“A general and efficient method for finding cycles in 3D curve networks” by Zhuang, Zou, Carr and Ju
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- A general and efficient method for finding cycles in 3D curve networks
Session/Category Title: Modeling Primitives
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
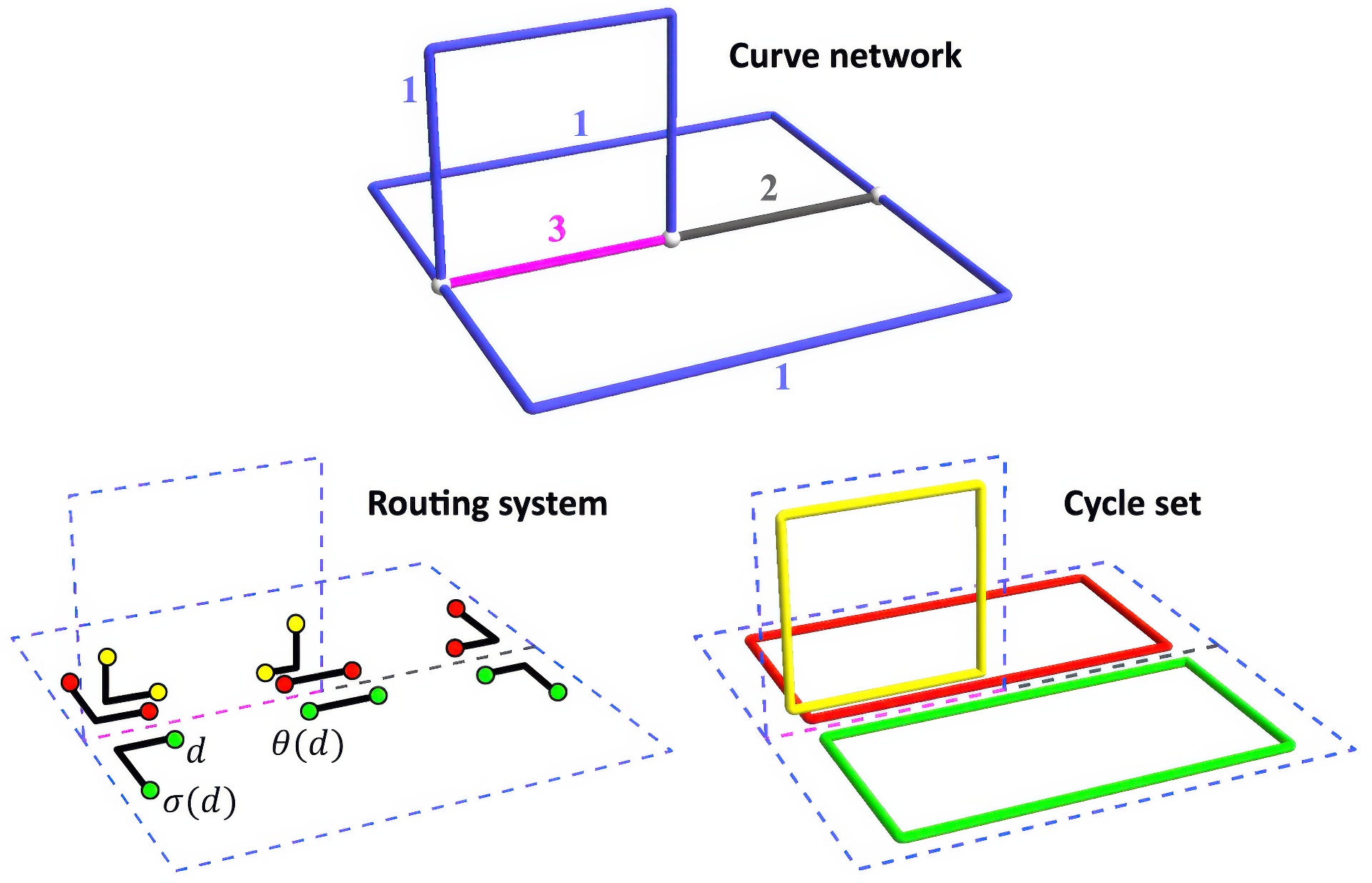
Generating surfaces from 3D curve networks has been a longstanding problem in computer graphics. Recent attention to this area has resurfaced as a result of new sketch based modeling systems. In this work we present a new algorithm for finding cycles that bound surface patches. Unlike prior art in this area, the output of our technique is unrestricted, generating both manifold and non-manifold geometry with arbitrary genus. The novel insight behind our method is to formulate our problem as finding local mappings at the vertices and curves of our network, where each mapping describes how incident curves are grouped into cycles. This approach lends us the efficiency necessary to present our system in an interactive design modeler, whereby the user can adjust patch constraints and change the manifold properties of curves while the system automatically re-optimizes the solution.
