“Conjoining Gestalt rules for abstraction of architectural drawings”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Conjoining Gestalt rules for abstraction of architectural drawings
Session/Category Title: Architectural Design and Analysis
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
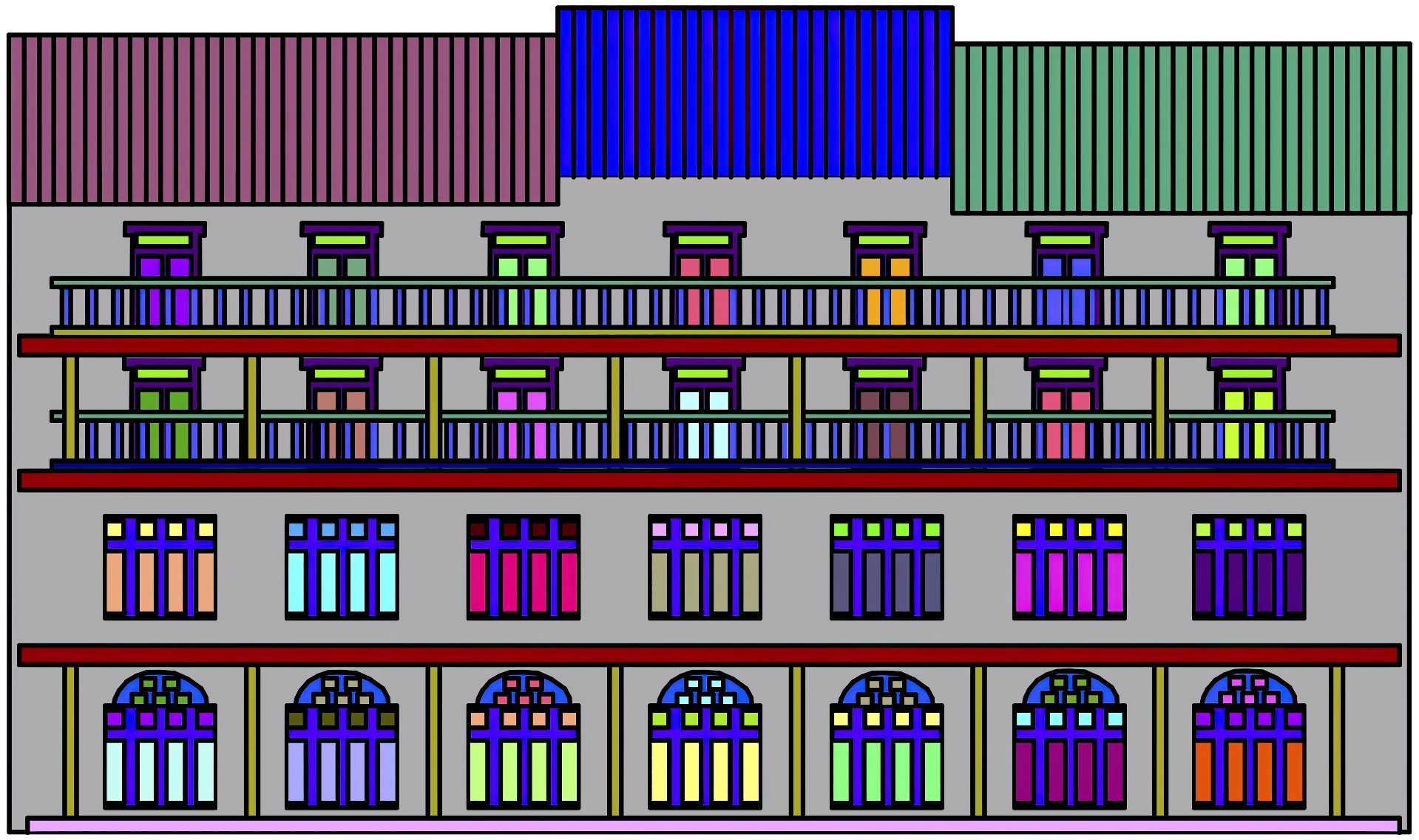
We present a method for structural summarization and abstraction of complex spatial arrangements found in architectural drawings. The method is based on the well-known Gestalt rules, which summarize how forms, patterns, and semantics are perceived by humans from bits and pieces of geometric information. Although defining a computational model for each rule alone has been extensively studied, modeling a conjoint of Gestalt rules remains a challenge. In this work, we develop a computational framework which models Gestalt rules and more importantly, their complex interactions. We apply conjoining rules to line drawings, to detect groups of objects and repetitions that conform to Gestalt principles. We summarize and abstract such groups in ways that maintain structural semantics by displaying only a reduced number of repeated elements, or by replacing them with simpler shapes. We show an application of our method to line drawings of architectural models of various styles, and the potential of extending the technique to other computer-generated illustrations, and three-dimensional models.
