“Reproducing reality with a high-dynamic-range multi-focal stereo display” by Zhong, Jindal, Yöntem, Hanji, Watt, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Reproducing reality with a high-dynamic-range multi-focal stereo display
Session/Category Title:
- Audio and Visual Displays
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
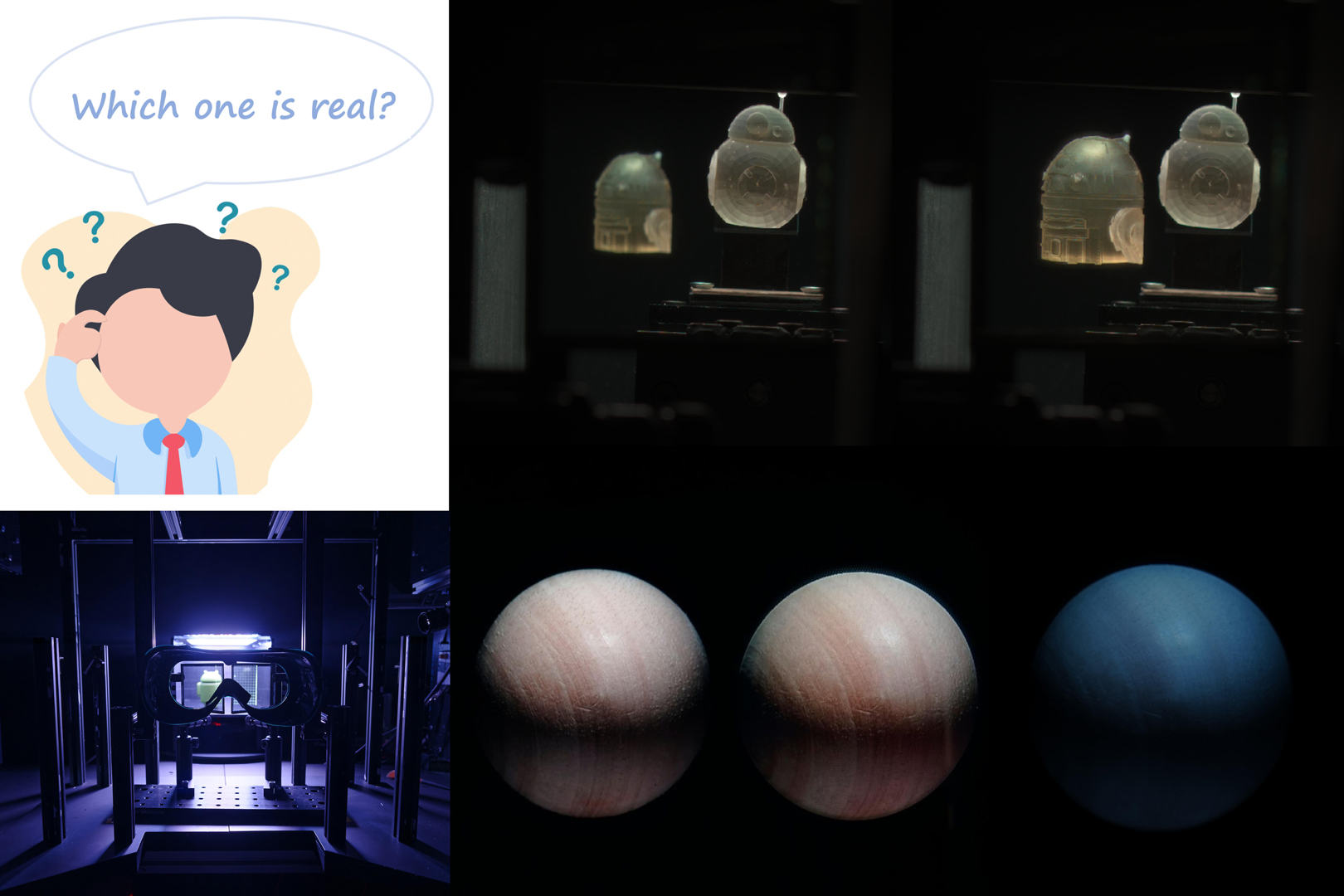
With well-established methods for producing photo-realistic results, the next big challenge of graphics and display technologies is to achieve perceptual realism — producing imagery indistinguishable from real-world 3D scenes. To deliver all necessary visual cues for perceptual realism, we built a High-Dynamic-Range Multi-Focal Stereo Display that achieves high resolution, accurate color, a wide dynamic range, and most depth cues, including binocular presentation and a range of focal depth. The display and associated imaging system have been designed to capture and reproduce a small near-eye three-dimensional object and to allow for a direct comparison between virtual and real scenes. To assess our reproduction of realism and demonstrate the capability of the display and imaging system, we conducted an experiment in which the participants were asked to discriminate between a virtual object and its physical counterpart. Our results indicate that the participants can only detect the discrepancy with a probability of 0.44. With such a level of perceptual realism, our display apparatus can facilitate a range of visual experiments that require the highest fidelity of reproduction while allowing for the full control of the displayed stimuli.
