“Softshell: dynamic scheduling on GPUs”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Softshell: dynamic scheduling on GPUs
Session/Category Title:
- GPU's and Rendering
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
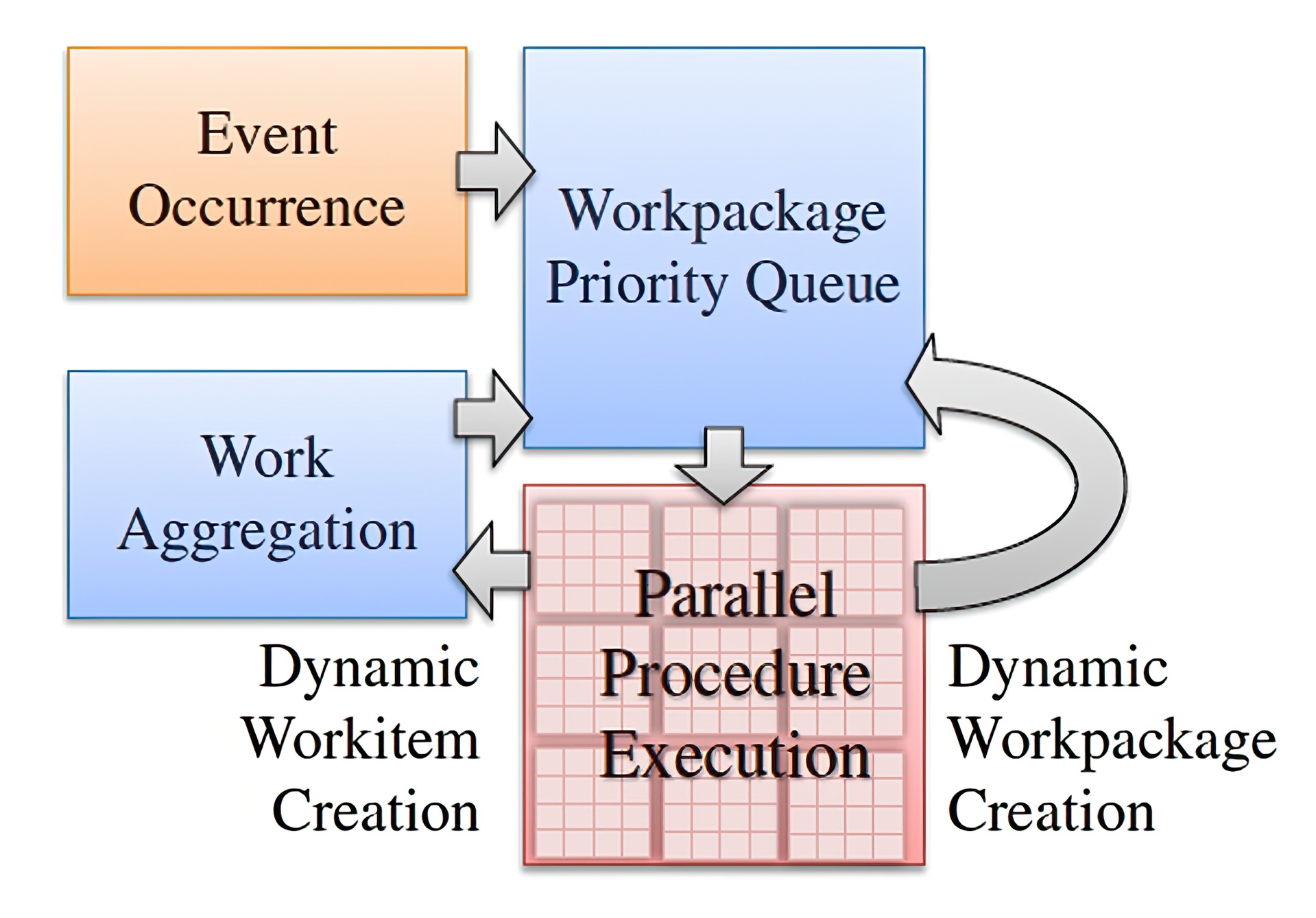
In this paper we present Softshell, a novel execution model for devices composed of multiple processing cores operating in a single instruction, multiple data fashion, such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The Softshell model is intuitive and more flexible than the kernel-based adaption of the stream processing model, which is currently the dominant model for general purpose GPU computation. Using the Softshell model, algorithms with a relatively low local degree of parallelism can execute efficiently on massively parallel architectures. Softshell has the following distinct advantages: (1) work can be dynamically issued directly on the device, eliminating the need for synchronization with an external source, i.e., the CPU; (2) its three-tier dynamic scheduler supports arbitrary scheduling strategies, including dynamic priorities and real-time scheduling; and (3) the user can influence, pause, and cancel work already submitted for parallel execution. The Softshell processing model thus brings capabilities to GPU architectures that were previously only known from operating-system designs and reserved for CPU programming. As a proof of our claims, we present a publicly available implementation of the Softshell processing model realized on top of CUDA. The benchmarks of this implementation demonstrate that our processing model is easy to use and also performs substantially better than the state-of-the-art kernel-based processing model for problems that have been difficult to parallelize in the past.
