“Subdivision shading”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Subdivision shading
Session/Category Title:
- Reflectance & subdivision
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
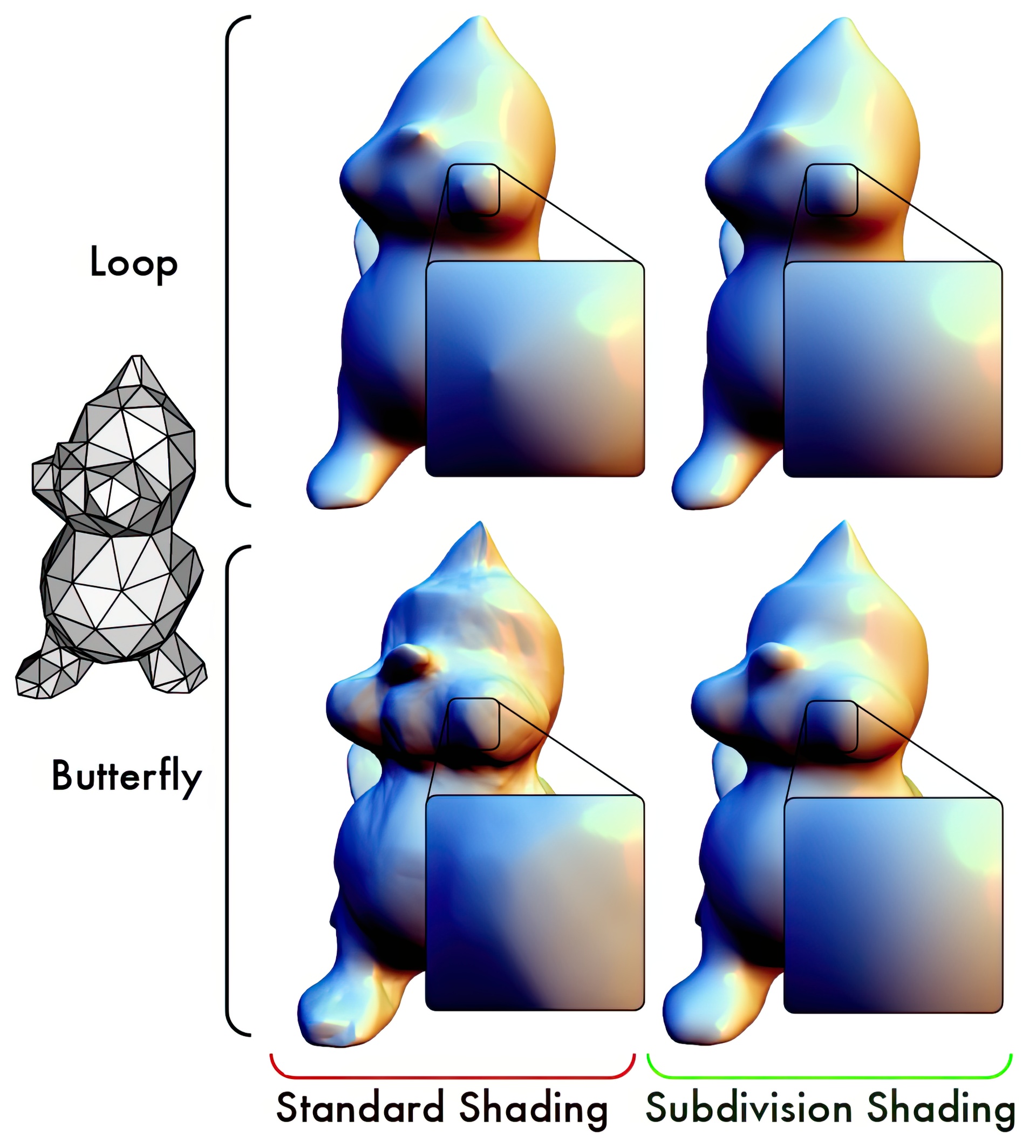
The idea of Phong Shading is applied to subdivision surfaces: normals are associated with vertices and the same construction is used for both locations and normals. This creates vertex positions and normals. The vertex normals are smoother than the normals of the subdivision surface and using vertex normals for shading attenuates the well known visual artifacts of many subdivision schemes. We demonstrate how to apply subdivision to normals and how blend and combine different normals for achieving a variety of effects.
