“Transparent Object Reconstruction via Implicit Differentiable Refraction Rendering” by Gao, Zhang, Wang, Cheng and Zhang
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Transparent Object Reconstruction via Implicit Differentiable Refraction Rendering
Session/Category Title:
- From Pixels to Gradients
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
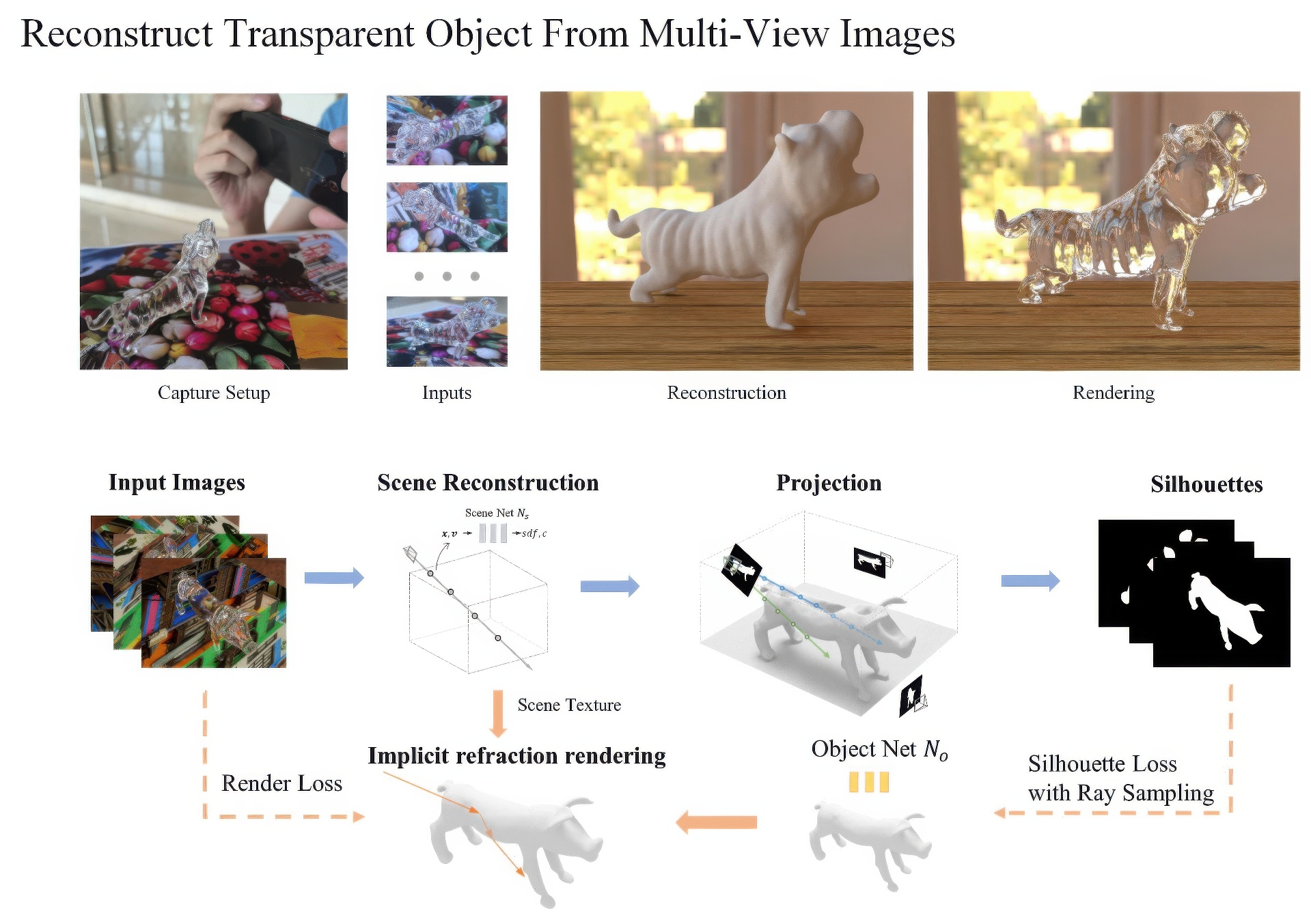
Reconstructing the geometry of transparent objects has been a long-standing challenge. Existing methods rely on complex setups, such as manual annotation or darkroom conditions, to obtain object silhouettes and usually require controlled environments with designed patterns to infer ray-background correspondence. However, these intricate arrangements limit the practical application for common users. In this paper, we significantly simplify the setups and present a novel method that reconstructs transparent objects in unknown natural scenes without manual assistance. Our method incorporates two key technologies. Firstly, we introduce a volume rendering-based method that estimates object silhouettes by projecting the 3D neural field onto 2D images. This automated process yields highly accurate multi-view object silhouettes from images captured in natural scenes. Secondly, we propose transparent object optimization through differentiable refraction rendering with the neural SDF field, enabling us to optimize the refraction ray based on color rather than explicit ray-background correspondence. Additionally, our optimization includes a ray sampling method to supervise the object silhouette at a low computational cost. Extensive experiments and comparisons demonstrate that our method produces high-quality results while offering much more convenient setups.
