“Stochastic structural analysis for context-aware design and fabrication”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Stochastic structural analysis for context-aware design and fabrication
Session/Category Title: Fabrication
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
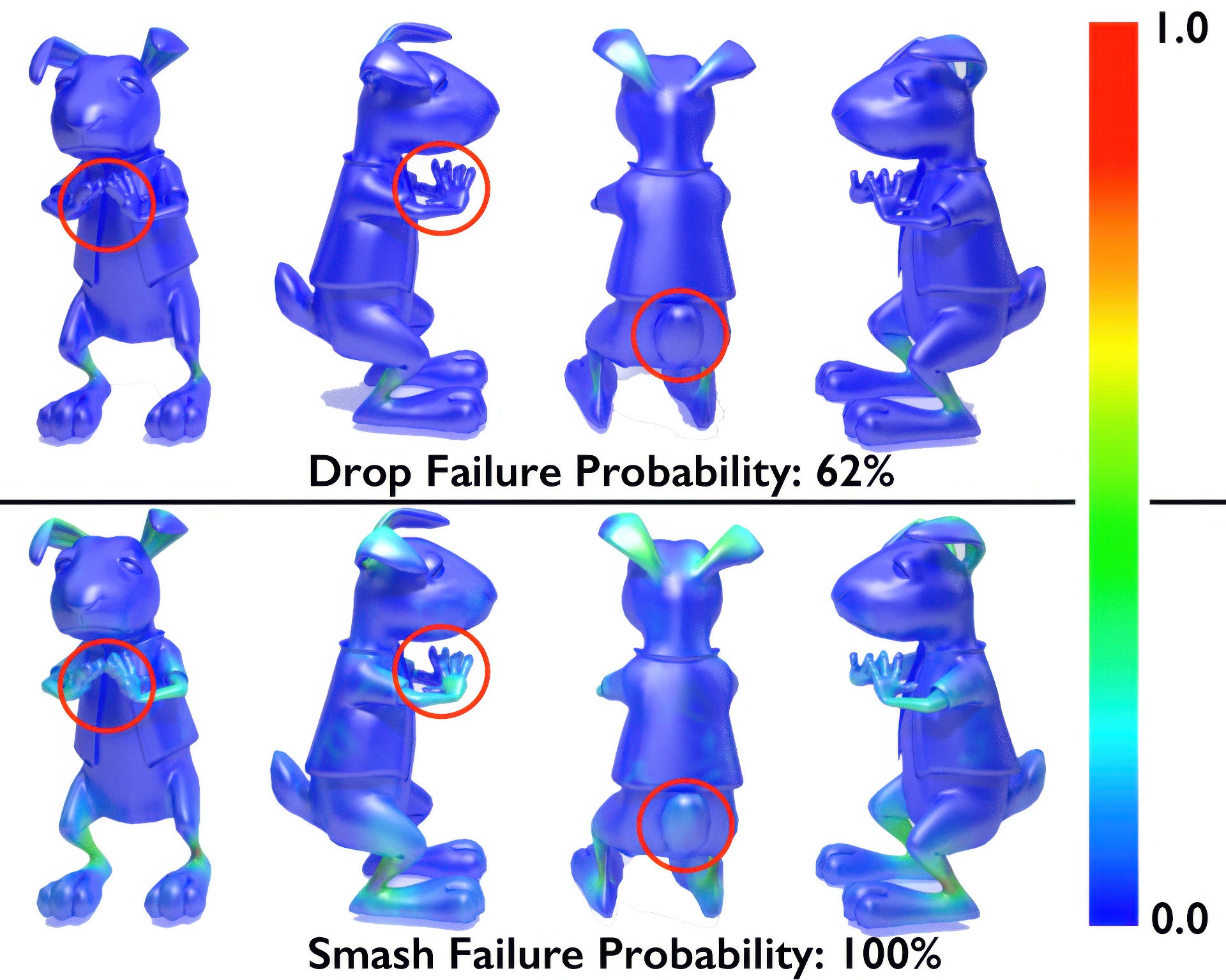
In this paper we propose failure probabilities as a semantically and mechanically meaningful measure of object fragility. We present a stochastic finite element method which exploits fast rigid body simulation and reduced-space approaches to compute spatially varying failure probabilities. We use an explicit rigid body simulation to emulate the real-world loading conditions an object might experience, including persistent and transient frictional contact, while allowing us to combine several such scenarios together. Thus, our estimates better reflect real-world failure modes than previous methods. We validate our results using a series of real-world tests. Finally, we show how to embed failure probabilities into a stress constrained topology optimization which we use to design objects such as weight bearing brackets and robust 3D printable objects.
