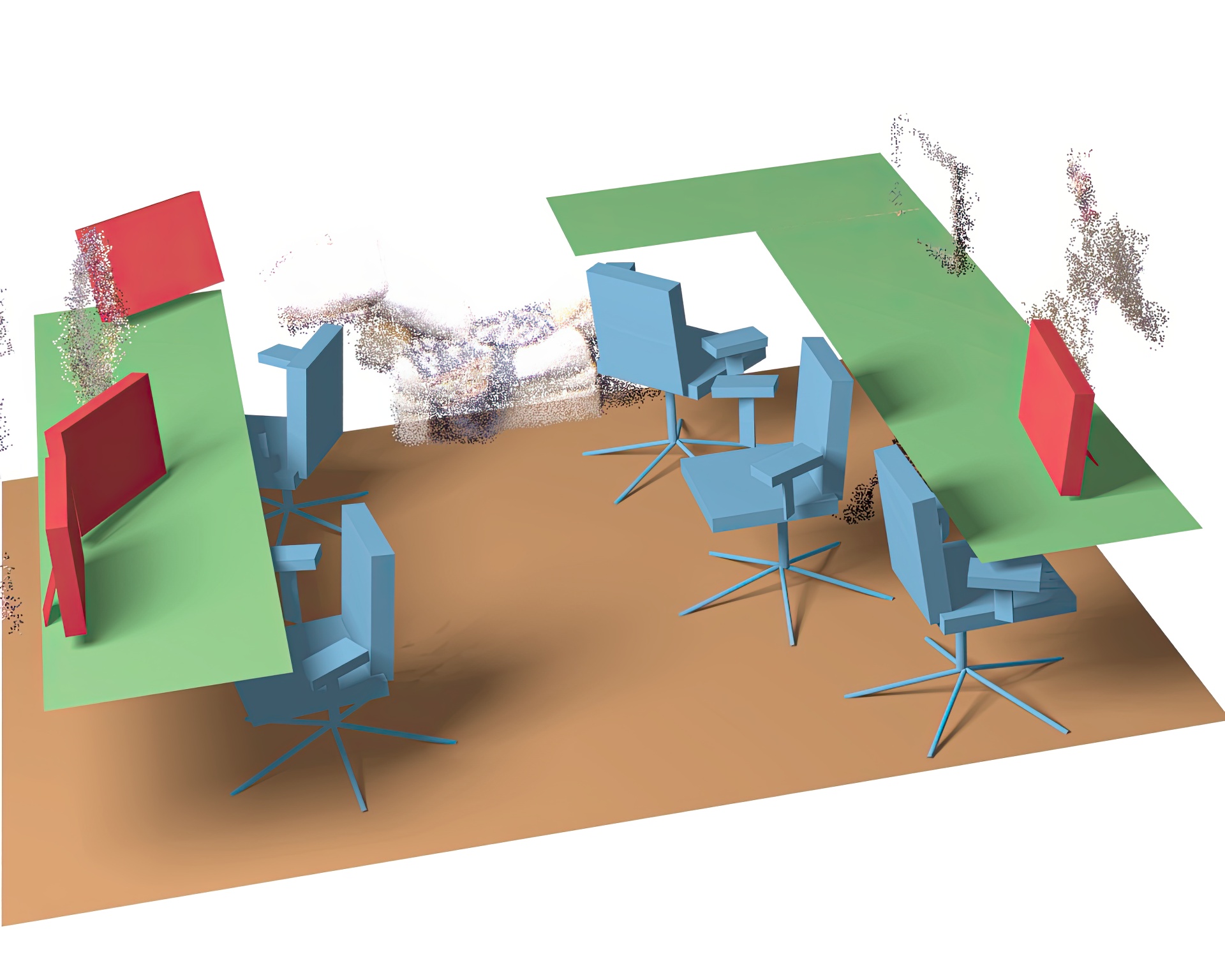
“Acquiring 3D indoor environments with variability and repetition” by Kim, Mitra, Yan and Guibas
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Acquiring 3D indoor environments with variability and repetition
Session/Category Title:
- Acquiring and Synthesizing Indoor Scenes
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
Large-scale acquisition of exterior urban environments is by now a well-established technology, supporting many applications in search, navigation, and commerce. The same is, however, not the case for indoor environments, where access is often restricted and the spaces are cluttered. Further, such environments typically contain a high density of repeated objects (e.g., tables, chairs, monitors, etc.) in regular or non-regular arrangements with significant pose variations and articulations. In this paper, we exploit the special structure of indoor environments to accelerate their 3D acquisition and recognition with a low-end handheld scanner. Our approach runs in two phases: (i) a learning phase wherein we acquire 3D models of frequently occurring objects and capture their variability modes from only a few scans, and (ii) a recognition phase wherein from a single scan of a new area, we identify previously seen objects but in different poses and locations at an average recognition time of 200ms/model. We evaluate the robustness and limits of the proposed recognition system using a range of synthetic and real world scans under challenging settings.
References:
1. Besl, P. J., and McKay, N. D. 1992. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE PAMI 14, 2, 239–256.
2. Chang, W., and Zwicker, M. 2011. Global registration of dynamic range scans for articulated model reconstruction. ACM TOG 30, 3, 26:1–26:15.
