“Scalable Multi-Class Sampling via Filtered Sliced Optimal Transport” by Salaün, Georgiev, Seidel and Singh
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Scalable Multi-Class Sampling via Filtered Sliced Optimal Transport
Session/Category Title:
- Sampling and Reconstruction
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
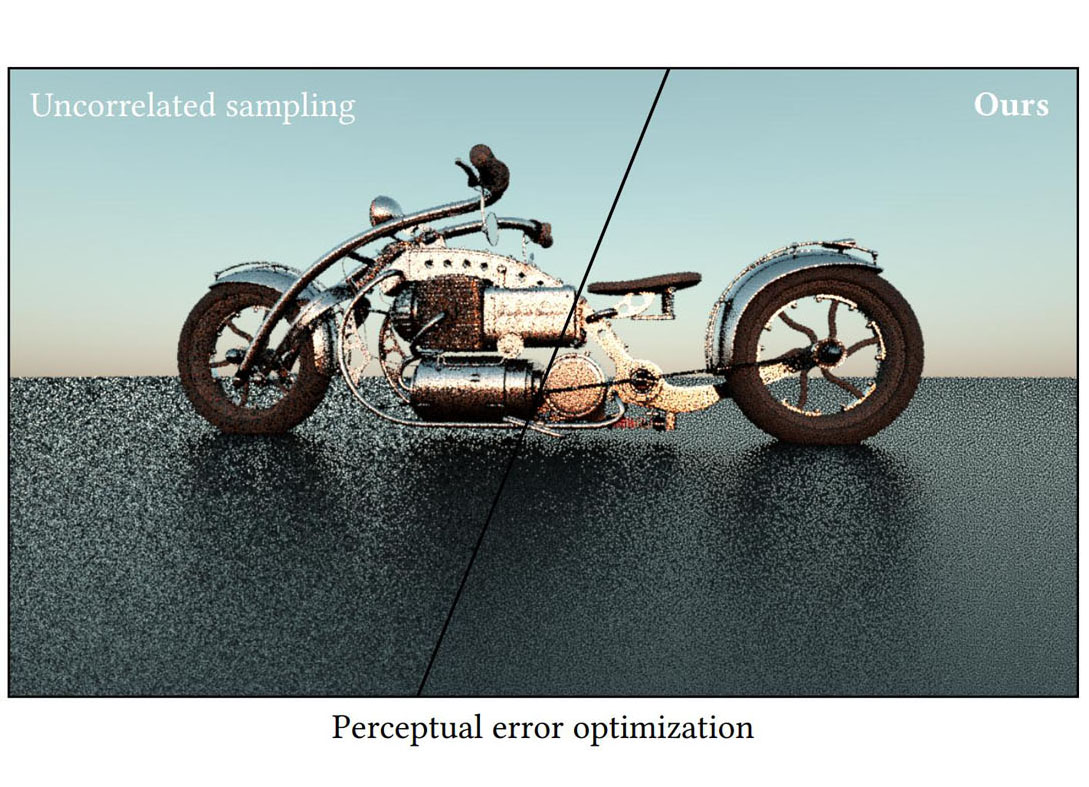
We propose a multi-class point optimization formulation based on continuous Wasserstein barycenters. Our formulation is designed to handle hundreds to thousands of optimization objectives and comes with a practical optimization scheme. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework on various sampling applications like stippling, object placement, and Monte-Carlo integration. We a derive multi-class error bound for perceptual rendering error which can be minimized using our optimization. We provide source code at https://github.com/iribis/filtered-sliced-optimal-transport.
References:
1. Martial Agueh and Guillaume Carlier. 2011. Barycenters in the Wasserstein Space. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis 43, 2 (2011), 904–924.
2. Abdalla G. M. Ahmed and Peter Wonka. 2020. Screen-space blue-noise diffusion of Monte Carlo sampling error via hierarchical ordering of pixels. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 6 (2020), 244:1–244:15.
3. Abdalla G. M. Ahmed and Peter Wonka. 2021. Optimizing Dyadic Nets. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4, Article 141 (jul 2021), 17 pages.