References:
[1]
Eirikur Agustsson and Radu Timofte. 2017. Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Dataset and study. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. 126–135.
[2]
Nicolas Alt, Patrick Rives, and Eckehard Steinbach. 2013. Reconstruction of transparent objects in unstructured scenes with a depth camera. In 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. IEEE, 4131–4135.
[3]
Mojtaba Bemana, Karol Myszkowski, Jeppe Revall Frisvad, Hans-Peter Seidel, and Tobias Ritschel. 2022. Eikonal fields for refractive novel-view synthesis. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 Conference Proceedings. 1–9.
[4]
François Darmon, Bénédicte Bascle, Jean-Clément Devaux, Pascal Monasse, and Mathieu Aubry. 2022. Improving neural implicit surfaces geometry with patch warping. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 6260–6269.
[5]
Qiancheng Fu, Qingshan Xu, Yew Soon Ong, and Wenbing Tao. 2022. Geo-Neus: geometry-consistent neural implicit surfaces learning for multi-view reconstruction. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35 (2022), 3403–3416.
[6]
Amos Gropp, Lior Yariv, Niv Haim, Matan Atzmon, and Yaron Lipman. 2020. Implicit geometric regularization for learning shapes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.10099 (2020).
[7]
Cong Huynh, Antonio Robles-Kelly, and Edwin Hancock. 2010. Shape and refractive index recovery from single-view polarisation images. In 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2010.5539828
[8]
Jeffrey Ichnowski, Yahav Avigal, Justin Kerr, and Ken Goldberg. 2021. Dex-NeRF: Using a Neural Radiance Field to Grasp Transparent Objects.
[9]
Ivo Ihrke, Kiriakos N Kutulakos, Hendrik PA Lensch, Marcus Magnor, and Wolfgang Heidrich. 2010. Transparent and specular object reconstruction. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 29. Wiley Online Library, 2400–2426.
[10]
Kiriakos N Kutulakos and Eron Steger. 2008. A theory of refractive and specular 3D shape by light-path triangulation. International Journal of Computer Vision 76 (2008), 13–29.
[11]
Zhengqin Li, Yu-Ying Yeh, and Manmohan Chandraker. 2020. Through the looking glass: Neural 3d reconstruction of transparent shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 1262–1271.
[12]
Jiahui Lyu, Bojian Wu, Dani Lischinski, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Hui Huang. 2020. Differentiable refraction-tracing for mesh reconstruction of transparent objects. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 39, 6 (2020), 1–13.
[13]
Ben Mildenhall, Pratul P. Srinivasan, Matthew Tancik, Jonathan T. Barron, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Ren Ng. 2020. NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis. 405–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_24
[14]
Daisuke Miyazaki and Katsushi Ikeuchi. 2005. Inverse polarization raytracing: estimating surface shapes of transparent objects. In 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), Vol. 2. IEEE, 910–917.
[15]
Nigel JW Morris and Kiriakos N Kutulakos. 2007. Reconstructing the surface of inhomogeneous transparent scenes by scatter-trace photography. In 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 1–8.
[16]
Nigel JW Morris and Kiriakos N Kutulakos. 2011. Dynamic refraction stereo. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 33, 8 (2011), 1518–1531.
[17]
Michael Niemeyer, Lars Mescheder, Michael Oechsle, and Andreas Geiger. 2020. Differentiable volumetric rendering: Learning implicit 3d representations without 3d supervision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 3504–3515.
[18]
Merlin Nimier-David, Delio Vicini, Tizian Zeltner, and Wenzel Jakob. 2019. Mitsuba 2: A retargetable forward and inverse renderer. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6 (2019), 1–17.
