskopf. 2019. Consistent shepard interpolation for SPH-based fluid animation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6 (2019), 189.Google ScholarDigital Library
51. Bo Ren, Chenfeng Li, Xiao Yan, Ming C Lin, Javier Bonet, and Shi-Min Hu. 2014. Multiple-fluid SPH simulation using a mixture model. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 5 (2014), 171.Google ScholarDigital Library
52. Rajsekhar Setaluri, Mridul Aanjaneya, Sean Bauer, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2014. SPGrid: a sparse paged grid structure applied to adaptive smoke simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 33, 6 (Nov. 2014), 205:1–205:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
53. Barbara Solenthaler and Renato Pajarola. 2008. Density contrast SPH interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on computer animation. Eurographics Association, 211–218.Google ScholarDigital Library
54. Barbara Solenthaler and Renato Pajarola. 2009. Predictive-corrective incompressible SPH. In ACM transactions on graphics (TOG), Vol. 28. ACM, 40.Google Scholar
55. Alexey Stomakhin, Craig Schroeder, Lawrence Chai, Joseph Teran, and Andrew Selle. 2013. A material point method for snow simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4 (2013), 102.Google ScholarDigital Library
56. Alexey Stomakhin, Craig Schroeder, Chenfanfu Jiang, Lawrence Chai, Joseph Teran, and Andrew Selle. 2014. Augmented MPM for phase-change and varied materials. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 4 (2014), 138.Google ScholarDigital Library
57. Tetsuya Takahashi and Ming C Lin. 2019. A Geometrically Consistent Viscous Fluid Solver with Two-Way Fluid-Solid Coupling. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 38. Wiley Online Library, 49–58.Google Scholar
58. Andre Pradhana Tampubolon, Theodore Gast, Gergely Klár, Chuyuan Fu, Joseph Teran, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Ken Museth. 2017. Multi-species simulation of porous sand and water mixtures. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 105.Google ScholarDigital Library
59. Marcel Weiler, Dan Koschier, Magnus Brand, and Jan Bender. 2018. A physically consistent implicit viscosity solver for SPH fluids. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. Wiley Online Library, 145–155.Google Scholar
60. Xiao Yan, Yun-Tao Jiang, Chen-Feng Li, Ralph R Martin, and Shi-Min Hu. 2016. Multiphase SPH simulation for interactive fluids and solids. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 4 (2016), 79.Google ScholarDigital Library
61. Xiao Yan, C-F Li, X-S Chen, and S-M Hu. 2018. MPM simulation of interacting fluids and solids. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. Wiley Online Library, 183–193.Google Scholar
62. Tao Yang, Jian Chang, Ming C Lin, Ralph R Martin, Jian J Zhang, and Shi-Min Hu. 2017. A unified particle system framework for multi-phase, multi-material visual simulations. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 6 (2017), 224.Google ScholarDigital Library
63. Tao Yang, Jian Chang, Bo Ren, Ming C Lin, Jian Jun Zhang, and Shi-Min Hu. 2015. Fast multiple-fluid simulation using Helmholtz free energy. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 6 (2015), 201.Google ScholarDigital Library
64. Edouard Yreux and Jiun-Shyan Chen. 2017. A quasi-linear reproducing kernel particle method. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 109, 7 (2017), 1045–1064.Google ScholarCross Ref
65. Yongning Zhu and Robert Bridson. 2005. Animating sand as a fluid. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 24, 3 (2005), 965–972.Google ScholarDigital Library
ACM Digital Library Publication:
- A moving least square reproducing kernel particle method for unified multiphase continuum simulation