“RBF liquids: an adaptive PIC solver using RBF-FD” by Nakanishi, Nascimento, Campos, Pagliosa and Paiva
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- RBF liquids: an adaptive PIC solver using RBF-FD
Session/Category Title: Animation: Fluid
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
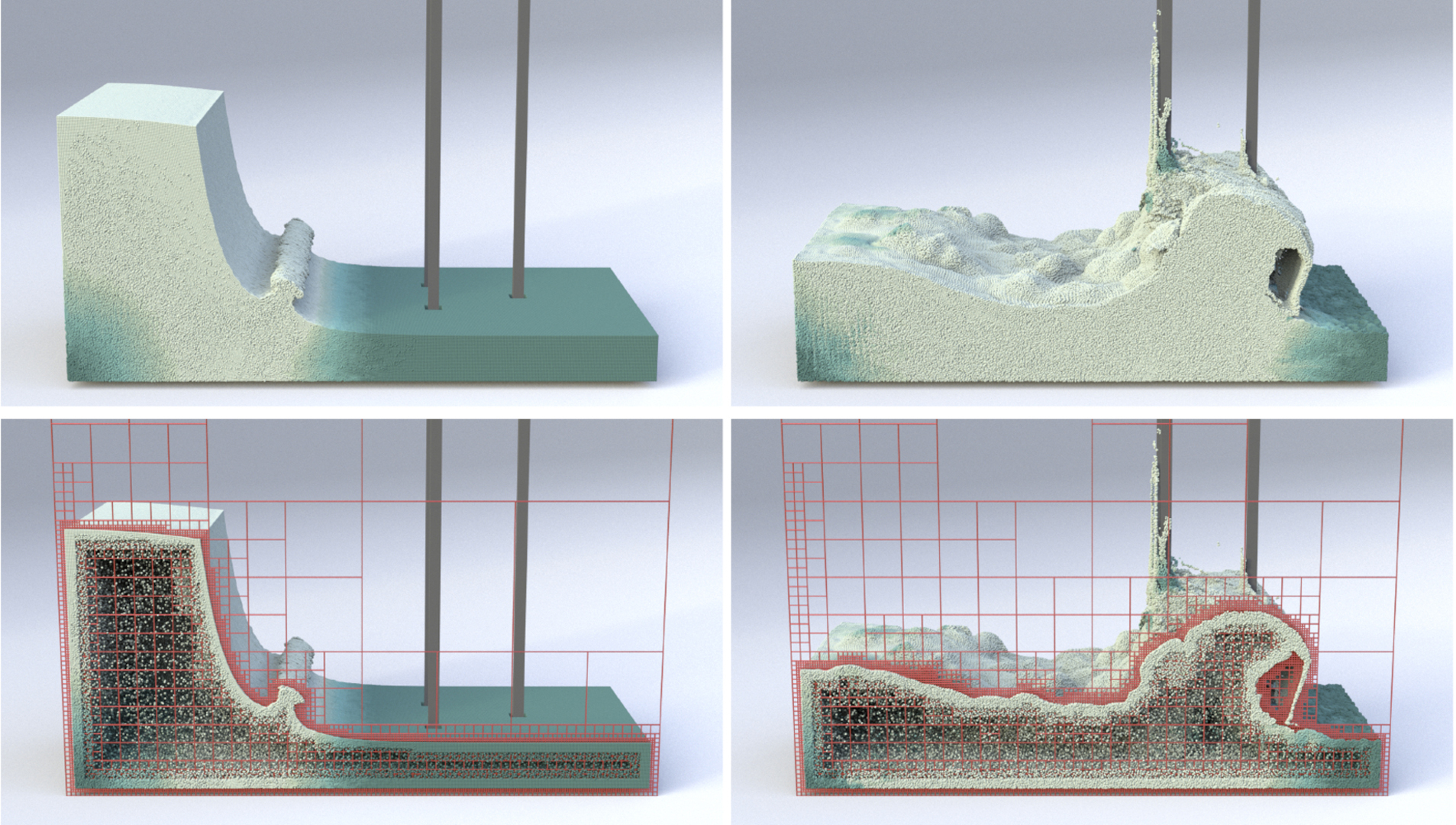
We introduce a novel liquid simulation approach that combines a spatially adaptive pressure projection solver with the Particle-in-Cell (PIC) method. The solver relies on a generalized version of the Finite Difference (FD) method to approximate the pressure field and its gradients in tree-based grid discretizations, possibly non-graded. In our approach, FD stencils are computed by using meshfree interpolations provided by a variant of Radial Basis Function (RBF), known as RBF-Finite-Difference (RBF-FD). This meshfree version of the FD produces differentiation weights on scattered nodes with high-order accuracy. Our method adapts a quadtree/octree dynamically in a narrow-band around the liquid interface, providing an adaptive particle sampling for the PIC advection step. Furthermore, RBF affords an accurate scheme for velocity transfer between the grid and particles, keeping the system’s stability and avoiding numerical dissipation. We also present a data structure that connects the spatial subdivision of a quadtree/octree with the topology of its corresponding dual-graph. Our data structure makes the setup of stencils straightforward, allowing its updating without the need to rebuild it from scratch at each time-step. We show the effectiveness and accuracy of our solver by simulating incompressible inviscid fluids and comparing results with regular PIC-based solvers available in the literature.