[19]
Michael Oechsle, Songyou Peng, and Andreas Geiger. 2021. Unisurf: Unifying neural implicit surfaces and radiance fields for multi-view reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 5589–5599.
[20]
Yiming Qian, Minglun Gong, and Yee-Hong Yang. 2016. 3D Reconstruction of Transparent Objects with Position-Normal Consistency. In 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.473
[21]
Yiming Qian, Minglun Gong, and Yee-Hong Yang. 2017. Stereo-Based 3D Reconstruction of Dynamic Fluid Surfaces by Global Optimization. In 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2017.704
[22]
Shreeyak Sajjan, Matthew Moore, Mike Pan, Ganesh Nagaraja, Johnny Lee, Andy Zeng, and Shuran Song. 2020. Clear Grasp: 3D Shape Estimation of Transparent Objects for Manipulation. In 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). https://doi.org/10.1109/icra40945.2020.9197518
[23]
Johannes L. Schonberger and Jan-Michael Frahm. 2016. Structure-from-Motion Revisited. In 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.445
[24]
Qi Shan, S. Agarwal, and B. Curless. 2012. Refractive height fields from single and multiple images. In 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2012.6247687
[25]
Jonathan Stets, Zhengqin Li, Jeppe Revall Frisvad, and Manmohan Chandraker. 2019. Single-Shot Analysis of Refractive Shape Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). https://doi.org/10.1109/wacv.2019.00111
[26]
Kenichiro Tanaka, Yasuhiro Mukaigawa, Hiroyuki Kubo, Yasuyuki Matsushita, and Yasushi Yagi. 2016. Recovering Transparent Shape from Time-of-Flight Distortion. In 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.475
[27]
Borislav Trifonov, Derek Bradley, and Wolfgang Heidrich. 2006. Tomographic reconstruction of transparent objects. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Sketches. 55–es.
[28]
Peng Wang, Lingjie Liu, Yuan Liu, Christian Theobalt, Taku Komura, and Wenping Wang. 2021. NeuS: Learning Neural Implicit Surfaces by Volume Rendering for Multi-view Reconstruction. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
[29]
Gordon Wetzstein, David Roodnick, Wolfgang Heidrich, and Ramesh Raskar. 2011. Refractive shape from light field distortion. In 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 1180–1186.
[30]
Bojian Wu, Yang Zhou, Yiming Qian, Minglun Cong, and Hui Huang. 2018. Full 3D reconstruction of transparent objects. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 1–11.
[31]
Jinhui Xiong and Wolfgang Heidrich. 2021. In-the-wild single camera 3D reconstruction through moving water surfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 12558–12567.
[32]
Jiamin Xu, Zihan Zhu, Hujun Bao, and Weiwei Xu. 2022. A hybrid mesh-neural representation for 3D transparent object reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph 1, 1 (2022).
[33]
Lior Yariv, Jiatao Gu, Yoni Kasten, and Yaron Lipman. 2021. Volume rendering of neural implicit surfaces. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (2021), 4805–4815.
[34]
Lior Yariv, Yoni Kasten, Dror Moran, Meirav Galun, Matan Atzmon, Basri Ronen, and Yaron Lipman. 2020. Multiview neural surface reconstruction by disentangling geometry and appearance. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33 (2020), 2492–2502.
[35]
Sai-Kit Yeung, Tai-Pang Wu, Chi-Keung Tang, Tony F Chan, and Stanley Osher. 2011. Adequate reconstruction of transparent objects on a shoestring budget. In CVPR 2011. IEEE, 2513–2520.
[36]
Kai Zhang, Fujun Luan, Zhengqi Li, and Noah Snavely. 2022. Iron: Inverse rendering by optimizing neural sdfs and materials from photometric images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 5565–5574.
[37]
Kai Zhang, Gernot Riegler, Noah Snavely, and Vladlen Koltun. 2020. Nerf++: Analyzing and improving neural radiance fields. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.07492 (2020).
[38]
Mingjie Zhang, Xing Lin, Mohit Gupta, Jinli Suo, and Qionghai Dai. 2014. Recovering scene geometry under wavy fluid via distortion and defocus analysis. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer, 234–250.
[39]
Luyang Zhu, Arsalan Mousavian, Yu Xiang, Hammad Mazhar, Jozef van Eenbergen, Shoubhik Debnath, and Dieter Fox. 2021. RGB-D local implicit function for depth completion of transparent objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 4649–4658.