References:
1. Adabala, N., Varma, M., Toyama, K., and Bangalore, S. N. 2007. Computer aided generation of stylized maps. Comp. Anim. Virtual Worlds 18, 133–140. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Adabala, N. 2009. Building representation in oblique-view maps of modern urban areas. Cartographic Journal 46, 2, 104–114.Google ScholarCross Ref
3. Barla, P., Thollot, J., and Sillion, F. X. 2005. Geometric clustering for line drawing simplification. In In Proceedings of the Eurographics Symposium on Rendering. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Barla, P., Breslav, S., Thollot, J., Sillion, F. X., and Markosian, L. 2006. Stroke pattern analysis and synthesis. Comp. Graph. Forum 25, 3, 663–671.Google ScholarCross Ref
5. Belongie, S., Malik, J., and Puzicha, J. 2002. Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 24, 509–522. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Cao, F., Delon, J., Desolneux, A., Muse, P., and Sur, F. 2007. A unified framework for detecting groups and application to shape recognition. J Math Imaging Vis 27, 91–119. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Claessens, P., and Wagemans, J. 2008. A bayesian framework for cue integration in multistable grouping: Proximity, collinearity, and orientation priors in zigzag lattices. Journal of Vision 8, 4, 33:1–23.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Cole, F., Golovinskiy, A., Limpaecher, A., Barros, H., Finkelstein, A., Funkhouser, T., and Rusinkiewicz, S. 2008. Where do people draw lines? In ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 papers, ACM, 1–11. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Cole, F., Sanik, K., DeCarlo, D., Finkelstein, A., Funkhouser, T., Rusinkiewicz, S., and Singh, M. 2009. How well do line drawings depict shape? In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), vol. 28, ACM, 28. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. DeCarlo, D., and Santella, A. 2002. Stylization and abstraction of photographs. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), vol. 21, ACM, 769–776. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Delong, A., Osokin, A., Isack, H. N., and Boykov, Y. 2010. Fast approximate energy minimization with label costs. In CVPR, 2173–2180.Google Scholar
12. Desolneux, A., Moisan, L., and michel Morel, J. 2002. Gestalt theory and Computer Vision.Google Scholar
13. Drori, I., Cohen-Or, D., and Yeshurun, H. 2003. Fragment-based image completion. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH 2003, 303–312. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Elder, J. H., and Goldberg, R. M. 2002. Ecological statistics of gestalt laws for the perceptual organization of contours. Journal of Vision, 4.Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Feldman, J. 2003. Perceptual grouping by selection of a logically minimal model. International Journal of Computer Vision 55, 1, 5–25. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Glander, T., and Dllner, J. 2009. Abstract representations for interactive visualization of virtual 3d city models. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems 33, 5, 375–387.Google ScholarCross Ref
17. Glander, T., and Döllner, J. 2008. Techniques for generalizing building geometry of complex virtual 3d city models. In Advances in 3D Geoinformation Systems, Springer, P. van Oosterom, S. Zlatanova, F. Penninga, and E. M. Fendel, Eds., Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography, 381–400.Google Scholar
18. Grabler, F., Agrawala, M., Sumner, R. W., and Pauly, M. 2008. Automatic generation of tourist maps. ACM Trans. Graph. 27 (August), 100:1–100:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Grabli, S., Durand, F., and Sillion, F. 2004. Density measure for line-drawing simplification. In Proceedings of Pacific Graphics. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Hurtut, T., Landes, P., Thollot, J., Gousseau, Y., Drouillhet, R., and Coeurjolly, J. 2009. Appearance-guided synthesis of element arrangements by example. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering, ACM, 51–60. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Ijiri, T., Mech, R., Igarashi, T., and Miller, G. 2008. An Example-based Procedural System for Element Arrangement. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 27, Wiley Online Library, 429–436.Google Scholar
22. Kanizsa, G. 1980. Grammatica del Vedere.Google Scholar
23. Kubovy, M., and van den Berg, M. 2008. The whole is equal to the sum of its parts: A probabilistic model of grouping by proximity and similarity in regular patterns. Psychological Review 1.Google Scholar
24. Liu, Y., Collins, R. T., and Tsin, Y. 2004. A computational model for periodic pattern perception based on frieze and wallpaper groups. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26, 3, 354–371. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Loya, A., Adabala, N., Das, A., and Mishra, P. 2008. A practical approach to image-guided building facade abstraction. In Computer Graphics International 2008.Google Scholar
26. Mehra, R., Zhou, Q., Long, J., Sheffer, A., Gooch, A., and Mitra, N. J. 2009. Abstraction of man-made shapes. ACM Transactions on Graphics 28, 5, 137:1–137:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Mi, X., DeCarlo, D., and Stone, M. 2009. Abstraction of 2D shapes in terms of parts. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering, ACM, 15–24. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Mitra, N. J., Chu, H.-K., Lee, T.-Y., Wolf, L., Yeshurun, H., and Cohen-Or, D. 2009. Emerging images. ACM Transactions on Graphics 28, 5 (December), 163:1–163:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Shesh, A., and Chen, B. 2008. Efficient and dynamic simplification of line drawings. Comput. Graph. Forum 27, 2, 537–545.Google ScholarCross Ref
30. Sidiropoulos, G., and Vasilakos, A. 2006. Ultra-real or symbolic visualization? the case of the city through time. Computers & Graphics 30, 2, 299–310. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Wang, J., Xu, Y., Shum, H.-Y., and Cohen, M. F. 2004. Video tooning. ACM Trans. Graph. 23 (August), 574–583. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Wertheimer, M. 1923. Untersuchungen zur lehre der gestalt ii,. Psychol. Forsch., 4, 301–350. Translation published as Laws of Organization in Perceptual Forms, in: W. Ellis, A Source Book of Gestalt Psychology, Routledge and Kegan Paul, London, 1938, pp. 71–88.Google ScholarCross Ref