“SAME: Skeleton-Agnostic Motion Embedding for Character Animation” by Lee, Kang, Park, Lee and Won
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- SAME: Skeleton-Agnostic Motion Embedding for Character Animation
Session/Category Title:
- Motion Synthesis With Awareness, Part II
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
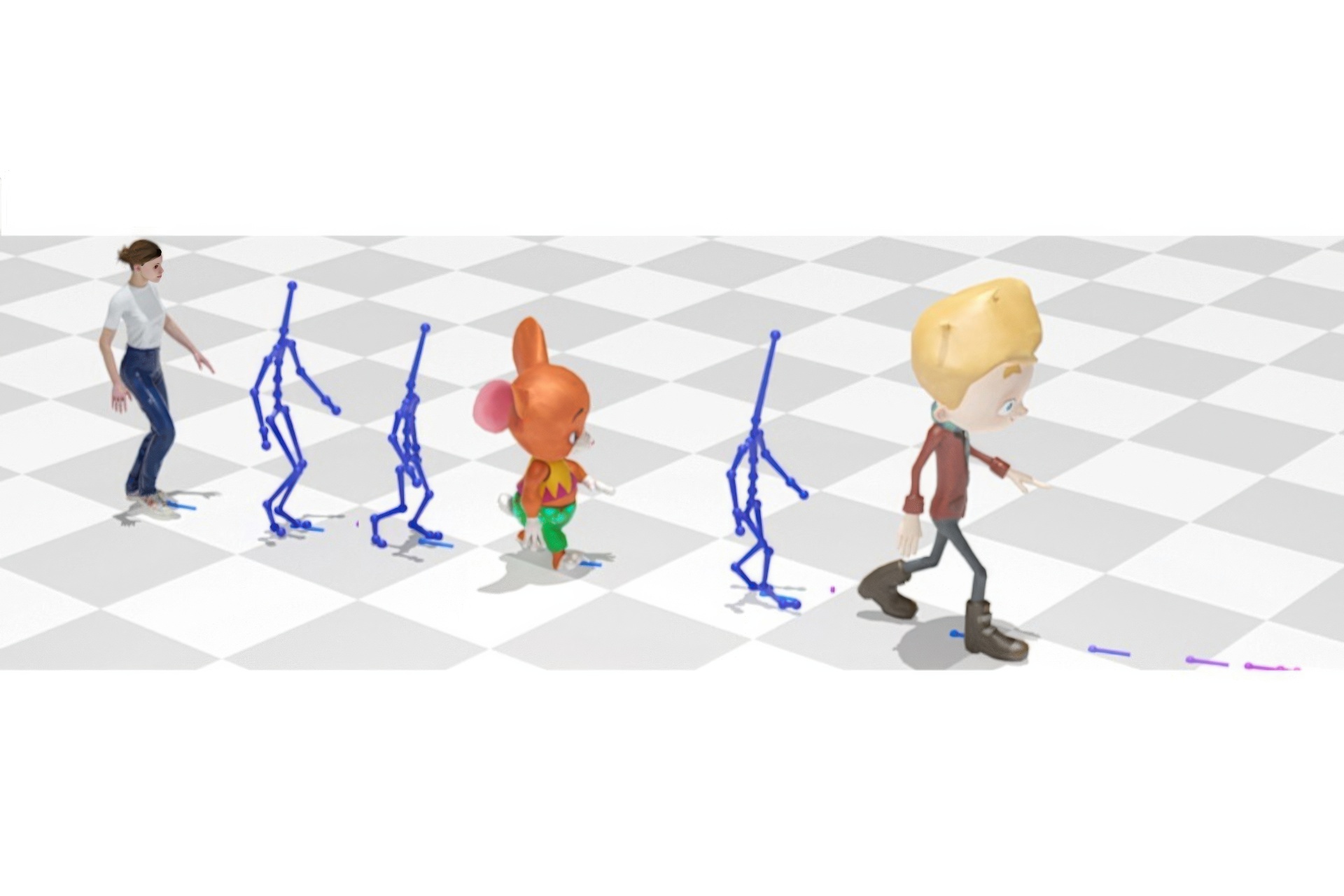
Learning deep neural networks on human motion data has become common in computer graphics research, but the heterogeneity of available datasets poses challenges for training large-scale networks. This paper presents a framework that allows us to solve various animation tasks in a skeleton-agnostic manner. The core of our framework is to learn an embedding space to disentangle skeleton-related information from input motion while preserving semantics, which we call Skeleton-Agnostic Motion Embedding (SAME). To efficiently learn the embedding space, we develop a novel autoencoder with graph convolution networks, and we provide new formulations of various animation tasks operating in the SAME space. We showcase various examples, including retargeting, reconstruction, and interactive character control, and conduct an ablation study to validate design choices made during development.