References:
1. Advanced Micro Devices. 2011. AMD Accelerated Parallel Processing OpenCL – Programming Guide.
2. Agullo, E., Augonnet, C., Dongarra, J., Ltaief, H., Namyst, R., Thibault, S., and Tomov, S. 2010. Faster, cheaper, better — a hybridization methodology to develop linear algebra software for gpus. In GPU Computing Gems, vol. 2. Morgan Kaufmann, Sept.
3. Aila, T., and Laine, S. 2009. Understanding the efficiency of ray traversal on GPUs. In Proc. High Performance Graphics, ACM, HPG ’09, 145–149.
4. Batcher, K. E. 1968. Sorting networks and their applications. In Proc. Spring Joint Computer Conference, ACM, AFIPS ’68, 307–314.
5. Buck, I., Foley, T., Horn, D., Sugerman, J., Fatahalian, K., Houston, M., and Hanrahan, P. 2004. Brook for GPUs: stream computing on graphics hardware. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug.), 777–786.
6. Cederman, D., and Tsigas, P. 2008. On dynamic load balancing on graphics processors. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH/EUROGRAPHICS symposium on Graphics hardware, Eurographics Association, GH ’08, 57–64.
7. Chatterjee, S., Grossman, M., Sbirlea, A., and Sarkar, V. 2011. Dynamic task parallelism with a GPU work-stealing runtime system. In Proc. Workshop on Languages and Compilers for Parallel Computing, LCPC ’11.
8. Chen, L., Villa, O., Krishnamoorthy, S., and Gao, G. 2010. Dynamic load balancing on single- and multi-GPU systems. In Proc. Parallel Distributed Processing, IEEE, IPDPS, 1–12.
9. Frey, S., and Ertl, T. 2010. PaTraCo: A Framework Enabling the Transparent and Efficient Programming of Heterogeneous Compute Networks. In Proc. Eurographics Symposium on Parallel Graphics and Visualization, EGPGV10, 131–140.
10. Fung, W. W. L., Sham, I., Yuan, G., and Aamodt, T. M. 2007. Dynamic warp formation and scheduling for efficient GPU control flow. In Proc. IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, IEEE, MICRO 40, 407–420.
11. Gupta, K., Stuart, J. A., and Owens, J. D. 2012. A study of persistent threads style gpu programming for gpgpu workloads. In Innovative Parallel Computing, 14.
12. Hauswiesner, S., Straka, M., and Reitmayr, G. 2011. Coherent image-based rendering of real-world objects. In Proc. Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, ACM, I3D ’11, 183–190.
13. Hormati, A. H., Samadi, M., Woh, M., Mudge, T., and Mahlke, S. 2011. Sponge: portable stream programming on graphics engines. In Proc. Architectural support for programming languages and operating systems, ACM, ASPLOS ’11, 381–392.
14. Hou, Q., Zhou, K., and Guo, B. 2008. BSGP: bulk-synchronous GPU programming. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug.), 19:1–19:12.
15. Hou, Q., Zhou, K., and Guo, B. 2009. Debugging GPU stream programs through automatic dataflow recording and visualization. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 5 (Dec.), 153:1–153:11.
16. Kajiya, J. T. 1986. The rendering equation. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 20, 4 (Aug.), 143–150.
