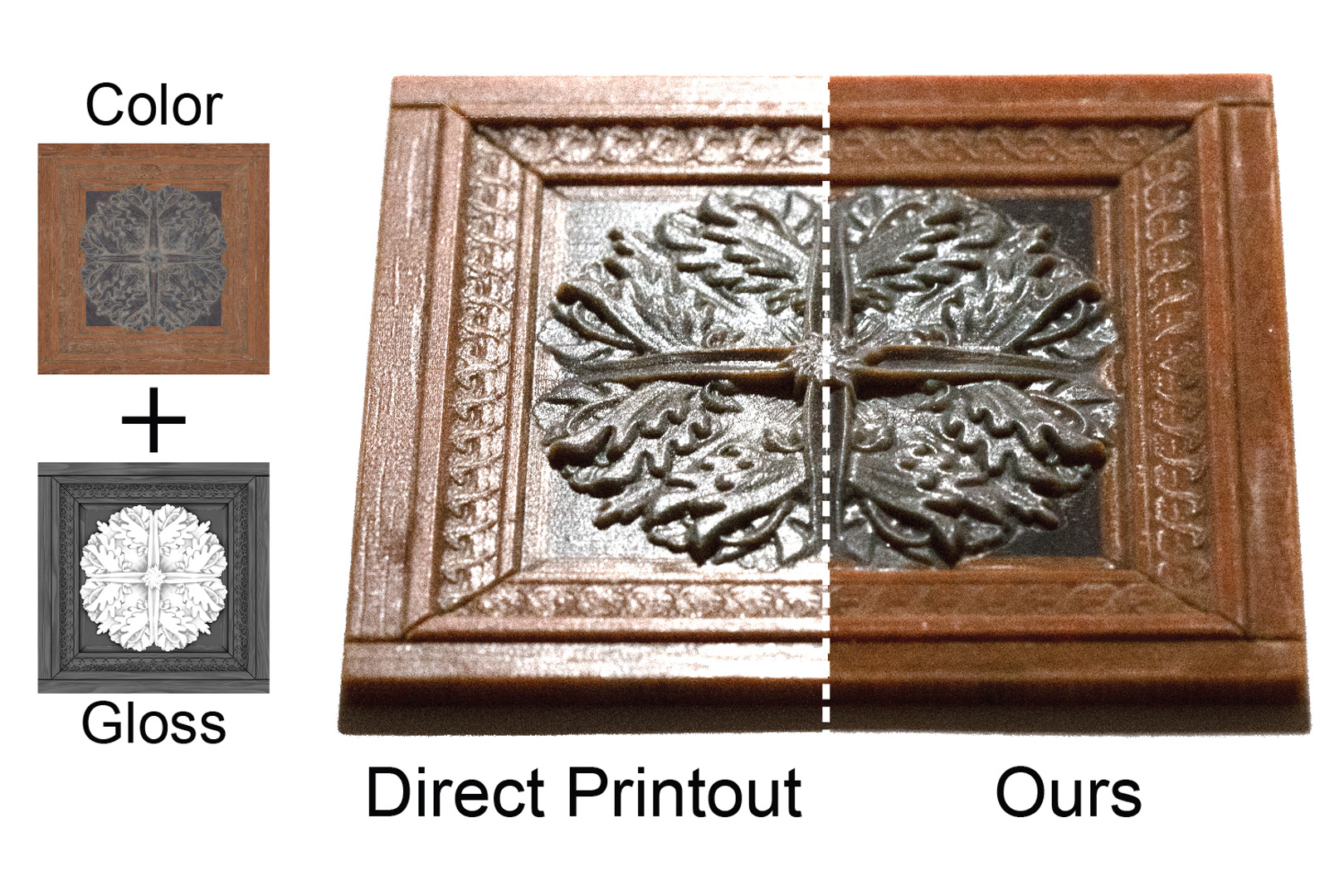
“Towards spatially varying gloss reproduction for 3D printing” by Piovarči, Foshey, Babaei, Rusinkiewicz, Matusik, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Towards spatially varying gloss reproduction for 3D printing
Session/Category Title:
- Fabrication: Carving, Dicing, and Printing
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
3D printing technology is a powerful tool for manufacturing complex shapes with high-quality textures. Gloss, next to color and shape, is one of the most salient visual aspects of an object. Unfortunately, printing a wide range of spatially-varying gloss properties using state-of-the-art 3D printers is challenging as it relies on geometrical modifications to achieve the desired appearance. A common post-processing step is to apply off-the-shelf varnishes that modify the final gloss. The main difficulty in automating this process lies in the physical properties of the varnishes which owe their appearance to a high concentration of large particles and as such, they cannot be easily deposited with current 3D color printers. As a result, fine-grained control of gloss properties using today’s 3D printing technologies is limited in terms of both spatial resolution and the range of achievable gloss. We address the above limitations and propose new printing hardware based on piezo-actuated needle valves capable of jetting highly viscous varnishes. Based on the new hardware setup, we present the complete pipeline for controlling the gloss of a given 2.5 D object, from printer calibration, through material selection, to the manufacturing of models with spatially-varying reflectance. Furthermore, we discuss the potential integration with current 3D printing technology. Apart from being a viable solution for 3D printing, our method offers an additional and essential benefit of separating color and gloss fabrication which makes the process more flexible and enables high-quality color and gloss reproduction.