References:
1. M. Aanjaneya, M. Gao, H. Liu, C. Batty, and E. Sifakis. 2017. Power diagrams and sparse paged grids for high resolution adaptive liquids. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
2. B. Adams, M. Pauly, R. Keiser, and L. J. Guibas. 2007. Adaptively sampled particle fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (2007).Google ScholarDigital Library
3. R. Ando, N. Thurey, and R. Tsuruno. 2012. Preserving fluid sheets with adaptively sampled anisotropic particles. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 18, 8 (2012), 1202–1214.Google ScholarDigital Library
4. R. Ando, N. Thürey, and C. Wojtan. 2013. Highly adaptive liquid simulations on tetrahedral meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (2013), 103:1–103:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. R. Barrett, M. Berry, T. F. Chan, J. Demmel, J. Donato, J. Dongarra, V. Eijkhout, R. Pozo, C. Romine, and H. van der Vorst. 1994. Templates for the Solution of Linear Systems: Building Blocks for Iterative Methods. SIAM.Google Scholar
6. C. Batty. 2017. A cell-centred finite volume method for the Poisson problem on non-graded quadtrees with second order accurate gradients. J. Comput. Phys. 331 (2017), 49–72.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. C. Batty, S. Xenos, and B. Houston. 2010. Tetrahedral embedded boundary methods for accurate and flexible adaptive fluids. Comput. Graph. Forum 29, 2 (2010), 695–704.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. V. Bayona, N. Flyer, and B. Fornberg. 2019. On the role of polynomials in RBF-FD approximations: III. Behavior near domain boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 380 (2019), 378 — 399.Google ScholarDigital Library
9. V. Bayona, N. Flyer, B. Fornberg, and G. A. Barnett. 2017. On the role of polynomials in RBF-FD approximations: II. Numerical solution of elliptic PDEs. J. Comput. Phys. 332 (2017), 257–273.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. R. Bridson. 2015. Fluid Simulation (2nd ed.). A. K. Peters.Google Scholar
11. T. Brochu, C. Batty, and R. Bridson. 2010. Matching fluid simulation elements to surface geometry and topology. In ACM Trans. Graph., Vol. 29.Google ScholarDigital Library
12. J. C. Carr, R. K. Beatson, J. B. Cherrie, T. J. Mitchell, W. R. Fright, B. C. McCallum, and T. R. Evans. 2001. Reconstruction and representation of 3D objects with radial basis functions. In SIGGRAPH ’01. ACM, 67–76.Google Scholar
13. N. Chentanez, B. E. Feldman, F. Labelle, J. F. O’Brien, and J. R. Shewchuk. 2007. Liquid Simulation on Lattice-Based Tetrahedral Meshes. In SCA ’07. 219–228.Google Scholar
14. N. Chentanez and M. Müller. 2011. Real-time Eulerian water simulation using a restricted tall cell grid. In ACM Trans. Graph., Vol. 30. 82:1–82:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
15. F. Da, D. Hahn, C. Batty, C. Wojtan, and E. Grinspun. 2016. Surface-only liquids. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4 (2016), 1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
16. E. Edwards and R. Bridson. 2012. A high-order accurate particle-in-cell method. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 90, 9 (2012), 1073–1088.Google ScholarCross Ref
17. S. Elliott, R. R. P. Kumar, N. Flyer, T. Ta, and R. Loft. 2019. Implementation of a scalable, performance portable shallow water equation solver using radial basis function-generated finite difference methods. Int. J. High Perform. Comput. Appl. 33, 4 (2019), 619–631.Google ScholarDigital Library
18. D. Enright, D. Nguyen, F. Gibou, and R. Fedkiw. 2003. Using the particle level set method and a second order accurate pressure boundary condition for free surface flows. In Proc. of the 4th ASME-JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference. 337–342.Google Scholar
19. G. F. Fasshauer. 2007. Meshfree Approximation Methods with MATLAB. World Scientific.Google Scholar