4. Michael Balzer, Thomas Schlömer, and Oliver Deussen. 2009. Capacity-Constrained Point Distributions: A Variant of Lloyd’s Method. 28, 3, Article 86 (July 2009), 8 pages.
5. Laurent Belcour and Eric Heitz. 2021. Lessons Learned and Improvements When Building Screen-Space Samplers with Blue-Noise Error Distribution. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2021 Talks (Virtual Event, USA) (SIGGRAPH ’21). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 9, 2 pages.
6. Nicolas Bonneel and David Coeurjolly. 2019. SPOT: Sliced Partial Optimal Transport. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4, Article 89 (July 2019), 13 pages.
7. Nicolas Bonneel and Hanspeter Pfister. 2013. Sliced Wasserstein Barycenter of Multiple Densities. Technical Report. Harvard Technical Report TR-02-13.
8. Nicolas Bonneel, Julien Rabin, Gabriel Peyré, and Hanspeter Pfister. 2015. Sliced and Radon Wasserstein Barycenters of Measures. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 51, 1 (2015).
9. Nicolas Bonnotte. 2013. Unidimensional and evolution methods for optimal transportation. Ph.D. Dissertation. Paris 11.
10. Léon Bottou. 1998. Online Algorithms and Stochastic Approximations. In Online Learning and Neural Networks, David Saad (Ed.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
11. Jiating Chen, Xiaoyin Ge, Li-Yi Wei, Bin Wang, Yusu Wang, Huamin Wang, Yun Fei, Kang-Lai Qian, Jun-Hai Yong, and Wenping Wang. 2013. Bilateral Blue Noise Sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6, Article 216 (nov 2013), 11 pages.
12. Zhonggui Chen, Zhan Yuan, Yi-King Choi, Ligang Liu, and Wenping Wang. 2012. Variational Blue Noise Sampling. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18, 10 (2012), 1784–1796.
13. Vassillen Chizhov, Iliyan Georgiev, Karol Myszkowski, and Gurprit Singh. 2022. Perceptual Error Optimization for Monte Carlo Rendering. ACM Trans. Graph. 41, 3, Article 26 (mar 2022), 17 pages.
14. Sebastian Claici, Edward Chien, and Justin Solomon. 2018. Stochastic wasserstein barycenters. In International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 999–1008.
15. Robert L. Cook. 1986. Stochastic sampling in computer graphics. 5, 1 (1986), 51–72.
16. Marco Cuturi. 2013. Sinkhorn Distances: Lightspeed Computation of Optimal Transport. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, C. J. C. Burges, L. Bottou, M. Welling, Z. Ghahramani, and K. Q. Weinberger (Eds.), Vol. 26. Curran Associates, Inc. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2013/file/af21d0c97db2e27e13572cbf59eb343d-Paper.pdf
17. Fernando de Goes, Katherine Breeden, Victor Ostromoukhov, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2012. Blue Noise Through Optimal Transport. 31, 6, Article 171 (Nov. 2012), 11 pages.
18. Mark A. Z. Dippé and Erling Henry Wold. 1985. Antialiasing Through Stochastic Sampling. 19, 3 (July 1985), 69–78.
19. Fredo Durand. 2011. A frequency analysis of Monte-Carlo and other numerical integration schemes. Technical Report MIT-CSAILTR-2011-052. CSAIL, MIT,.
20. Sergey Ermakov and Svetlana Leora. 2019. Monte Carlo Methods and the Koksma-Hlawka Inequality. Mathematics 7, 8 (2019).
21. Iliyan Georgiev and Marcos Fajardo. 2016. Blue-Noise Dithered Sampling. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2016 Talks (Anaheim, California) (SIGGRAPH ’16). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 35, 1 pages.
22. Alvaro J. González, Jan Bacca Rodríguez, Gonzalo R. Arce, and Daniel Leo Lau. 2006. Alpha stable human visual system models for digital halftoning. In Electronic Imaging.