References:
1. Teun Baar, Sepideh Samadzadegan, Hans Brettel, Philipp Urban, and Maria V Ortiz Segovia. 2014. Printing gloss effects in a 2.5 D system. In Measuring, Modeling, and Reproducing Material Appearance, Vol. 9018. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 90180M.Google Scholar
2. Vahid Babaei and Roger D Hersch. 2016. N-Ink Printer Characterization With Barycentric Subdivision. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 25, 7 (2016), 3023–3031.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Vahid Babaei, Kiril Vidimče, Michael Foshey, Alexandre Kaspar, Piotr Didyk, and Wojciech Matusik. 2017. Color contoning for 3D printing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 124.Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Alan Brunton, Can Ates Arikan, Tejas Madan Tanksale, and Philipp Urban. 2018. 3D printing spatially varying color and translucency. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 157.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Alan Brunton, Can Ates Arikan, and Philipp Urban. 2015. Pushing the limits of 3D color printing: Error diffusion with translucent materials. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 1 (2015), 4.Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Robert L Cook and Kenneth E Torrance. 1982. A reflectance model for computer graphics. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 1, 1 (1982), 7–24.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. E. René de la Rie, John K. Delaney, Kathryn M. Morales, Christopher A. Maines, and Li-Piin Sung. 2010. Modification of Surface Roughness by Various Varnishes and Effect on Light Reflection. Studies in Conservation 55, 2 (2010), 134–143. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1179/sic.2010.55.2.134 Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Yue Dong, Jiaping Wang, Fabio Pellacini, Xin Tong, and Baining Guo. 2010. Fabricating spatially-varying subsurface scattering. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 29, 4 (2010), 62.Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Oskar Elek, Denis Sumin, Ran Zhang, Tim Weyrich, Karol Myszkowski, Bernd Bickel, Alexander Wilkie, and Jaroslav Křivánek. 2017. Scattering-aware texture reproduction for 3D printing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 6 (2017), 241.Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Willemijn Elkhuizen, Tessa Essers, Yu Song, Jo Geraedts, Clemens Weijkamp, Joris Dik, and Sylvia Pont. 2019. Gloss, Color, and Topography Scanning for Reproducing a Painting’s Appearance Using 3D Printing. Journal on Computing and Cultural Heritage (JOCCH) 12, 4 (2019), 1–22.Google Scholar
11. Adria Fores, James Ferwerda, and Jinwei Gu. 2012. Toward a perceptually based metric for BRDF modeling. In Color and imaging conference, Vol. 2012. Society for Imaging Science and Technology, 142–148.Google Scholar
12. Miloš Hašan, Martin Fuchs, Wojciech Matusik, Hanspeter Pfister, and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2010. Physical reproduction of materials with specified subsurface scattering. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 29. ACM, 61.Google Scholar
13. Philipp Herholz, Wojciech Matusik, and Marc Alexa. 2015. Approximating Free-form Geometry with Height Fields for Manufacturing. Computer Graphics Forum 34, 2 (2015), 239–251.Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Yun-Xian Ho, Michael S. Landy, and Laurence T. Maloney. 2008. Conjoint Measurement of Gloss and Surface Texture. Psychological Science 19, 2 (2008), 196–204. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02067.x PMID: 18271869. Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Matthias B. Hullin, Ivo Ihrke, Wolfgang Heidrich, Tim Weyrich, Gerwin Damberg, and Martin Fuchs. 2013. State of the Art in Computational Fabrication and Display of Material Appearance. In Eurographics Annual Conference (STAR). Girona, Spain. https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00809477Google Scholar
16. Matthias B. Hullin, Hendrik P. A. Lensch, Ramesh Raskar, Hans-Peter Seidel, and Ivo Ihrke. 2011. Dynamic Display of BRDFs. In Computer Graphics Forum (Proc. EUROGRAPHICS), Oliver Deussen and Min Chen (Eds.). Eurographics, Blackwell, Llandudno, UK, 475–483.Google Scholar
