“Creating consistent scene graphs using a probabilistic grammar” by Liu, Chaudhuri, Kim, Huang, Mitra, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Creating consistent scene graphs using a probabilistic grammar
Session/Category Title:
- Scenes, Syntax, Statistics and Semantics
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
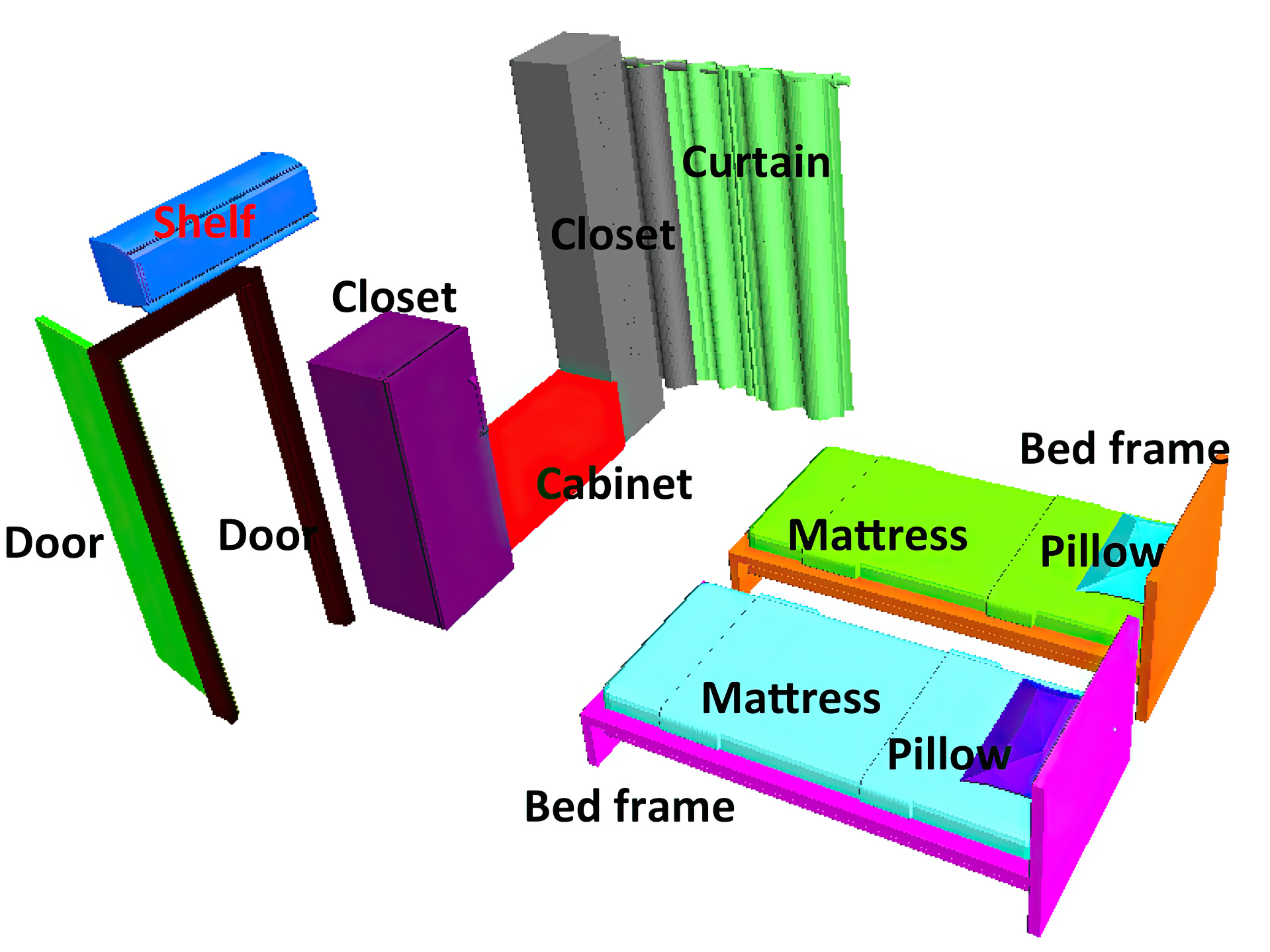
Growing numbers of 3D scenes in online repositories provide new opportunities for data-driven scene understanding, editing, and synthesis. Despite the plethora of data now available online, most of it cannot be effectively used for data-driven applications because it lacks consistent segmentations, category labels, and/or functional groupings required for co-analysis. In this paper, we develop algorithms that infer such information via parsing with a probabilistic grammar learned from examples. First, given a collection of scene graphs with consistent hierarchies and labels, we train a probabilistic hierarchical grammar to represent the distributions of shapes, cardinalities, and spatial relationships of semantic objects within the collection. Then, we use the learned grammar to parse new scenes to assign them segmentations, labels, and hierarchies consistent with the collection. During experiments with these algorithms, we find that: they work effectively for scene graphs for indoor scenes commonly found online (bedrooms, classrooms, and libraries); they outperform alternative approaches that consider only shape similarities and/or spatial relationships without hierarchy; they require relatively small sets of training data; they are robust to moderate over-segmentation in the inputs; and, they can robustly transfer labels from one data set to another. As a result, the proposed algorithms can be used to provide consistent hierarchies for large collections of scenes within the same semantic class.
References:
1. Bishop, C. M. 2006. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer-Verlag New York, Inc.
2. Bokeloh, M., Wand, M., and Seidel, H.-P. 2010. A connection between partial symmetry and inverse procedural modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4, 104.