References:
1. Ang, A. H.-S., and Tang, W. H. 2007. Probability concepts in engineering planning and design. Wiley.
2. Bächer, M., Whiting, E., Bickel, B., and Sorkine-Hornung, O. 2014. Spin-it: Optimizing moment of inertia for spinnable objects. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July), 96:1–96:10.
3. Barbič, J., and James, D. L. 2005. Real-time subspace integration for st. venant-kirchhoff deformable models. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (July), 982–990.
4. Belytschko, T., Liu, W. K., Moran, B., and Elkhodary, K. 2013. Nonlinear finite elements for continua and structures. John Wiley & Sons.
5. Bendsøe, M. P., and Sigmund, O. 2009. Topology Optimization. World Scientific.
6. Chen, S., Chen, W., and Lee, S. 2010. Level set based robust shape and topology optimization under random field uncertainties. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 41, 4, 507–524. Cross Ref
7. Coumans, E., et al. 2015. Bullet physics library. Open source: bulletphysics. org.
8. Crapo, H., and Whiteley, W. 1989. The geometry of rigid structures. Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications.
9. Crapo, H. 1979. Structural rigidity. Structural Topology 1, 26–45.
10. Der Kiureghian, A., and Ke, J.-B. 1987. The stochastic finite element method in structural reliability. In Stochastic Structural Mechanics, Y. Lin, G. Schuller, and P. Spanos, Eds., vol. 31 of LNE. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 84–109.
11. Dumas, J., Lu, A., Lefebvre, S., Wu, J., and Dick, C. 2015. By-Example Synthesis of Structurally Sound Patterns. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (July).
12. Eiermann, M., Ernst, O., and Ullmann, E. 2007. Computational aspects of the stochastic finite element method. Computing and Visualization in Science 10, 1, 3–15.
13. Evgrafov, A., Patriksson, M., and Petersson, J. 2003. Stochastic structural topology optimization: existence of solutions and sensitivity analyses. ZAMM 83, 7, 479–492. Cross Ref
14. Faravelli, L., and Bigi, D. 1990. Stochastic finite elements for crash problems. Structural Safety 8, 1, 113 — 130. Cross Ref
15. Gounaris, G., and Dimarogonas, A. 1988. A finite element of a cracked prismatic beam for structural analysis. Computers & Structures 28, 3, 309–313. Cross Ref
16. Halko, N., Martinsson, P.-G., and Tropp, J. A. 2011. Finding structure with randomness: Probabilistic algorithms for constructing approximate matrix decompositions. SIAM review 53, 2, 217–288.
17. Hughes, T. J. 2012. The finite element method: linear static and dynamic finite element analysis. Courier Corporation.
18. Lee, E., James, K., and Martins, J. 2012. Stress-constrained topology optimization with design-dependent loading. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 46, 5, 647–661.
19. Liu, W. K., Belytschko, T., and Mani, A. 1986. Probabilistic finite elements for nonlinear structural dynamics. Comput Method Appl M 56, 1, 61 — 81.
20. Liu, W. K., Belytschko, T., and Mani, A. 1986. Random field finite elements. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 23, 10, 1831–1845. Cross Ref
21. Lu, L., Sharf, A., Zhao, H., Wei, Y., Fan, Q., Chen, X., Savoye, Y., Tu, C., Cohen-Or, D., and Chen, B. 2014. Build-to-last: Strength to weight 3d printed objects. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July), 97:1–97:10.