17. Wenzel Jakob. 2010. Mitsuba renderer. http://www.mitsuba-renderer.org.Google Scholar
18. Eric P. F. Lafortune, Sing-Choong Foo, Kenneth E. Torrance, and Donald P. Greenberg. 1997. Non-Linear Approximation of Reflectance Functions. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’97). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., USA, 117–126. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Yanxiang Lan, Yue Dong, Fabio Pellacini, and Xin Tong. 2013. Bi-scale appearance fabrication. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (2013), 145–1.Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Daniel L. Lau and Gonzalo R. Arce. 2007. Modern Digital Halftoning, Second Edition. CRC Press, Inc., USA.Google Scholar
21. Anat Levin, Daniel Glasner, Ying Xiong, Frédo Durand, William Freeman, Wojciech Matusik, and Todd Zickler. 2013. Fabricating BRDFs at high spatial resolution using wave optics. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4 (2013), 144.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. A Luongo, V Falster, MB Doest, MM Ribo, ER Eiriksson, DB Pedersen, and JR Frisvad. 2019. Microstructure Control in 3D Printing with Digital Light Processing. In Computer Graphics Forum. Wiley Online Library.Google Scholar
23. Tom Malzbender, Ramin Samadani, Steven Scher, Adam Crume, Douglas Dunn, and James Davis. 2012. Printing reflectance functions. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 3 (2012), 20.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Wojciech Matusik, Boris Ajdin, Jinwei Gu, Jason Lawrence, Hendrik P. A. Lensch, Fabio Pellacini, and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2009. Printing Spatially-Varying Reflectance. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 5 (2009), 1–9.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Addy Ngan, Frédo Durand, and Wojciech Matusik. 2005. Experimental Analysis of BRDF Models. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Eurographics Conference on Rendering Techniques (EGSR ’05). Eurographics Association, Goslar, DEU, 117–126.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Jorge Nocedal and Stephen Wright. 2006. Numerical optimization. Springer New York.Google Scholar
27. Daniele Panozzo, Olga Diamanti, Sylvain Paris, Marco Tarini, Evgeni Sorkine, and Olga Sorkine-Hornung. 2015. Texture Mapping Real-World Objects with Hydrographics. Computer Graphics Forum 34, 5 (2015), 65–75. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Marios Papas, Christian Regg, Wojciech Jarosz, Bernd Bickel, Philip Jackson, Wojciech Matusik, Steve Marschner, and Markus Gross. 2013. Fabricating translucent materials using continuous pigment mixtures. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4 (2013), 146.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Thiago Pereira, Carolina L. A. Paes Leme, Steve Marschner, and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2017. Printing Anisotropic Appearance with Magnetic Flakes. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 123 (July 2017), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Thiago Pereira and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2012. Gamut mapping spatially varying reflectance with an improved BRDF similarity metric. In Computer graphics forum, Vol. 31. Wiley Online Library, 1557–1566.Google Scholar
31. Michal Piovarči, Michael Wessely, Michał Jagielski, Marc Alexa, Wojciech Matusik, and Piotr Didyk. 2017. Directional screens. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual ACM Symposium on Computational Fabrication. ACM, 1.Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Olivier Rouiller, Bernd Bickel, Jan Kautz, Wojciech Matusik, and Marc Alexa. 2013. 3D-printing spatially varying BRDFs. IEEE computer graphics and applications 33, 6 (2013), 48–57.Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Sepideh Samadzadegan, Teun Baar, Philipp Urban, Maria V Ortiz Segovia, and Jana Blahová. 2015. Controlling colour-printed gloss by varnish-halftones. In Measuring, Modeling, and Reproducing Material Appearance 2015, Vol. 9398. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 93980V.Google Scholar