References:
[1]
Kfir Aberman, Peizhuo Li, Dani Lischinski, Olga Sorkine-Hornung, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Baoquan Chen. 2020. Skeleton-aware networks for deep motion retargeting. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 39, 4 (2020), 62–1.
[2]
Kfir Aberman, Rundi Wu, Dani Lischinski, Baoquan Chen, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2019. Learning character-agnostic motion for motion retargeting in 2d. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.01680 (2019).
[3]
Adobe. 2021. Mixamo Animation Dataset. https://www.mixamo.com/
[4]
Andreas Aristidou, Daniel Cohen-Or, Jessica K Hodgins, Yiorgos Chrysanthou, and Ariel Shamir. 2018. Deep motifs and motion signatures. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 6 (2018), 1–13.
[5]
Autodesk. 2021. Motion Builder – a 3D character animation software. Autodesk. https://www.autodesk.com/
[6]
Tom B. Brown, Benjamin Mann, Nick Ryder, Melanie Subbiah, Jared Kaplan, Prafulla Dhariwal, Arvind Neelakantan, Pranav Shyam, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Sandhini Agarwal, Ariel Herbert-Voss, Gretchen Krueger, Tom Henighan, Rewon Child, Aditya Ramesh, Daniel M. Ziegler, Jeffrey Wu, Clemens Winter, Christopher Hesse, Mark Chen, Eric Sigler, Mateusz Litwin, Scott Gray, Benjamin Chess, Jack Clark, Christopher Berner, Sam McCandlish, Alec Radford, Ilya Sutskever, and Dario Amodei. 2020. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arxiv:2005.14165 [cs.CL]
[7]
Jinxiang Chai and Jessica K Hodgins. 2005. Performance animation from low-dimensional control signals. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers. 686–696.
[8]
Kwang-Jin Choi and Hyeong-Seok Ko. 1999. On-line motion retargetting. In Proceedings of Pacific Graphics. 32–42.
[9]
Aakanksha Chowdhery, Sharan Narang, Jacob Devlin, Maarten Bosma, Gaurav Mishra, Adam Roberts, Paul Barham, Hyung Won Chung, Charles Sutton, Sebastian Gehrmann, Parker Schuh, Kensen Shi, Sasha Tsvyashchenko, Joshua Maynez, Abhishek Rao, Parker Barnes, Yi Tay, Noam Shazeer, Vinodkumar Prabhakaran, Emily Reif, Nan Du, Ben Hutchinson, Reiner Pope, James Bradbury, Jacob Austin, Michael Isard, Guy Gur-Ari, Pengcheng Yin, Toju Duke, Anselm Levskaya, Sanjay Ghemawat, Sunipa Dev, Henryk Michalewski, Xavier Garcia, Vedant Misra, Kevin Robinson, Liam Fedus, Denny Zhou, Daphne Ippolito, David Luan, Hyeontaek Lim, Barret Zoph, Alexander Spiridonov, Ryan Sepassi, David Dohan, Shivani Agrawal, Mark Omernick, Andrew M. Dai, Thanumalayan Sankaranarayana Pillai, Marie Pellat, Aitor Lewkowycz, Erica Moreira, Rewon Child, Oleksandr Polozov, Katherine Lee, Zongwei Zhou, Xuezhi Wang, Brennan Saeta, Mark Diaz, Orhan Firat, Michele Catasta, Jason Wei, Kathy Meier-Hellstern, Douglas Eck, Jeff Dean, Slav Petrov, and Noah Fiedel. 2022. PaLM: Scaling Language Modeling with Pathways. arxiv:2204.02311 [cs.CL]
[10]
CMU. 2006. CMU Graphics Lab Motion Capture Database. http://mocap.cs.cmu.edu/
[11]
Matthias Fey and Jan E. Lenssen. 2019. Fast Graph Representation Learning with PyTorch Geometric. In ICLR Workshop on Representation Learning on Graphs and Manifolds.
[12]
Saeed Ghorbani, Calden Wloka, Ali Etemad, Marcus A Brubaker, and Nikolaus F Troje. 2020. Probabilistic character motion synthesis using a hierarchical deep latent variable model. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 39. 225–239.
[13]
Michael Gleicher. 1998. Retargetting motion to new characters. In Proceedings of the 25th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques (I3D). 33–42.
[14]
Ikhsanul Habibie, Daniel Holden, Jonathan Schwarz, Joe Yearsley, and Taku Komura. 2017. A recurrent variational autoencoder for human motion synthesis. In Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC).
[15]
Félix G. Harvey, Mike Yurick, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Christopher Pal. 2020a. Robust Motion In-Betweening. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4, Article 60 (aug 2020), 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3386569.3392480
[16]
Félix G. Harvey, Mike Yurick, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Christopher Pal. 2020b. Robust Motion In-Betweening. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4 (2020).