References:
1. Biermann, H., Levin, A., and Zorin, D. 2000. Piecewise smooth subdivision surfaces with normal control. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2000, 113–120. Google Scholar
2. Boubekeur, T., and Alexa, M. 2008. Phong tessellation. In ACM Trans. Graph (Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia). Google Scholar
3. Boubekeur, T., and Schlick, C. 2007. QAS: Real-time quadratic approximation of subdivision surfaces. In Proceedings of Pacific Graphics 2007, 453–456. Google Scholar
4. Buss, S. R., and Fillmore, J. P. 2001. Spherical averages and applications to spherical splines and interpolation. ACM Trans. Graph. 20, 2 (Apr.), 95–126. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Catmull, E., and Clark, J. 1978. Recursively generated B-spline surfaces on arbitrary topological meshes. Computer-Aided Design 10, 6 (Sept.), 350–355.Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Cignoni, P., Scopigno, R., and Tarini, M. 2005. A simple normal enhancement technique for interactive non-photorealistic renderings. C&G 29, 1 (feb), 125–133. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. DeRose, T., Kass, M., and Truong, T. 1998. Subdivision surfaces in character animation. In ACM SIGGRAPH. Google Scholar
8. Doo, D., and Sabin, M. 1978. Behaviour of recursive division surfaces near extraordinary points. Computer-aided Design 10, 6, 356–360.Google ScholarCross Ref
9. Dyn, N., Levin, D., and Gregory, J. A. 1990. A butterfly subdivision scheme for surface interpolation with tension control. ACM Trans. Graph. 9, 2, 160–169. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Karčiauskas, K., and Peters, J. 2007. Bicubic polar subdivision. ACM Transactions on Graphics 26, 4 (Oct.), 14:1–14:6. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Karčiauskas, K., Peters, J., and Reif, U. 2004. Shape characterization of subdivision surfaces–case studies. CAGD 21, 6, 601–614. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Levin, A. 2006. Modified subdivision surfaces with continuous curvature. ACM Transactions on Graphics 25, 3 (July), 1035–1040. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Loop, C., and Schaefer, S. 2008. Approximating catmull-clark subdivision surfaces with bicubic patches. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 1, 1–11. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Loop, C. 1987. Smooth subdivisions surfaces based on triangles. Master’s thesis, Department of Mathematica, University of Utah.Google Scholar
15. Olano, T. M., and Yoo, T. S. 1993. Precision normals (beyond Phong). Tech. rep., University of North Carolina.Google Scholar
16. Peters, J., and Reif, U. 2004. Shape characterization of subdivision surfaces–basic principles. Computer Aided Geometric Design 21, 6, 585–599. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Peters, J., and Reif, U. 2008. Subdivision surfaces. Springer. Google Scholar
18. Phong, B. T. 1975. Illumination for computer generated pictures. Commun. ACM 18, 6, 311–317. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Prautzsch, H. 1998. Analysis of Ck-subdivision surfaces at extraordinary points. Tech. Rep. iratr-1998-4, University of Karlsruhe, Germany, Computer Science.Google Scholar
20. Reif, U. 1995. A unified approach to subdivision algorithms near extraordinary vertices. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 12, 2, 153–174. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Rusinkiewicz, S., Burns, M., and DeCarlo, D. 2006. Exaggerated shading for depicting shape and detail. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3, 1199–1205. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Shiue, L.-J., Jones, I., and Peters, J. 2005. A realtime gpu subdivision kernel. ACM Transactions on Graphics 24, 3 (Aug.), 1010–1015. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Stam, J. 1998. Exact evaluation of catmull-clark subdivision surfaces at arbitrary parameter values. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH 98, 395–404. Google Scholar
24. van Overveld, C. W. A. M., and Wyvill, B. 1997. Phong normal interpolation revisited. ACM Trans. Graph. 16, 4, 397–419. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Vlachos, A., Peters, J., Boyd, C., and Mitchell, J. L. 2001. Curved PN triangles. In 2001 ACM Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics, 159–166. Google Scholar
26. Wallner, J., and Dyn, N. 2005. Convergence and c1 analysis of subdivision schemes on manifolds by proximity. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 22, 7, 593–622. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Zorin, D. 1998. Smoothness of stationary subdivision on irregular meshes. Technical Report CSL-TR-98-752, Stanford University, Computer Systems Laboratory, Jan. Google ScholarDigital Library