17. Kato, S., Lakshmanan, K., Rajkumar, R., and Ishikawa, Y. 2011. TimeGraph: GPU scheduling for real-time multitasking environments. In Proc. USENIX annual technical conference, USENIX Association, USENIXATC’11, 2–2.
18. Khronos. 2008. OpenCL The standard for heterogeneous parallel programming. Khronos OpenCL Working Group.
19. Liu, C. L., and Layland, J. W. 1973. Scheduling algorithms for multiprogramming in a hard-real-time environment. J. ACM 20 (January), 46–61.
20. Luebke, D., and Erikson, C. 1997. View-dependent simplification of arbitrary polygonal environments. In Proc. SIGGRAPH ’97, ACM, 199–208.
21. Matusik, W., Buehler, C., Raskar, R., Gortler, S. J., and McMillan, L. 2000. Image-based visual hulls. In Proc. SIGGRAPH ’00, ACM, SIGGRAPH ’00, 369–374.
22. McCool, M. D., Qin, Z., and Popa, T. S. 2002. Shader metaprogramming. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH/EUROGRAPHICS conference on Graphics hardware, HWWS ’02, 57–68.
23. NVIDIA, 2009. NVIDIA’s next generation CUDA compute architecture: Fermi. White paper. Available online.
24. NVIDIA. 2011. NVIDIA CUDA Compute Unified Device Architecture – Programming Guide. NVIDIA.
25. NVIDIA. 2012. NVIDIAs NextGeneration CUDA Compute Architecture: Kepler TM GK110, May.
26. Parker, S. G., Bigler, J., Dietrich, A., Friedrich, H., Hoberock, J., Luebke, D., McAllister, D., McGuire, M., Morley, K., Robison, A., and Stich, M. 2010. OptiX: a general purpose ray tracing engine. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4 (July), 66:1–66:13.
27. Poincaré, H. 1913. The Measure of Time. New York: Science Press.
28. Rossbach, C. J., Currey, J., Silberstein, M., Ray, B., and Witchel, E. 2011. PTask: operating system abstractions to manage gpus as compute devices. In Proc. ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, ACM, SOSP ’11, 233–248.
29. Sanchez, D., Lo, D., Yoo, R. M., Sugerman, J., and Kozyrakis, C. 2011. Dynamic fine-grain scheduling of pipeline parallelism. In Proc. International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques, IEEE, PACT ’11, 22–32.
30. Seiler, L., Carmean, D., Sprangle, E., Forsyth, T., Abrash, M., Dubey, P., Junkins, S., Lake, A., Sugerman, J., Cavin, R., Espasa, R., Grochowski, E., Juan, T., and Hanrahan, P. 2008. Larrabee: a many-core x86 architecture for visual computing. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug.), 18:1–18:15.
31. Sha, L., Abdelzaher, T., Arzen, K.-E., Cervin, A., Baker, T., Burns, A., Buttazzo, G., Caccamo, M., Lehoczky, J., and Mok, A. K. 2004. Real time scheduling theory: A historical perspective. Real-Time Syst. 28, 2, 101–155.
32. Steinberger, M., Kenzel, M., Kainz, B., and Schmalstieg, D. 2012. ScatterAlloc: Massively Parallel Dynamic Memory Allocation for the GPU. In Proceedings of Innovative Parallel Computing (InPar12).
33. Sugerman, J., Fatahalian, K., Boulos, S., Akeley, K., and Hanrahan, P. 2009. GRAMPS: A programming model for graphics pipelines. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 1, 1–11.
34. Tanenbaum, A. S. 2007. Modern Operating Systems. Prentice Hall Press, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
35. Tzeng, S., Patney, A., and Owens, J. D. 2010. Task management for irregular-parallel workloads on the GPU. In Proc. High Performance Graphics, Eurographics Association, HPG ’10, 29–37.
36. Zhou, K., Hou, Q., Ren, Z., Gong, M., Sun, X., and Guo, B. 2009. RenderAnts: interactive Reyes rendering on GPUs. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 5 (Dec.), 155:1–155:11.
37. Zhou, K., Gong, M., Huang, X., and Guo, B. 2011. Data-parallel octrees for surface reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 17, 5 (May), 669–681.