[17]
Chengan He, Jun Saito, James Zachary, Holly Rushmeier, and Yi Zhou. 2022. Nemf: Neural motion fields for kinematic animation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.03287 (2022).
[18]
Daniel Holden, Taku Komura, and Jun Saito. 2017. Phase-functioned neural networks for character control. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 1–13.
[19]
Daniel Holden, Jun Saito, Taku Komura, and Thomas Joyce. 2015. Learning motion manifolds with convolutional autoencoders. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2015 technical briefs. 1–4.
[20]
Shuaiying Hou, Weiwei Xu, Jinxiang Chai, Congyi Wang, Wenlin Zhuang, Yu Chen, Hujun Bao, and Yangang Wang. 2021. A Causal Convolutional Neural Network for Motion Modeling and Synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.12276 (2021).
[21]
Linjiang Huang, Yan Huang, Wanli Ouyang, and Liang Wang. 2020. Part-level graph convolutional network for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 34. 11045–11052.
[22]
Deok-Kyeong Jang, Soomin Park, and Sung-Hee Lee. 2022. Motion Puzzle: Arbitrary Motion Style Transfer by Body Part. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.05274 (2022).
[23]
Jehee Lee, Jinxiang Chai, Paul SA Reitsma, Jessica K Hodgins, and Nancy S Pollard. 2002. Interactive control of avatars animated with human motion data. In Proceedings of the 29th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 491–500.
[24]
Jehee Lee and Sung Yong Shin. 1999. A hierarchical approach to interactive motion editing for human-like figures. In Proceedings of the 26th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques (I3D). 39–48.
[25]
Kyungho Lee, Seyoung Lee, and Jehee Lee. 2018. Interactive Character Animation by Learning Multi-Objective Control. 37, 6, Article 180 (dec 2018), 10 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3272127.3275071
[26]
Jiaman Li, Ruben Villegas, Duygu Ceylan, Jimei Yang, Zhengfei Kuang, Hao Li, and Yajie Zhao. 2021. Task-generic hierarchical human motion prior using vaes. In 2021 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). 771–781.
[27]
Maosen Li, Siheng Chen, Xu Chen, Ya Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, and Qi Tian. 2019. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). 3595–3603.
[28]
Jongin Lim, Hyung Jin Chang, and Jin Young Choi. 2019. PMnet: Learning of Disentangled Pose and Movement for Unsupervised Motion Retargeting. In Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Vol. 2. 7.
[29]
Hung Yu Ling, Fabio Zinno, George Cheng, and Michiel van de Panne. 2020. Character Controllers Using Motion VAEs. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4 (2020).
[30]
Matthew Loper, Naureen Mahmood, Javier Romero, Gerard Pons-Moll, and Michael J. Black. 2015. SMPL: A Skinned Multi-Person Linear Model. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6 (Oct. 2015), 248:1–248:16.
[31]
Naureen Mahmood, Nima Ghorbani, Nikolaus F Troje, Gerard Pons-Moll, and Michael J Black. 2019. AMASS: Archive of motion capture as surface shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (CVPR). 5442–5451.
[32]
Meinard Müller. 2007. Dynamic time warping. Information retrieval for music and motion (2007), 69–84.
[33]
Meinard Müller and Tido Röder. 2006. Motion templates for automatic classification and retrieval of motion capture data. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. 137–146.
[34]
OSU. [n. d.]. OSU ACCAD. https://accad.osu.edu/
[35]
Jungnam Park, Sehee Min, Phil Sik Chang, Jaedong Lee, Moonseok Park, and Jehee Lee. 2022. Generative GaitNet. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.12044 (2022).
[36]
Adam Paszke, Sam Gross, Francisco Massa, Adam Lerer, James Bradbury, Gregory Chanan, Trevor Killeen, Zeming Lin, Natalia Gimelshein, Luca Antiga, Alban Desmaison, Andreas Kopf, Edward Yang, Zachary DeVito, Martin Raison, Alykhan Tejani, Sasank Chilamkurthy, Benoit Steiner, Lu Fang, Junjie Bai, and Soumith Chintala. 2019. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32. 8024–8035.
[37]
Georgios Pavlakos, Vasileios Choutas, Nima Ghorbani, Timo Bolkart, Ahmed A. A. Osman, Dimitrios Tzionas, and Michael J. Black. 2019. Expressive Body Capture: 3D Hands, Face, and Body from a Single Image. In Proceedings IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 10975–10985.
[38]
Dario Pavllo, David Grangier, and Michael Auli. 2018. Quaternet: A quaternion-based recurrent model for human motion. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.06485 (2018).
[39]
Sigal Raab, Inbal Leibovitch, Peizhuo Li, Kfir Aberman, Olga Sorkine-Hornung, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2023. Modi: Unconditional motion synthesis from diverse data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 13873–13883.
