“RPM-Net: recurrent prediction of motion and parts from point cloud” by Yan, Hu, Yan, Chen, Kaick, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- RPM-Net: recurrent prediction of motion and parts from point cloud
Session/Category Title: Geometry Off the Deep End
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
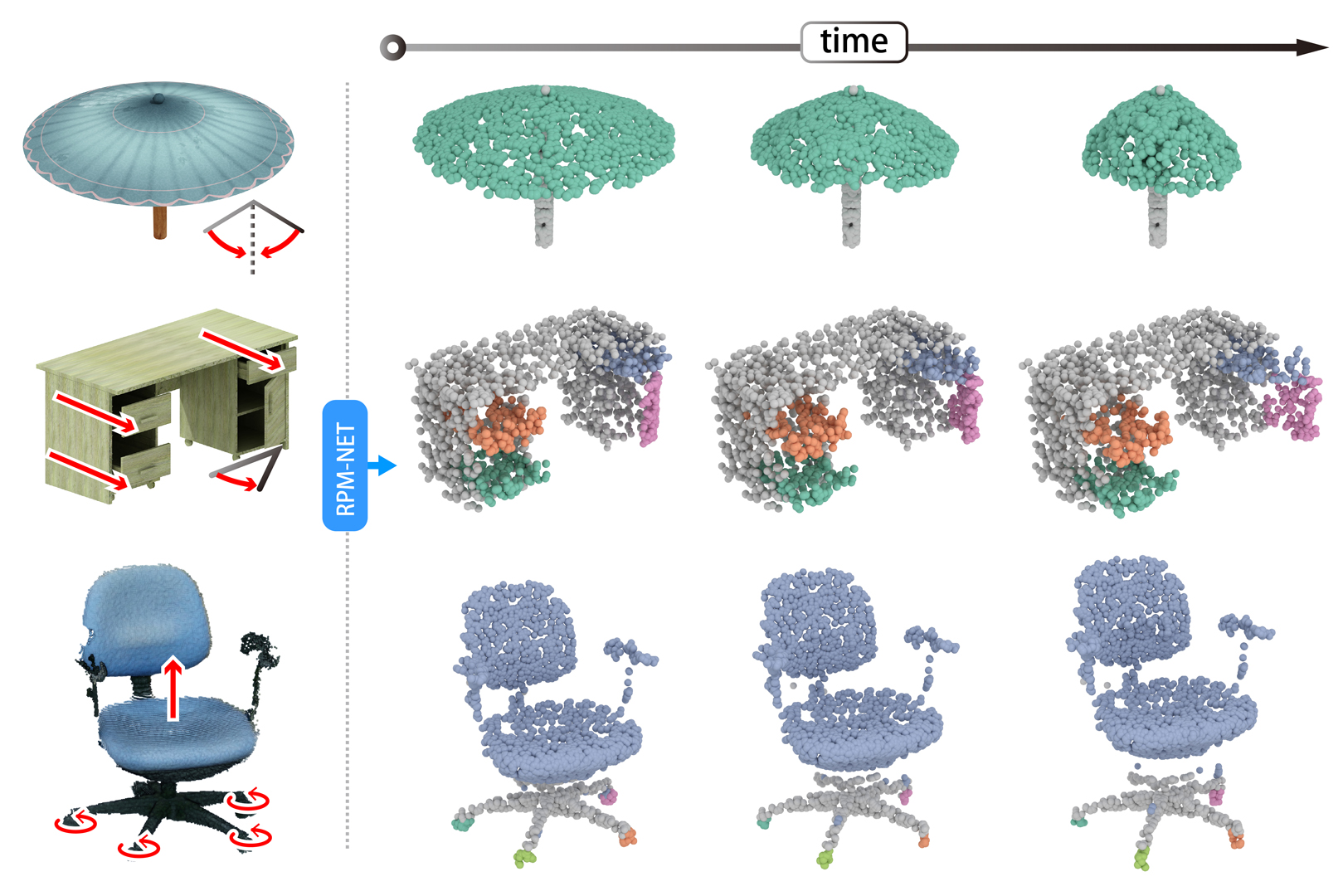
We introduce RPM-Net, a deep learning-based approach which simultaneously infers movable parts and hallucinates their motions from a single, un-segmented, and possibly partial, 3D point cloud shape. RPM-Net is a novel Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), composed of an encoder-decoder pair with interleaved Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) components, which together predict a temporal sequence of pointwise displacements for the input point cloud. At the same time, the displacements allow the network to learn movable parts, resulting in a motion-based shape segmentation. Recursive applications of RPM-Net on the obtained parts can predict finer-level part motions, resulting in a hierarchical object segmentation. Furthermore, we develop a separate network to estimate part mobilities, e.g., per-part motion parameters, from the segmented motion sequence. Both networks learn deep predictive models from a training set that exemplifies a variety of mobilities for diverse objects. We show results of simultaneous motion and part predictions from synthetic and real scans of 3D objects exhibiting a variety of part mobilities, possibly involving multiple movable parts.