References:
1. Abbasinejad, F., Joshi, P., and Amenta, N. 2011. Surface patches from unorganized space curves. Comput. Graph. Forum 30, 5, 1379–1387.
2. Agarwal, S. C., and Waggenspack, W. N. 1992. Decomposition method for extracting face topologies from wireframe models. Computer-Aided Design 24, 3, 123–140.
3. Andrews, J., Joshi, P., and Carr, N. A. 2011. A linear variational system for modeling from curves. Comput. Graph. Forum 30, 6, 1850–1861.
4. Bae, S.-H., Balakrishnan, R., and Singh, K. 2008. Ilovesketch: as-natural-as-possible sketching system for creating 3D curve models. In Proceedings of the 21st annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, ACM, New York, NY, USA, UIST ’08, ACM, 151–160.
5. Bagali, S., and Waggenspack, Jr., W. N. 1995. A shortest path approach to wireframe to solid model conversion. In Proceedings of the third ACM Symposium on Solid modeling and applications, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SMA ’95, ACM, 339–350.
6. Bessmeltsev, M., Wang, C., Sheffer, A., and Singh, K. 2012. Design-driven quadrangulation of closed 3D curves. Transactions on Graphics (Proc. SIGGRAPH ASIA 2012) 31, 5.
7. Biondi, E., Divieti, L., and Guardabassi, G. 1970. Counting paths, circuits, chains, and cycles in graphs: a unified approach. Canad. J. Math. 22, 22–35.
8. Brewer, III, J. A., and Courter, S. M. 1986. Automated conversion of curvilinear wire-frame models to surface boundary models; a topological approach. In Proceedings of of ACM SIGGRAPH 1986, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH ’86, ACM, 171–178.
9. Dutton, R. D., and Brigham, R. C. 1983. Efficiently identifying the faces of a solid. Computers & Graphics in Mechanical Engineering 7, 2, 143–147.
10. Ganter, M. A., and Uicker, J. J. 1983. From wire-frame to solid geometric: Automated conversion of data representations. Computers in Mechanical Engineering 2 (sept), 40–45.
11. Grimm, C., and Joshi, P. 2012. Just DrawIt: a 3D sketching system. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling, SBIM ’12, ACM, 121–130.
12. Hanrahan, P. M. 1982. Creating volume models from edge-vertex graphs. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 1982, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH ’82, ACM, 77–84.
13. Inoue, K., Shimada, K., and Chilaka, K. 2003. Solid model reconstruction of wireframe cad models based on topological embeddings of planar graphs. Journal of Mechanical Design 125, 3, 434–442.
14. Liu, J., and Lee, Y. T. 2001. Graph-based method for face identification from a single 2D line drawing. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on 23, 10 (oct), 1106–1119.
15. Liu, J., Lee, Y. T., and Cham, W.-K. 2002. Identifying faces in a 2D line drawing representing a manifold object. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on 24, 12 (dec), 1579–1593.
16. Markowsky, G., and Wesley, M. A. 1980. Fleshing out wire frames. IBM J. Res. Dev. 24 (September), 582–597.
17. Mohar, B., and Thomassen, C. 2001. Graphs on Surfaces. The Johns Hopkins University Press.
18. Rose, K., Sheffer, A., Wither, J., Cani, M.-P., and Thibert, B. 2007. Developable surfaces from arbitrary sketched boundaries. In Proceedings of the fifth Eurographics symposium on Geometry processing, SGP ’07, ACM, 163–172.
19. Sakurai, H., and Gossard, D. C. 1983. Solid model input through orthographic views. In Proceedings of the 10th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, SIGGRAPH ’83, ACM, 243–252.
20. Schmidt, R., Khan, A., Singh, K., and Kurtenbach, G. 2009. Analytic drawing of 3D scaffolds. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2009, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH Asia ’09, ACM, 149:1–149:10.
21. Shpitalni, M., and Lipson, H. 1996. Identification of faces in a 2D line drawing projection of a wireframe object. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on 18, 10 (oct), 1000–1012.
22. Sun, Y., and Lee, Y. T. 2004. Topological analysis of a single line drawing for 3D shape recovery. In Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques in Australasia and South East Asia, GRAPHITE ’04, ACM, 167–172.
23. Varley, P. A., and Company, P. P. 2010. A new algorithm for finding faces in wireframes. Computer-Aided Design 42, 4, 279–309.
24. Wang, W., Jüttler, B., Zheng, D., and Liu, Y. 2008. Computation of rotation minimizing frames. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 1 (Mar.), 2:1–2:18.
25. Wesche, G., and Seidel, H.-P. 2001. Freedrawer: a free-form sketching system on the responsive workbench. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Virtual reality software and technology, ACM, New York, NY, USA, VRST ’01, ACM, 167–174.
26. Zou, M., Ju, T., and Carr, N. 2013. An algorithm for triangulating multiple 3D polygons. Computer Graphics Forum 32, 5, 157–166.