3. Boulch, A., Houllier, S., Marlet, R., and Tournaire, O. 2013. Semantizing complex 3D scenes using constrained attribute grammars. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 32, Wiley Online Library, 33–42.
4. Chaudhuri, S., Kalogerakis, E., Guibas, L., and Koltun, V. 2011. Probabilistic reasoning for assembly-based 3D modeling. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 30, ACM, 35.
5. Choi, W., Chao, Y. W., Pantofaru, C., and Savarese, S. 2013. Understanding indoor scenes using 3D geometric phrases. In CVPR.
6. Earley, J. 1970. An efficient context-free parsing algorithm. Communications of the ACM 13, 2, 94–102.
7. Fisher, M., and Hanrahan, P. 2010. Context-based search for 3D models. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 29, ACM, 182.
8. Fisher, M., Savva, M., and Hanrahan, P. 2011. Characterizing structural relationships in scenes using graph kernels. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 30, ACM, 34.
9. Fisher, M., Ritchie, D., Savva, M., Funkhouser, T., and Hanrahan, P. 2012. Example-based synthesis of 3D object arrangements. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, 135.
10. Golovinskiy, A., and Funkhouser, T. 2009. Consistent segmentation of 3D models. Computers & Graphics 33, 3, 262–269.
11. Hu, R., Fan, L., and Liu, L. 2012. Co-segmentation of 3D shapes via subspace clustering. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 31, Wiley Online Library, 1703–1713.
12. Huang, Q.-X., and Guibas, L. 2013. Consistent shape maps via semidefinite programming. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 32, Wiley Online Library, 177–186.
13. Huang, Q., Koltun, V., and Guibas, L. 2011. Joint shape segmentation with linear programming. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 30, ACM, 125.
14. Huang, Q.-X., Zhang, G.-X., Gao, L., Hu, S.-M., Butscher, A., and Guibas, L. 2012. An optimization approach for extracting and encoding consistent maps in a shape collection. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, 167.
15. Kalogerakis, E., Hertzmann, A., and Singh, K. 2010. Learning 3D mesh segmentation and labeling. In SIGGRAPH.
16. Kalogerakis, E., Chaudhuri, S., Koller, D., and Koltun, V. 2012. A probabilistic model for component-based shape synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4, 55.