20. F. Ferstl, R. Ando, C. Wojtan, R. Westermann, and N. Thuerey. 2016. Narrow band FLIP for liquid simulations. Comput. Graph. Forum 35, 2 (2016), 225–232.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. F. Ferstl, R. Westermann, and C. Dick. 2014. Large-scale liquid simulation on adaptive hexahedral grids. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 20, 10 (2014), 1405–1417.Google ScholarCross Ref
22. N. Flyer, G. A. Barnett, and L. J. Wicker. 2016a. Enhancing finite differences with radial basis functions: experiments on the Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 316 (2016), 39–62.Google ScholarDigital Library
23. N. Flyer, B. Fornberg, V. Bayona, and G. A. Barnett. 2016b. On the role of polynomials in RBF-FD approximations: I. Interpolation and accuracy. J. Comput. Phys. 321 (2016), 21–38.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. B. Fornberg and N. Flyer. 2015. Solving PDEs with radial basis functions. Acta Numerica 24 (2015), 215–258.Google ScholarCross Ref
25. M. Gao, A. P. Tampubolon, C. Jiang, and E. Sifakis. 2017. An adaptive generalized interpolation material point method for simulating elastoplastic materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6 (2017), 1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. R. Goldade, Y. Wang, M. Aanjaneya, and C. Batty. 2019. An adaptive variational finite difference framework for efficient symmetric octree viscosity. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4 (2019).Google ScholarDigital Library
27. G. Guennebaud, B. Jacob, and Others. 2010. Eigen v3. http://eigen.tuxfamily.org.Google Scholar
28. A. Guittet, M. Theillard, and F. Gibou. 2015. A stable projection method for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations on arbitrary geometries and adaptive quad/octrees. J. Comput. Phys. 292 (2015), 215–238.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. W. Hong, D. H. House, and J. Keyser. 2009. An Adaptive Sampling Approach to Incompressible Particle-Based Fluid. Ph.D. Dissertation. Texas A & M University.Google Scholar
30. M. Ihmsen, J. Orthmann, B. Solenthaler, A. Kolb, and M. Teschner. 2014. SPH Fluids in Computer Graphics. In Eurographics 2014 – State of the Art Reports.Google Scholar
31. G. Irving, E. Guendelman, F. Losasso, and R. Fedkiw. 2006. Efficient simulation of large bodies of water by coupling two and three dimensional techniques. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3 (2006), 805–811.Google ScholarDigital Library
32. C. Jiang, C. Schroeder, A. Selle, J. Teran, and A. Stomakhin. 2015. The affine particle-in-cell method. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (2015), 51:1–51:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
33. D. Kim. 2016. Fluid Engine Development. CRC Press.Google Scholar
34. B. M. Klingner, B. E. Feldman, N. Chentanez, and J. F. O’Brien. 2006. Fluid animation with dynamic meshes. In ACM Trans. Graph., Vol. 25. 820–825.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. F. Losasso, R. Fedkiw, and S. Osher. 2006. Spatially adaptive techniques for level set methods and incompressible flow. Computers & Fluids 35, 10 (2006), 995 — 1010.Google ScholarCross Ref
36. F. Losasso, F. Gibou, and R. Fedkiw. 2004. Simulating water and smoke with an octree data structure. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (2004), 457–462.Google ScholarDigital Library
37. I. Macêdo, J. P. Gois, and L. Velho. 2011. Hermite radial basis functions implicits. Comput. Graph. Forum 30, 1 (2011), 27–42.Google ScholarCross Ref
38. P. L. Manteaux, C. Wojtan, R. Narain, S. Redon, F. Faure, and M. P. Cani. 2017. Adaptive physically based models in computer graphics. Comput. Graph. Forum 36, 6 (2017), 312–337.Google ScholarDigital Library
39. S. McKee, M. F. Tomé, V. G. Ferreira, J. A. Cuminato, A. Castelo, F. S. Sousa, and N. Mangiavacchi. 2008. The MAC method. Computers & Fluids 37, 8 (2008), 907–930.Google ScholarCross Ref