References:
1. Kurt Akeley, Simon J. Watt, Ahna Reza Girshick, and Martin S. Banks. 2004. A Stereo Display Prototype with Multiple Focal Distances. <u>ACM Trans. Graph.</u> 23, 3 (Aug. 2004), 804–813.
2. AliceVision. 2018. Meshroom: A 3D reconstruction software. https://github.com/alicevision/meshroom
3. Martin S. Banks, David M. Hoffman, Joohwan Kim, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2016. 3D Displays. <u>Annual Review of Vision Science</u> 2, 1 (2016), 397–435. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-vision-082114-035800 PMID: 28532351.
4. M. Borg, S. S. Johansen, D. L. Thomsen, and M. Kraus. 2012. Practical Implementation of a Graphics Turing Test. In <u>Advances in Visual Computing</u>, George Bebis, Richard Boyle, Bahram Parvin, Darko Koracin, Charless Fowlkes, Sen Wang, Min-Hyung Choi, Stephan Mantler, Jürgen Schulze, Daniel Acevedo, Klaus Mueller, and Michael Papka (Eds.). Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 305–313.
5. Jen-Hao Rick Chang, B. V. K. Vijaya Kumar, and Aswin C. Sankaranarayanan. 2018. Towards Multifocal Displays with Dense Focal Stacks. <u>ACM Trans. Graph.</u> 37, 6, Article 198 (Dec. 2018), 13 pages.
6. CIE170-1:2006. 2016. <u>Fundamental chromacity diagram with psychological axes – part 1.</u> Technical Report. Central Bureau of the Commission Internationale de l’ Éclairage. http://www.cie.co.at/publications/fundamental-chromaticity-diagram-physiological-axes-part-1
7. David Dunn, Cary Tippets, Kent Torell, Petr Kellnhofer, Kaan Akşit, Piotr Didyk, Karol Myszkowski, David Luebke, and Henry Fuchs. 2017. Wide Field Of View Varifocal Near-Eye Display Using See-Through Deformable Membrane Mirrors. <u>IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics</u> 23, 4 (2017), 1322–1331.
8. G. Eilertsen, R. K. Mantiuk, and J. Unger. 2017. A comparative review of tone-mapping algorithms for high dynamic range video. <u>Computer Graphics Forum</u> 36, 2 (may 2017), 565–592.
9. Cindy M. Goral, Kenneth E. Torrance, Donald P. Greenberg, and Bennett Battaile. 1984. Modeling the interaction of light between diffuse surfaces. <u>ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics</u> 18, 3 (jul 1984), 213–222.
10. Steven J. Gortler, Radek Grzeszczuk, Richard Szeliski, and Michael F. Cohen. 1996. The lumigraph. In <u>Proc. of SIGGRAPH ’96.</u> ACM Press, 43–54. arXiv:0070242542
11. Param Hanji, Fangcheng Zhong, and Rafał K. Mantiuk. 2020. Noise-Aware Merging of High Dynamic Range Image Stacks without Camera Calibration. In <u>Advances in Image Manipulation (ECCV workshop).</u> Springer, 376–391. http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/research/rainbow/projects/noise-aware-merging/
12. David M. Hoffman, Ahna R. Girshick, Kurt Akeley, and Martin S. Banks. 2008. Vergence-accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue. <u>Journal of Vision</u> 8, 3 (mar 2008), 33.
13. Fu-Chung Huang, Kevin Chen, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2015. The Light Field Stereoscope: Immersive Computer Graphics via Factored near-Eye Light Field Displays with Focus Cues. <u>ACM Trans. Graph.</u> 34, 4, Article 60 (July 2015), 12 pages.
14. Shichen Liu, Tianye Li, Weikai Chen, and Hao Li. 2019. Soft Rasterizer: A Differentiable Renderer for Image-based 3D Reasoning. <u>The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)</u> (Oct 2019). https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01786
15. Mark E. Lucente. 2012. Electronic Holographic Displays: 20 Years of Interactive Spatial Imaging. In <u>Handbook of Visual Display Technology</u>, Janglin Chen, Wayne Cranton, and Mark Fihn (Eds.). Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Bristol, 2721–2740.
16. Kevin J. MacKenzie, Ruth A. Dickson, and Simon J. Watt. 2012. Vergence and accommodation to multiple-image-plane stereoscopic displays: “real world” responses with practical image-plane separations? <u>Journal of Electronic Imaging</u> 21, 1 (feb 2012), 011002.
17. Kevin J MacKenzie, David M Hoffman, and Simon J Watt. 2010. Accommodation to multiple-focal-plane displays: Implications for improving stereoscopic displays and for accommodation control. <u>Journal of vision</u> 10, 8 (jan 2010), 22.