17. Kim, V. G., Li, W., Mitra, N. J., DiVerdi, S., and Funkhouser, T. 2012. Exploring collections of 3D models using fuzzy correspondences. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (July), 54:1–54:11.
18. Kim, V. G., Li, W., Mitra, N. J., Chaudhuri, S., DiVerdi, S., and Funkhouser, T. 2013. Learning part-based templates from large collections of 3D shapes. ACM Trans. Graph..
19. Martinović, A., and Van Gool, L. 2013. Bayesian grammar learning for inverse procedural modeling. In CVPR.
20. Mathias, M., Martinovic, A., Weissenberg, J., and van Gool, L. 2011. Procedural 3D building reconstruction using shape grammars and detectors. In 3DIMPVT.
21. Nguyen, A., Ben-Chen, M., Welnicka, K., Ye, Y., and Guibas, L. 2011. An optimization approach to improving collections of shape maps. In CGF, vol. 30, 1481–1491.Cross Ref
22. Parzen, E. 1962. On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 33, 3, 1065–1076.Cross Ref
23. Sidi, O., van Kaick, O., Kleiman, Y., Zhang, H., and Cohen-Or, D. 2011. Unsupervised co-segmentation of a set of shapes via descriptor-space spectral clustering. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 30, ACM, 126.
24. Socher, R., Lin, C. C., Ng, A., and Manning, C. 2011. Parsing natural scenes and natural language with recursive neural networks. In ICML, 129–136.
25. Št’ava, O., Beneš, B., Měch, R., Aliaga, D. G., and Krištof, P. 2010. Inverse procedural modeling by automatic generation of L-systems. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 29, Wiley Online Library, 665–674.
26. Talton, J., Yang, L., Kumar, R., Lim, M., Goodman, N., and Měch, R. 2012. Learning design patterns with bayesian grammar induction. In UIST, ACM, 63–74.
27. Teboul, O., Kokkinos, I., Simon, L., Koutsourakis, P., and Paragios, N. 2013. Parsing facades with shape grammars and reinforcement learning. Trans. PAMI 35, 7, 1744–1756.
28. Trimble, 2012. Trimble 3D warehouse, http://sketchup.google.com/3Dwarehouse/.
29. van Kaick, O., Xu, K., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Sun, S., Shamir, A., and Cohen-Or, D. 2013. Co-hierarchical analysis of shape structures. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, 69.
30. Wang, Y., Xu, K., Li, J., Zhang, H., Shamir, A., Liu, L., Cheng, Z., and Xiong, Y. 2011. Symmetry hierarchy of man-made objects. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 30,Wiley Online Library, 287–296.
31. Wu, F., Yan, D.-M., Dong, W., Zhang, X., and Wonka, P. 2014. Inverse procedural modeling of facade layouts. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4.
32. Xu, K., Chen, K., Fu, H., Sun, W.-L., and Hu, S.-M. 2013. Sketch2Scene: sketch-based co-retrieval and co-placement of 3D models. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, 123:1–123:12.
33. Xu, K., Ma, R., Zhang, H., Zhu, C., Shamir, A., Cohen-Or, D., and Huang, H. 2014. Organizing heterogeneous scene collection through contextual focal points. ACM Transactions on Graphics, (Proc. of SIGGRAPH 2014) 33, 4, to appear.
34. Yeh, Y.-T., Yang, L., Watson, M., Goodman, N. D., and Hanrahan, P. 2012. Synthesizing open worlds with constraints using locally annealed reversible jump mcmc. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4, 56.
35. Zhang, H., Xu, K., Jiang, W., Lin, J., Cohen-Or, D., and Chen, B. 2013. Layered analysis of irregular facades via symmetry maximization. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, 121.
36. Zhao, Y., and Zhu, S.-C. 2013. Scene parsing by integrating function, geometry and appearance models. CVPR.
37. Zheng, Y., Cohen-Or, D., Averkiou, M., and Mitra, N. J. 2014. Recurring part arrangements in shape collections. Computer Graphics Forum (Special issue of Eurographics 2014).