23. Eric Heitz, Laurent Belcour, Victor Ostromoukhov, David Coeurjolly, and Jean-Claude Iehl. 2019. A low-discrepancy sampler that distributes Monte Carlo errors as a blue noise in screen space. 1–2.
24. Hu, Sha Ruizhen, van Kaick Tingkai, Deussen Oliver, Huang Oliver, and Hui. 2020. Data Sampling in Multi-view and Multi-class Scatterplots via Set Cover Optimization. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (Proceedings of InfoVis 2019) 26, 1 (2020), 739–748.
25. Min Jiang, Yahan Zhou, Rui Wang, Richard Southern, and Jian Jun Zhang. 2015. Blue Noise Sampling Using an SPH-Based Method. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6, Article 211 (oct 2015), 11 pages.
26. Rabin Julien, Gabriel Peyré, Julie Delon, and Bernot Marc. 2011. Wasserstein Barycenter and its Application to Texture Mixing. In SSVM’11. Springer, Israel, 435–446. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00476064
27. Leonid V. Kantorovich and Gennady S. Rubinstein. 1958. On a space of completely additive functions. Vestnik Leningrad Univ 13 7 (1958), 52–59.
28. Alexander Keller. 2013. Quasi-Monte Carlo Image Synthesis in a Nutshell. In Monte Carlo and Quasi-Monte Carlo Methods 2012, Josef Dick, Frances Y. Kuo, Gareth W. Peters, and Ian H. Sloan (Eds.). Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 213–249.
29. Johannes Kopf, Daniel Cohen-Or, Oliver Deussen, and Dani Lischinski. 2006. Recursive Wang tiles for real-time blue noise. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. SIGGRAPH) 25, 3 (2006).
30. Alexander Korotin, Daniil Selikhanovych, and Evgeny Burnaev. 2022. Neural optimal transport. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.12220 (2022).
31. Lauwerens Kuipers and Harald Niederreiter. 1974. Uniform Distribution of Sequences. Wiley, New York, USA.
32. Don P. Mitchell. 1991. Spectrally Optimal Sampling for Distribution Ray Tracing. SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics 25, 4 (July 1991), 157–164.
33. R. Näsänen. 1984. Visibility of halftone dot textures. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics SMC-14, 6 (1984), 920–924.
34. Harald Niederreiter. 1992. Random Number Generation and quasi-Monte Carlo Methods. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
35. Yann Ollivier, Herve Pajot, and Cédric Villani (Eds.). 2014. Optimal Transport – Theory and Applications. London Mathematical Society lecture note series, Vol. 413. Cambridge University Press.
36. Christian van Onzenoodt, Gurprit Singh, Timo Ropinski, and Tobias Ritschel. 2021. Blue Noise Plots. Computer Graphics Forum (2021).
37. Victor Ostromoukhov. 2007. Sampling with Polyominoes. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Papers (San Diego, California) (SIGGRAPH ’07). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 78–es.
38. Victor Ostromoukhov, Charles Donohue, and Pierre-Marc Jodoin. 2004. Fast Hierarchical Importance Sampling with Blue Noise Properties. 23, 3 (aug 2004), 488–495.
39. Thrasyvoulos N. Pappas and David L. Neuhoff. 1999. Least-squares model-based halftoning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 8, 8 (Aug 1999), 1102–1116.
40. Lois Paulin, Nicolas Bonneel, David Coeurjolly, Jean-Claude Iehl, Antoine Webanck, Mathieu Desbrun, and Victor Ostromoukhov. 2020. Sliced Optimal Transport Sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4, Article 99 (July 2020), 17 pages.
41. Gabriel Peyré and Marco Cuturi. 2018. Computational Optimal Transport. (2018).
42. Matt Pharr, Wenzel Jakob, and Greg Humphreys. 2016. Physically based rendering: From theory to implementation. Morgan Kaufmann.
43. Adrien Pilleboue, Gurprit Singh, David Coeurjolly, Michael Kazhdan, and Victor Ostromoukhov. 2015. Variance Analysis for Monte Carlo Integration. 34, 4, Article 124 (July 2015), 14 pages.