34. Christian Schüller, Daniele Panozzo, Anselm Grundhöfer, Henning Zimmer, Evgeni Sorkine, and Olga Sorkine-Hornung. 2016. Computational Thermoforming. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4, Article 43 (July 2016), 9 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Liang Shi, Vahid Babaei, Changil Kim, Michael Foshey, Yuanming Hu, Pitchaya Sitthi-Amorn, Szymon Rusinkiewicz, and Wojciech Matusik. 2019. Deep multispectral painting reproduction via multi-layer, custom-ink printing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 6 (2019), 271.Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Pitchaya Sitthi-Amorn, Javier E Ramos, Yuwang Wangy, Joyce Kwan, Justin Lan, Wenshou Wang, and Wojciech Matusik. 2015. MultiFab: a machine vision assisted platform for multi-material 3D printing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 129.Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Stratasys. 2016. Stratasys J750 the ultimate full-color multi-material 3D printer. http://www.stratasys.com/3d-printers/production-series/stratasys-j750. [Online; Accessed 15-08-2017].Google Scholar
38. P. Stucki. 1982. A Multiple-error Correction Computation Algorithm for Bi-level Image Hardcopy Reproduction. R. Oldenbourg. https://books.google.ch/books?id=iaT_GwAACAAJGoogle Scholar
39. Denis Sumin, Tobias Rittig, Vahid Babaei, Thomas Nindel, Alexander Wilkie, Piotr Didyk, Bernd Bickel, J Křivánek, Karol Myszkowski, and Tim Weyrich. 2019. Geometry-Aware Scattering Compensation for 3D Printing. ACM Transactions on Graphics 38 (2019).Google Scholar
40. Tiancheng Sun, Ana Serrano, Diego Gutierrez, and Belen Masia. 2017. Attribute-preserving gamut mapping of measured BRDFs. In Computer graphics forum, Vol. 36. Wiley Online Library, 47–54.Google Scholar
41. Nitus Tipsotnaiyana, Lerpong Jarupan, and Chiravoot Pechyen. 2013. Printing Qualities on Inkjet-Printed Paper from Varnish Coating Agent with Rice Husk Silica Particles. In Advanced Materials Engineering and Technology (Advanced Materials Research), Vol. 626. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 691–695. Google ScholarCross Ref
42. TS Trowbridge and Karl P Reitz. 1975. Average irregularity representation of a rough surface for ray reflection. JOSA 65, 5 (1975), 531–536.Google ScholarCross Ref
43. Philipp Urban, Tejas Madan Tanksale, Alan Brunton, Bui Minh Vu, and Shigeki Nakauchi. 2019. Redefining a in rgba: Towards a standard for graphical 3d printing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 3 (2019), 1–14.Google ScholarDigital Library
44. Bruce Walter, Stephen R. Marschner, Hongsong Li, and Kenneth E. Torrance. 2007. Microfacet Models for Refraction through Rough Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 18th Eurographics Conference on Rendering Techniques (EGSR’07). Eurographics Association, Goslar, DEU, 195–206.Google ScholarDigital Library
45. Tim Warburton. 2006. An explicit construction of interpolation nodes on the simplex. Journal of engineering mathematics 56, 3 (2006), 247–262.Google ScholarCross Ref
46. Gregory J. Ward. 1992. Measuring and Modeling Anisotropic Reflection. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 26, 2 (July 1992), 265–272. Google ScholarDigital Library
47. Tim Weyrich, Pieter Peers, Wojciech Matusik, and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2009. Fabricating microgeometry for custom surface reflectance. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 28, 3 (2009), 32.Google ScholarDigital Library
48. Josh Wills, Sameer Agarwal, David Kriegman, and Serge Belongie. 2009. Toward a perceptual space for gloss. ACM Transactions on Graphics 28, 4 (2009), 1–15.Google ScholarDigital Library
49. Wenzhen Yuan, Siyuan Dong, and Edward H. Adelson. 2017. GelSight: High-Resolution Robot Tactile Sensors for Estimating Geometry and Force. Sensors 17, 12 (2017). Google ScholarCross Ref
50. Yizhong Zhang, Chunji Yin, Changxi Zheng, and Kun Zhou. 2015. Computational Hydrographic Printing. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, Article 131 (July 2015), 11 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library