22. Ma, F. 1987. Extension of second moment analysis to vector-valued and matrix-valued functions. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics 22, 3, 251 — 260. Cross Ref
23. Mahadevan, S., and Haldar, A. 1991. Practical random field discretization in stochastic finite element analysis. Structural Safety 9, 4, 283 — 304. Cross Ref
24. Martínez, J., Dumas, J., Lefebvre, S., and Wei, L.-Y. 2015. Structure and appearance optimization for controllable shape design. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 6, 229.
25. Matthies, H. G., and Keese, A. 2005. Galerkin methods for linear and nonlinear elliptic stochastic partial differential equations. Comput Method Appl M 194, 1216, 1295 — 1331.
26. Maute, K. 2014. Topology optimization under uncertainty. In Topology Optimization in Structural and Continuum Mechanics, G. Rozvany and T. Lewiski, Eds., vol. 549 of CISM. Springer Vienna, 457–471.
27. McCormac, J. C., and Elling, R. E. 1984. Structural analysis. Harper & Row New York.
28. McNamara, A., Treuille, A., Popović, Z., and Stam, J. 2004. Fluid control using the adjoint method. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug.), 449–456.
29. Melosh, R. J. 1974. Finite element analysis of automobile structures. Tech. rep., SAE Technical Paper.
30. Musialski, P., Auzinger, T., Birsak, M., Wimmer, M., and Kobbelt, L. 2015. Reduced-order shape optimization using offset surfaces. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (July), 102:1–102:9.
31. Musialski, P., Hafner, C., Rist, F., Birsak, M., Wimmer, M., and Kobbelt, L. 2016. Non-linear shape optimization using local subspace projections. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4 (July), 87:1–87:13.
32. Prévost, R., Whiting, E., Lefebvre, S., and Sorkine-Hornung, O. 2013. Make it stand: Balancing shapes for 3d fabrication. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (July), 81:1–81:10.
33. Schumacher, C., Bickel, B., Rys, J., Marschner, S., Daraio, C., and Gross, M. 2015. Microstructures to control elasticity in 3d printing. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4.
34. Schuller, G. 2006. Developments in stochastic structural mechanics. Archive of Applied Mechanics 75, 10–12, 755–773.
35. Sigmund, O. 1997. On the design of compliant mechanisms using topology optimization*. J Struct Mech 25, 4, 493–524. Cross Ref
36. Stava, O., Vanek, J., Benes, B., Carr, N., and Měch, R. 2012. Stress relief: Improving structural strength of 3d printable objects. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (July), 48:1–48:11.
37. Stefanou, G. 2009. The stochastic finite element method: Past, present and future. Comput Method Appl M 198, 912, 1031 — 1051.
38. Svanberg, K. 1987. The method of moving asymptotes- a new method for structural optimization. International journal for numerical methods in engineering 24, 2, 359–373.
39. Tomlow, J. 1989. The model-antoni gaudís hanging model and its reconstruction-new light on the design of the church of colonia güell. Institute for Lightweight Structures (IL): University of Stuttgart. Germany, 34.
40. Umetani, N., and Schmidt, R. 2013. Cross-sectional structural analysis for 3d printing optimization. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2013 Technical Briefs, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SA ’13, 5:1–5:4.
41. Wang, W., Wang, T. Y., Yang, Z., Liu, L., Tong, X., Tong, W., Deng, J., Chen, F., and Liu, X. 2013. Cost-effective printing of 3d objects with skin-frame structures. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6 (Nov.), 177:1–177:10.
42. Wu, J., Dick, C., and Westermann, R. 2016. A system for high-resolution topology optimization. IEEE T Vis Comput Gr 22, 3 (Mar.), 1195–1208.
43. Zhang, Z., Jiang, C., Han, X., Hu, D., and Yu, S. 2014. A response surface approach for structural reliability analysis using evidence theory. Advances in Engineering Software 69, 37 — 45.
44. Zhou, Q., Panetta, J., and Zorin, D. 2013. Worst-case structural analysis. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (July), 137:1–137:12.