“Shape space exploration of constrained meshes”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Shape space exploration of constrained meshes
Session/Category Title:
- Shape Analysis and Deformation
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
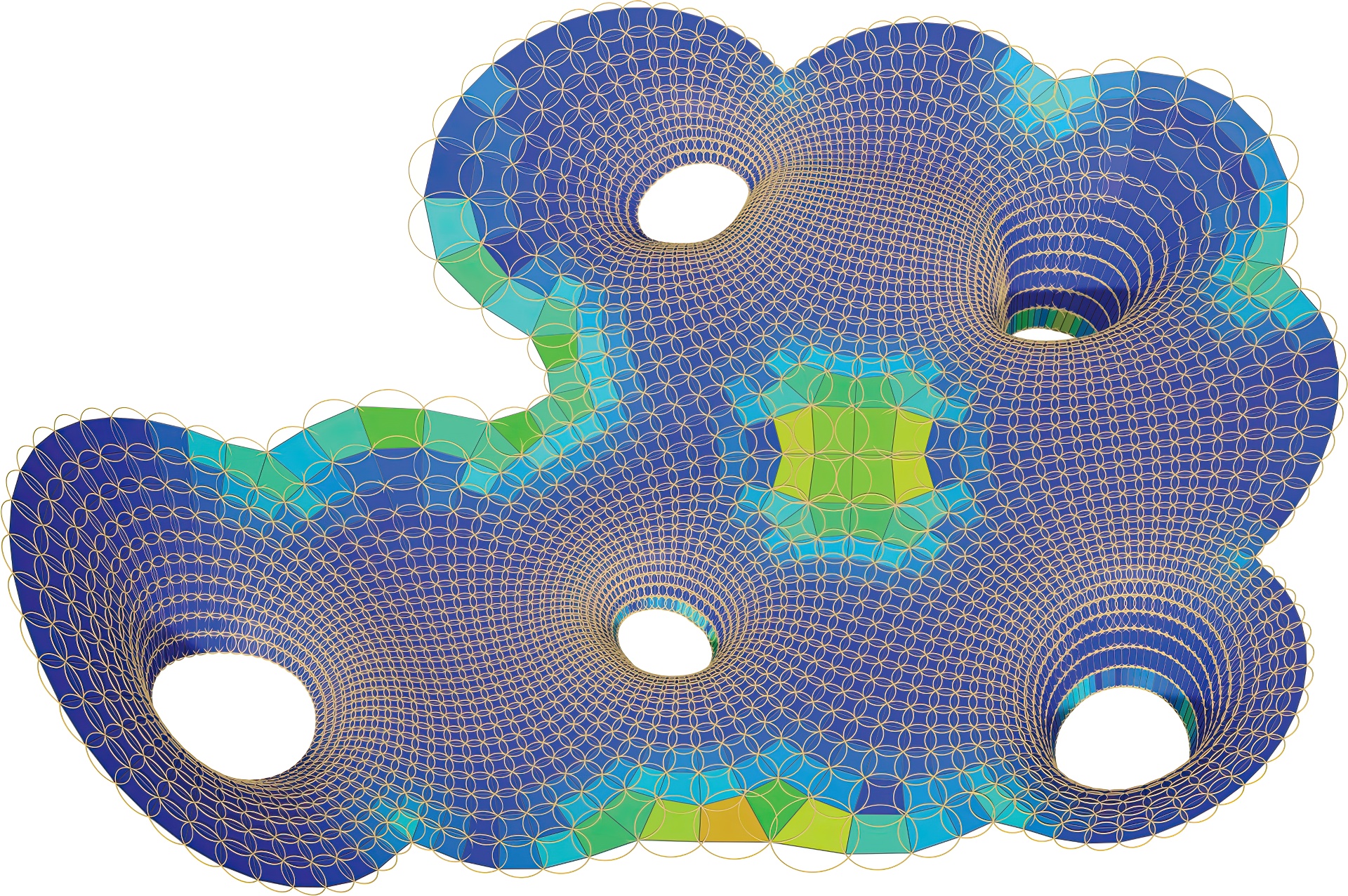
We present a general computational framework to locally characterize any shape space of meshes implicitly prescribed by a collection of non-linear constraints. We computationally access such manifolds, typically of high dimension and co-dimension, through first and second order approximants, namely tangent spaces and quadratically parameterized osculant surfaces. Exploration and navigation of desirable subspaces of the shape space with regard to application specific quality measures are enabled using approximants that are intrinsic to the underlying manifold and directly computable in the parameter space of the osculant surface. We demonstrate our framework on shape spaces of planar quad (PQ) meshes, where each mesh face is constrained to be (nearly) planar, and circular meshes, where each face has a circumcircle. We evaluate our framework for navigation and design exploration on a variety of inputs, while keeping context specific properties such as fairness, proximity to a reference surface, etc.