44. F. Pitie, A.C. Kokaram, and R. Dahyot. 2005. N-dimensional probability density function transfer and its application to color transfer. In Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1, Vol. 2. 1434–1439 Vol. 2.
45. François Pitié, Anil C. Kokaram, and Rozenn Dahyot. 2005. N-Dimensional Probablility Density Function Transfer and its Application to Colour Transfer. In 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE Computer Society.
46. Hongxing Qin, Yi Chen, Jinlong He, and Baoquan Chen. 2017. Wasserstein Blue Noise Sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 5, Article 168 (Oct. 2017), 13 pages.
47. Julien Rabin, Gabriel Peyré, Julie Delon, and Marc Bernot. 2011. Wasserstein Barycenter and Its Application to Texture Mixing. In Scale Space and Variational Methods in Computer Vision – Third International Conference, SSVM 2011, Ein-Gedi, Israel, May 29 – June 2, 2011, Revised Selected Papers (Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 6667), Alfred M. Bruckstein, Bart M. ter Haar Romeny, Alexander M. Bronstein, and Michael M. Bronstein (Eds.).
48. Svetlozar Rachev and Ludger Rüschendorf. 1998. Mass Transportation Problems: Volume I: Theory. Springer.
49. Bernhard Reinert, Tobias Ritschel, Hans-Peter Seidel, and Iliyan Georgiev. 2016. Projective Blue-Noise Sampling. Comp. Graph. Forum 35, 1 (2016).
50. F. Santambrogio. 2015. Optimal Transport for Applied Mathematicians: Calculus of Variations, PDEs, and Modeling. Springer International Publishing.
51. C. Schmaltz, P. Gwosdek, and J. Weickert. 2012. Multi-Class Anisotropic Electrostatic Halftoning. Comput. Graph. Forum 31, 6 (sep 2012), 1924–1935.
52. Christoph Schulz, Kin Chung Kwan, Michael Becher, Daniel Baumgartner, Guido Reina, Oliver Deussen, and Daniel Weiskopf. 2021. Multi-Class Inverted Stippling. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 6, Article 245 (dec 2021), 12 pages.
53. Adrian Secord. 2002. Weighted Voronoi stippling. In Proc. NPAR.
54. Gurprit Singh and Wojciech Jarosz. 2017. Convergence Analysis for Anisotropic Monte Carlo Sampling Spectra. 36, 4, Article 137 (July 2017), 14 pages.
55. Gurprit Singh, Cengiz Öztireli, Abdalla G.M. Ahmed, David Coeurjolly, Kartic Subr, Oliver Deussen, Victor Ostromoukhov, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Wojciech Jarosz. 2019. Analysis of Sample Correlations for Monte Carlo Rendering. Computer Graphics Forum 38, 2 (2019), 473–491. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/cgf.13653
56. Kartic Subr and Jan Kautz. 2013. Fourier Analysis of Stochastic Sampling Strategies for Assessing Bias and Variance in Integration. 32, 4, Article 128 (July 2013), 12 pages.
57. Robert Ulichney. 1987. Digital Halftoning. MIT Press.
58. C. Villani. 2008. Optimal Transport: Old and New. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://books.google.fr/books?id=hV8o5R7_5tkC
59. Florent Wachtel, Adrien Pilleboue, David Coeurjolly, Katherine Breeden, Gurprit Singh, Gaël Cathelin, Fernando de Goes, Mathieu Desbrun, and Victor Ostromoukhov. 2014. Fast Tile-based Adaptive Sampling with User-specified Fourier Spectra. 33, 4, Article 56 (July 2014), 11 pages.
60. Muge Wang and Kevin J. Parker. 1999. Properties of combined blue noise patterns. Proceedings 1999 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. 99CH36348) 4 (1999), 328–332 vol.4.
61. Li-Yi Wei. 2010. Multi-Class Blue Noise Sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4, Article 79 (July 2010), 8 pages.