References:
1. Luca Bogoni and Ruzena Bajcsy. 1995. Interactive Recognition and Representation of Functionality. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 62, 2 (1995), 194–214.Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Jeannette Bohg, Javier Romero, Alexander Herzog, and Stefan Schaal. 2014. Robot arm pose estimation through pixel-wise part classification. In Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2014 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 3143–3150.Google ScholarCross Ref
3. Michael Caine. 1994. The design of shape interactions using motion constraints. In IEEE Conference of Robotics and Automation, Vol. 1. 366–371.Google ScholarCross Ref
4. Y. Chao, J. Yang, B. Price, S. Cohen, and J. Deng. 2017. Forecasting Human Dynamics from Static Images. In Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. 3643–3651.Google Scholar
5. COCO. 2019. Common Objects in Context. http://cocodataset.org/#detection-eval.Google Scholar
6. Martin Ester, Hans-Peter Kriegel, Jörg Sander, Xiaowei Xu, et al. 1996. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise.. In Kdd, Vol. 96. 226–231.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. James J. Gibson. 1979. The ecological approach to visual perception. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.Google Scholar
8. Mohammed Hassanin, Salman Khan, and Murat Tahtali. 2018. Visual Affordance and Function Understanding: A Survey. arXiv:1807.06775 (2018).Google Scholar
9. T. Hermans, F. Li, J. M. Rehg, and A. F. Bobick. 2013. Learning contact locations for pushing and orienting unknown objects. In Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots. IEEE, 435–442.Google Scholar
10. Ruizhen Hu, Wenchao Li, Oliver van Kaick, Ariel Shamir, Hao Zhang, and Hui Huang. 2017. Learning to Predict Part Mobility from a Single Static Snapshot. ACM Trans. on Graphics 36, 6 (2017), 227:1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Ruizhen Hu, Manolis Savva, and Oliver van Kaick. 2018. Functionality Representations and Applications for Shape Analysis. Computer Graphics Forum (Eurographics State-of-the-art Report) 37, 2 (2018), 603–624.Google ScholarCross Ref
12. Yun Jiang, Hema Koppula, and Ashutosh Saxena. 2013. Hallucinated humans as the hidden context for labeling 3D scenes. In Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2993–3000.Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Vladimir G Kim, Siddhartha Chaudhuri, Leonidas Guibas, and Thomas Funkhouser. 2014. Shape2pose: Human-centric shape analysis. ACM Trans. on Graphics 33, 4 (2014), 120:1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Hao Li, Guowei Wan, Honghua Li, Andrei Sharf, Kai Xu, and Baoquan Chen. 2016. Mobility Fitting using 4D RANSAC. Computer Graphics Forum 35, 5 (2016), 79–88.Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Niloy J. Mitra, Yong-Liang Yang, Dong-Ming Yan, Wilmot Li, and Maneesh Agrawala. 2010. Illustrating How Mechanical Assemblies Work. ACM Trans. on Graphics 29, 4 (2010), 58:1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Sören Pirk, Vojtech Krs, Kaimo Hu, Suren Deepak Rajasekaran, Hao Kang, Bedrich Benes, Yusuke Yoshiyasu, and Leonidas J. Guibas. 2017. Understanding and Exploiting Object Interaction Landscapes. ACM Trans. on Graphics 36, 3 (2017), 31:1–14.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Charles R. Qi, Li Yi, Hao Su, and Leonidas J. Guibas. 2017. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS).Google Scholar