References:
1. Blanz, V., and Vetter, T. 1999. A morphable model for the synthesis of 3d faces. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH, 187–194. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Bobenko, A. I., and Suris, Y. B. 2008. Discrete Differential Geometry: Integrable Structure, vol. 98. Graduate Studies in Mathematics.Google Scholar
3. Botsch, M., and Sorkine, O. 2008. On linear variational surface deformation methods. In IEEE Trans. on Vis. and Comp. Graphics, vol. 14, 213–230. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Botsch, M., Pauly, M., Gross, M., and Kobbelt, L. 2006. Primo: coupled prisms for intuitive surface modeling. In Proc. of Symp. of Geometry Processing, 11–20. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Ceccato, C., Hesselgren, P., Pauly, M., Pottmann, H., and Wallner, J., Eds. 2010. Advances in Architectural Geometry. Springer.Google Scholar
6. Coleman, T., and Li, Y. 1996. A reflective Newton method for minimizing a quadratic function subject to bounds on some of the variables. SIAM Journal on Optimization 6, 4, 1040–1058. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Deng, B., Pottmann, H., and Wallner, J. 2011. Functional webs for freeform architecture. In Proc. of Symp. of Geometry Processing, 1369–1378.Google Scholar
8. do Carmo, M. P. 1976. Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.Google Scholar
9. Gal, R., Sorkine, O., Mitra, N. J., and Cohen-Or, D. 2009. iwires: An analyze-and-edit approach to shape manipulation. ACM TOG 28, 3, #33, 1–10. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Gu, X. D., and Yau, S.-T. 2008. Computational Conformal Geometry. International Press.Google Scholar
11. Hoffmann, T. 2011. On local deformations of planar quad meshes, vol. 6327 of LNCS. 167–169. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Huang, Q., Wicke, M., Adams, B., and Guibas, L. 2009. Shape decomposition using modal analysis. Computer Graphics Forum (Proc. EUROGRAPHICS) 28, 2, 407–416.Google ScholarCross Ref
13. Kilian, M., Mitra, N. J., and Pottmann, H. 2007. Geometric modeling in shape space. ACM TOG 26, 3, #64, 1–8. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Lipman, Y., Levin, D., and Cohen-Or, D. 2008. Green coordinates. ACM TOG 27, 78:1–78:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Liu, Y., Pottmann, H., Wallner, J., Yang, Y.-L., and Wang, W. 2006. Geometric modeling with conical meshes and developable surfaces. ACM TOG 25, 3, 681–689. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Nocedal, J., and Wright, S. J. 2006. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed. Springer, New York.Google Scholar
17. Pottmann, H., Liu, Y., Wallner, J., Bobenko, A., and Wang, W. 2007. Geometry of multi-layer freeform structures for architecture. ACM TOG 26, 3, #65,1–11. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Pottmann, H., Schiftner, A., Bo, P., Schmiedhofer, H., Wang, W., Baldassini, N., and Wallner, J. 2008. Freeform surfaces from single curved panels. ACM TOG 27, 3, # 76,1–10. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Schouten, J. A., and Struik, D. J. 1931. Einfhrung in die Neuen Methoden der Differentialgeometrie. Groningen.Google Scholar
20. Sumner, R. W., Zwicker, M., Gotsman, C., and Popović, J. 2005. Mesh-based inverse kinematics. ACM TOG 24, 3, 488–495. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Zadravec, M., Schiftner, A., and Wallner, J. 2010. Designing quad-dominant meshes with planar faces. Computer Graphics Forum 29, 5, 1671–1679.Google ScholarCross Ref