40. C. Min and F. Gibou. 2007. A second order accurate level set method on non-graded adaptive cartesian grids. J. Comput. Phys. 225, 1 (2007), 300–321.Google ScholarDigital Library
41. C. Min, F. Gibou, and H. D. Ceniceros. 2006. A supra-convergent finite difference scheme for the variable coefficient Poisson equation on non-graded grids. J. Comput. Phys. 218, 1 (2006), 123–140.Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Y. T. Ng, C. Min, and F. Gibou. 2009. An efficient fluid-solid coupling algorithm for single-phase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 23 (2009), 8807–8829.Google ScholarDigital Library
43. M. B. Nielsen and R. Bridson. 2016. Spatially adaptive FLIP fluid simulations in Bifrost. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2016 Talks. 41:1–41:2.Google Scholar
44. Y. Ohtake, A. Belyaev, and H. Seidel. 2005. 3D scattered data interpolation and approximation with multilevel compactly supported RBFs. Graph. Models 67, 3 (2005), 150–165.Google ScholarDigital Library
45. M. A. Olshanskii, K. M. Terekhov, and Y. V. Vassilevski. 2013. An octree-based solver for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations with enhanced stability and low dissipation. Computers & Fluids 84 (2013), 231–246.Google ScholarCross Ref
46. M. Sandim, D. Cedrim, L. G. Nonato, P. Pagliosa, and A. Paiva. 2016. Boundary detection in particle-based fluids. Comput. Graph. Forum 35, 2 (2016), 215–224.Google ScholarCross Ref
47. M. Sandim, N. Oe, D. Cedrim, P. Pagliosa, and A. Paiva. 2019. Boundary particle resampling for surface reconstruction in liquid animation. Computers & Graphics 84 (2019), 55 — 65.Google ScholarDigital Library
48. M. Sandim, A. Paiva, and L. H. de Figueiredo. 2020. Simple and reliable boundary detection for meshfree particle methods using interval analysis. J. Comput. Phys. 420 (2020), 109702.Google ScholarCross Ref
49. T. Sato, C. Wojtan, N. Thuerey, T. Igarashi, and R. Ando. 2018. Extended narrow band FLIP for liquid simulations. Comput. Graph. Forum 37, 2 (2018), 169–177.Google ScholarCross Ref
50. B. Seibold. 2008. Minimal positive stencils in meshfree finite difference methods for the Poisson equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 3–4 (2008), 592–601.Google ScholarCross Ref
51. R. Setaluri, M. Aanjaneya, S. Bauer, and E. Sifakis. 2014. SPGrid: a sparse paged grid structure applied to adaptive smoke simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 6 (2014).Google ScholarDigital Library
52. F. Sin, A. W. Bargteil, and J. K. Hodgins. 2009. A point-based method for animating incompressible flow. In SCA ’09. 247–255.Google Scholar
53. B. Solenthaler and M. Gross. 2011. Two-scale particle simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (2011), 81:1–81:8.Google ScholarDigital Library
54. F. S. Sousa, C. F. Lages, J. L. Ansoni, A. Castelo, and A. Simao. 2019. A finite difference method with meshless interpolation for incompressible flows in non-graded tree-based grids. J. Comput. Phys. 396 (2019), 848–866.Google ScholarCross Ref
55. J. Stam. 1999. Stable fluids. In Proc. of SIGGRAPH ’99. ACM, 121–128.Google ScholarDigital Library
56. G. Turk and J. F. O’Brien. 2002. Modelling with implicit surfaces that interpolate. ACM Trans. Graph. 21, 4 (2002), 855–873.Google ScholarDigital Library
57. R. Winchenbach, H. Hochstetter, and A. Kolb. 2017. Infinite continuous adaptivity for incompressible SPH. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 102:1–102:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
58. G. B. Wright and B. Fornberg. 2006. Scattered node compact finite difference-type formulas generated from radial basis functions. J. Comput. Phys. 212, 1 (2006), 99–123.Google ScholarDigital Library
59. T. Yang, J. Chang, B. Ren, M. C. Lin, J. J. Zhang, and S. Hu. 2015. Fast Multiple-Fluid Simulation Using Helmholtz Free Energy. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6 (2015).Google ScholarDigital Library