18. K. Masaoka, Y. Nishida, M. Sugawara, E. Nakasu, and Y. Nojiri. 2013. Sensation of Realness From High-Resolution Images of Real Objects. <u>IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting</u> 59, 1 (mar 2013), 72–83.
19. Ann. M. McNamara. 2005. Exploring perceptual equivalence between real and simulated imagery. In <u>Proceedings of the 2nd symposium on Appied perception in graphics and visualization – APGV ’05.</u> ACM Press, New York, New York, USA, 123–128.
20. Daniele Menon, Stefano Andriani, and Giancarlo Calvagno. 2006. Demosaicing with directional filtering and a posteriori decision. <u>IEEE Transactions on Image Processing</u> 16, 1 (2006), 132–141.
21. Olivier Mercier, Yusufu Sulai, Kevin Mackenzie, Marina Zannoli, James Hillis, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Douglas Lanman. 2017. Fast Gaze-Contingent Optimal Decompositions for Multifocal Displays. <u>ACM Trans. Graph.</u> 36, 6, Article 237 (Nov. 2017), 15 pages.
22. G. W. Meyer. 1986. An experimental evaluation of computer graphics imagery. <u>ACM Transactions on Graphics</u> 5, 1 (jan 1986), 30–50.
23. Ben Mildenhall, Pratul P. Srinivasan, Matthew Tancik, Jonathan T. Barron, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Ren Ng. 2020. NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis. In <u>ECCV.</u>
24. Rahul Narain, Rachel A. Albert, Abdullah Bulbul, Gregory J. Ward, Martin S. Banks, and James F. O’Brien. 2015. Optimal Presentation of Imagery with Focus Cues on Multi-Plane Displays. 34, 4, Article 59 (July 2015), 12 pages.
25. Nikhila Ravi, Jeremy Reizenstein, David Novotny, Taylor Gordon, Wan-Yen Lo, Justin Johnson, and Georgia Gkioxari. 2020. Accelerating 3D Deep Learning with PyTorch3D. <u>arXiv:2007.08501</u> (2020).
26. Erik Reinhard, Michael Stark, Peter Shirley, and James Ferwerda. 2002. Photographic tone reproduction for digital images. <u>ACM Transactions on Graphics</u> 21, 3 (jul 2002), 267.
27. T Ritschel, M Ihrke, J. R. Frisvad, J. Coppens, K. Myszkowski, and H.-P. Seidel. 2009. Temporal Glare: Real-Time Dynamic Simulation of the Scattering in the Human Eye. <u>Computer Graphics Forum</u> 28, 2 (apr 2009), 183–192.
28. Carsten Rother, Vladimir Kolmogorov, and Andrew Blake. 2004. “GrabCut”: Interactive Foreground Extraction Using Iterated Graph Cuts. <u>ACM Trans. Graph.</u> 23, 3 (Aug. 2004), 309–314.
29. Helge Seetzen, Wolfgang Heidrich, Wolfgang Stuerzlinger, Greg Ward, Lorne White-head, Matthew Trentacoste, Abhijeet Ghosh, and Andrejs Vorozcovs. 2004. High Dynamic Range Display Systems. <u>ACM Trans. Graph.</u> 23, 3 (Aug. 2004), 760–768.
30. Phil Surman and Ian Sexton. 2012. Emerging Autostereoscopic Displays. In <u>Handbook of Visual Display Technology</u>, Janglin Chen, Wayne Cranton, and Mark Fihn (Eds.). Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Bristol, 2652–2667.
31. I.E. Sutherland. 1974. Three-dimensional data input by tablet. <u>Proc. IEEE</u> 62, 4 (1974), 453–461.
32. Peter Vangorp, Rafat K Mantiuk, Bartosz Bazyluk, Karol Myszkowski, Radosław Mantiuk, Simon J Watt, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2014. Depth from HDR: depth induction or increased realism?. In <u>ACM Symposium on Applied Perception – SAP ’14.</u> ACM Press, New York, New York, USA, 71–78.
33. Suttisak Wizadwongsa, Pakkapon Phongthawee, Jiraphon Yenphraphai, and Supasorn Suwajanakorn. 2021. NeX: Real-time View Synthesis with Neural Basis Expansion. In <u>IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).</u>
34. Akiko Yoshida, Rafał Mantiuk, Karol Myszkowski, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2006. Analysis of Reproducing Real-World Appearance on Displays of Varying Dynamic Range. <u>Computer Graphics Forum (Proc. of Eurographics)</u> 25, 3 (sep 2006), 415–426.
35. Hyeonseung Yu, Mojtaba Bemana, Marek Wernikowski, Michał Chwesiuk, Okan Tursun, Gurprit Singh, Karol Myszkowski, Radoslaw Mantiuk, Hans-Peter Seidel, and Piotr Didyk. 2019. A Perception-driven Hybrid Decomposition for Multi-layer Accommodative Displays. <u>IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics</u> PP (02 2019).