3. Dey, T. K. 2007. Curve and Surface Reconstruction: Algorithms with Mathematical Analysis. Cambridge University Press.
4. Engelhard, N., Endres, F., Hess, J., Sturm, J., and Burgard, W. 2011. Real-time 3D visual SLAM with a hand-held RGB-D camera. In Proc. of the RGB-D Workshop on 3D Perception in Robotics at the European Robotics Forum.
5. Fisher, M., Savva, M., and Hanrahan, P. 2011. Characterizing structural relationships in scenes using graph kernels. ACM TOG 30, 4, 34:1–34:11.
6. Gupta, A., Efros, A. A., and Hebert, M. 2010. Blocks world revisited: Image understanding using qualitative geometry and mechanics. In ECCV, 482–496.
7. Henry, P., Krainin, M., Herbst, E., Ren, X., and Fox, D. 2010. RGB-D mapping: Using depth cameras for dense 3D modeling of indoor environments. In International Symposium on Experimental Robotics.
8. Huang, Q., Koltun, V., and Guibas, L. 2011. Joint-shape segmentation with linear programming. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH Asia) 30, 6, 125:1–125:11.
9. Izadi, S., Kim, D., Hilliges, O., Molyneaux, D., Newcombe, R., Kohli, P., Shotton, J., Hodges, S., Freeman, D., Davison, A., and Fitzgibbon, A. 2011. Kinect-fusion: real-time 3D reconstruction and interaction using a moving depth camera. In Proc. UIST, 559–568.
10. Koppula, H., Anand, A., Joachims, T., and Saxena, A. 2011. Semantic labeling of 3D point clouds for indoor scenes. In NIPS, 244–252.
11. Lee, D. C., Gupta, A., Hebert, M., and Kanade, T. 2010. Estimating spatial layout of rooms using volumetric reasoning about objects and surfaces. In NIPS, 1288–1296.
12. Leordeanu, M., and Hebert, M. 2005. A spectral technique for correspondence problems using pairwise constraints. In ICCV, vol. 2, 1482–1489.
13. Li, H., Adams, B., Guibas, L. J., and Pauly, M. 2009. Robust single-view geometry and motion reconstruction. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH) 28, 5, 175:1–175:10.
14. Mehra, R., Zhou, Q., Long, J., Sheffer, A., Gooch, A., and Mitra, N. J. 2009. Abstraction of man-made shapes. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH Asia) 28, 5, #137, 1–10.
15. Mitra, N. J., Flory, S., Ovsjanikov, M., Gelfand, N., Guibas, L., and Pottmann, H. 2007. Dynamic geometry registration. In Symp. on Geometry Proc., 173–182.
16. Mitra, N., Yang, Y.-L., Yan, D.-M., Li, W., and Agrawala, M. 2010. Illustrating how mechanical assemblies work. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH) 29, 4, 58:1–58:12.
17. Mitra, N. J., Pauly, M., Wand, M., and Ceylan, D. 2012. Symmetry in 3d geometry: Extraction and applications. In EUROGRAPHICS State-of-the-art Report.
18. Nan, L., Xie, K., and Sharf, A. 2012. A search-classify approach for cluttered indoor scene understanding. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH Asia) 31, 6.
19. Ovsjanikov, M., Li, W., Guibas, L., and Mitra, N. J. 2011. Exploration of continuous variability in collections of 3D shapes. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH) 30, 4, 33:1–33:10.
20. Pauly, M., Mitra, N. J., Giesen, J., Gross, M., and Guibas, L. J. 2005. Example-based 3D scan completion. In Symp. on Geometry Proc., 23–32.
21. Rusinkiewicz, S., Hall-Holt, O., and Levoy, M. 2002. Real-time 3D model acquisition. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH) 21, 3, 438–446.
22. Schnabel, R., Wessel, R., Wahl, R., and Klein, R. 2008. Shape recognition in 3D point-clouds. In Proc. WSCG, 65–72.
23. Shao, T., Xu, W., Zhou, K., Wang, J., Li, D., and Guo, B. 2012. An interactive approach to semantic modeling of indoor scenes with an RGBD camera. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH Asia) 31, 6.
24. Sidi, O., van Kaick, O., Kleiman, Y., Zhang, H., and Cohen-Or, D. 2011. Unsupervised co-segmentation of a set of shapes via descriptor-space spectral clustering. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH Asia) 30, 6, 126:1–126:10.
25. Triebel, R., Shin, J., and Siegwart, R. 2010. Segmentation and unsupervised part-based discovery of repetitive objects. In Proceedings of Robotics: Science and Systems.
26. Xiang, Y., and Savarese, S. 2012. Estimating the aspect layout of object categories. In CVPR, 3410–3417.
27. Xu, K., Li, H., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D., Xiong, Y., and Cheng, Z. 2010. Style-content separation by anisotropic part scales. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH Asia) 29, 5, 184:1–184:10.
28. Xu, K., Zheng, H., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D., Liu, L., and Xiong, Y. 2011. Photo-inspired model-driven 3D object modeling. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH) 30, 4, 80:1–80:10.
29. Zheng, Y., Chen, X., Cheng, M.-M., Zhou, K., Hu, S.-M., and Mitra, N. J. 2012. Interactive images: Cuboid proxies for smart image manipulation. ACM TOG (SIGGRAPH) 31, 4, 99:1–99:11.