18. Anirban Roy and Sinisa Todorovic. 2016. A multi-scale CNN for affordance segmentation in RGB images. In Proc. Euro. Conf. on Computer Vision. Springer, 186–201.Google ScholarCross Ref
19. Manolis Savva, Angel X. Chang, Pat Hanrahan, Matthew Fisher, and Matthias Nießner. 2014. SceneGrok: Inferring Action Maps in 3D Environments. ACM Trans. on Graphics 33, 6 (2014), 212:1–212:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Tianjia Shao, Wilmot Li, Kun Zhou, Weiwei Xu, Baining Guo, and Niloy J. Mitra. 2013. Interpreting Concept Sketches. ACM Trans. on Graphics 32, 4 (2013), 56:1–10.Google ScholarDigital Library
21. A. Sharf, H. Huang, C. Liang, J. Zhang, B. Chen, and M. Gong. 2013. Mobility-Trees for Indoor Scenes Manipulation. Computer Graphics Forum 33, 1 (2013), 2–14.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Jörg Stückler, Benedikt Waldvogel, Hannes Schulz, and Sven Behnke. 2015. Dense Real-time Mapping of Object-class Semantics from RGB-D Video. J. Real-Time Image Process. 10, 4 (2015), 599–609.Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Art Tevs, Alexander Berner, Michael Wand, Ivo Ihrke, Martin Bokeloh, Jens Kerber, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2012. Animation Cartography – Intrinsic Reconstruction of Shape and Motion. ACM Trans. on Graphics 31, 2 (2012), 12:1–15.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Sergey Tulyakov, Ming-Yu Liu, Xiaodong Yang, and Jan Kautz. 2018. MoCoGAN: Decomposing motion and content for video generation. Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (2018).Google ScholarCross Ref
25. Weiyue Wang, Ronald Yu, Qiangui Huang, and Ulrich Neumann. 2018. SGPN: Similarity Group Proposal Network for 3D Point Cloud Instance Segmentation. In The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Google ScholarCross Ref
26. Xiaogang Wang, Bin Zhou, Yahao Shi, Xiaowu Chen, Qinping Zhao, and Kai Xu. 2019. Shape2Motion: Joint Analysis of Motion Parts and Attributes from 3D Shapes. In CVPR. to appear.Google Scholar
27. Wei Xiong, Wenhan Luo, Lin Ma, Wei Liu, and Jiebo Luo. 2018. Learning to Generate Time-Lapse Videos Using Multi-Stage Dynamic Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition.Google ScholarCross Ref
28. Li Yi, Haibin Huang, Difan Liu, Evangelos Kalogerakis, Hao Su, and Leonidas Guibas. 2018. Deep Part Induction from Articulated Object Pairs. ACM Trans. on Graphics 37, 6 (2018), 209:1–15.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Kangxue Yin, Hui Huang, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Hao Zhang. 2018. P2P-NET: Bidirectional Point Displacement Net for Shape Transform. ACM Trans. on Graphics 37, 4 (2018), 152:1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Yipin Zhou and Tamara L. Berg. 2016. Learning Temporal Transformations from Time-Lapse Videos. In Proc. Euro. Conf. on Computer Vision. 262–277.Google Scholar
31. Yixin Zhu, Chenfanfu Jiang, Yibiao Zhao, Demetri Terzopoulos, and Song-Chun Zhu. 2016. Inferring forces and learning human utilities from videos. In Proc. IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 3823–3833.Google ScholarCross Ref