[40]
Davis Rempe, Tolga Birdal, Aaron Hertzmann, Jimei Yang, Srinath Sridhar, and Leonidas J Guibas. 2021. Humor: 3d human motion model for robust pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 11488–11499.
[41]
Alla Safonova, Jessica K Hodgins, and Nancy S Pollard. 2004. Synthesizing physically realistic human motion in low-dimensional, behavior-specific spaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 23, 3 (2004), 514–521.
[42]
SFU. 2011. SFU Motion Capture Database. https://mocap.cs.sfu.ca/
[43]
Lei Shi, Yifan Zhang, Jian Cheng, and Hanqing Lu. 2019. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). 12026–12035.
[44]
Mingyi Shi, Kfir Aberman, Andreas Aristidou, Taku Komura, Dani Lischinski, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Baoquan Chen. 2020. MotioNet: 3D Human Motion Reconstruction from Monocular Video with Skeleton Consistency. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.12075 (2020).
[45]
Hyun Joon Shin and Jehee Lee. 2006. Motion synthesis and editing in low-dimensional spaces. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds (CASA 2006) 17 (2006), 219–227. Issue 3-4.
[46]
Hyun Joon Shin, Jehee Lee, Sung Yong Shin, and Michael Gleicher. 2001. Computer puppetry: An importance-based approach. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 20, 2 (2001), 67–94.
[47]
SNU. 2013. SNU Motion Database. https://mrl.snu.ac.kr/mdb/
[48]
Sebastian Starke, Ian Mason, and Taku Komura. 2022. DeepPhase: Periodic Autoencoders for Learning Motion Phase Manifolds. ACM Trans. Graph. 41, 4, Article 136 (jul 2022), 13 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3528223.3530178
[49]
David J Sturman. 1998. Computer puppetry. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 18, 1 (1998), 38–45.
[50]
Seyoon Tak and Hyeong-Seok Ko. 2005. A physically-based motion retargeting filter. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 24, 1 (2005), 98–117.
[51]
Guy Tevet, Sigal Raab, Brian Gordon, Yoni Shafir, Daniel Cohen-or, and Amit Haim Bermano. 2023. Human Motion Diffusion Model. In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations. https://openreview.net/forum?id=SJ1kSyO2jwu
[52]
Hugo Touvron, Thibaut Lavril, Gautier Izacard, Xavier Martinet, Marie-Anne Lachaux, Timothée Lacroix, Baptiste Rozière, Naman Goyal, Eric Hambro, Faisal Azhar, Aurelien Rodriguez, Armand Joulin, Edouard Grave, and Guillaume Lample. 2023. LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models. arxiv:2302.13971 [cs.CL]
[53]
Matt Trumble, Andrew Gilbert, Charles Malleson, Adrian Hilton, and John Collomosse. 2017. Total Capture: 3D Human Pose Estimation Fusing Video and Inertial Sensors. In 2017 British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC).
[54]
Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez, Łukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017).
[55]
Petar Veličković, Guillem Cucurull, Arantxa Casanova, Adriana Romero, Pietro Lio, and Yoshua Bengio. 2017. Graph attention networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10903 (2017).
[56]
Ruben Villegas, Jimei Yang, Duygu Ceylan, and Honglak Lee. 2018. Neural kinematic networks for unsupervised motion retargetting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 8639–8648.
[57]
Jack M Wang, David J Fleet, and Aaron Hertzmann. 2007. Gaussian process dynamical models for human motion. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 30, 2 (2007), 283–298.
[58]
Yue Wang, Yongbin Sun, Ziwei Liu, Sanjay E Sarma, Michael M Bronstein, and Justin M Solomon. 2019. Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. Acm Transactions On Graphics (tog) 38, 5 (2019), 1–12.
[59]
Jungdam Won and Jehee Lee. 2019. Learning body shape variation in physics-based characters. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6 (2019), 1–12.
[60]
Zhan Xu, Yang Zhou, Evangelos Kalogerakis, Chris Landreth, and Karan Singh. 2020. Rignet: Neural rigging for articulated characters. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.00559 (2020).
[61]
Sijie Yan, Yuanjun Xiong, and Dahua Lin. 2018. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence.
[62]
Ye Yuan, Jiaming Song, Umar Iqbal, Arash Vahdat, and Jan Kautz. 2022. PhysDiff: Physics-Guided Human Motion Diffusion Model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.02500 (2022).
[63]
Xinyi Zhang and Michiel van de Panne. 2018. Data-driven autocompletion for keyframe animation. In Proceedings of the 11th ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Motion, Interaction and Games. 1–11.
[64]
Yi Zhou, Connelly Barnes, Lu Jingwan, Yang Jimei, and Li Hao. 2019. On the Continuity of Rotation Representations in Neural Networks. In The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).