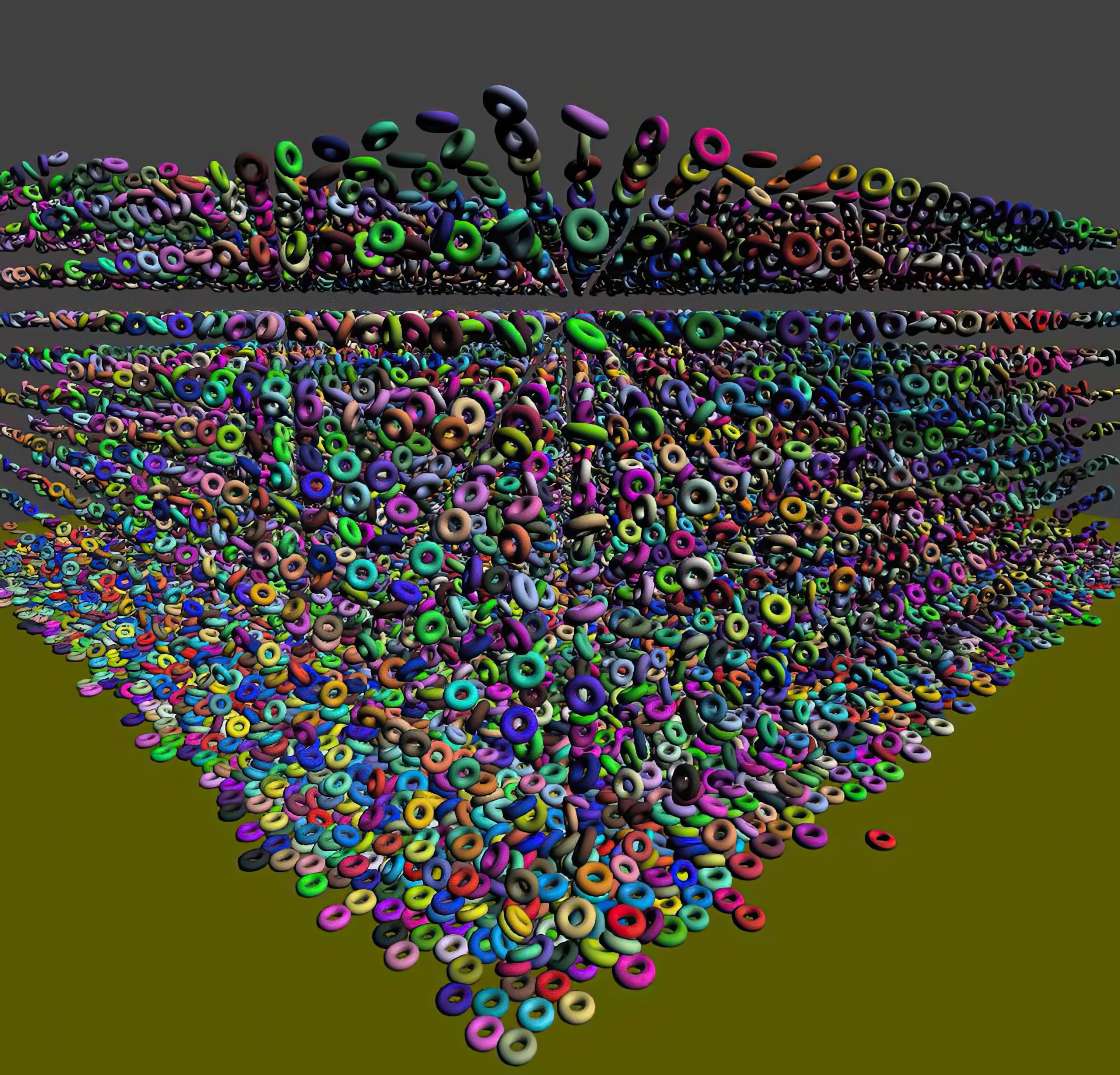
“Real-time collision culling of a million bodies on graphics processing units”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Real-time collision culling of a million bodies on graphics processing units
Session/Category Title: From rigid to soft
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
We cull collisions between very large numbers of moving bodies using graphics processing units (GPUs). To perform massively parallel sweep-and-prune (SaP), we mitigate the great density of intervals along the axis of sweep by using principal component analysis to choose the best sweep direction, together with spatial subdivisions to further reduce the number of false positive overlaps. Our algorithm implemented entirely on GPUs using the CUDA framework can handle a million moving objects at interactive rates. As application of our algorithm, we demonstrate the real-time simulation of very large numbers of particles and rigid-body dynamics.
References:
1. Andrecut, M. 2009. Parallel GPU implementation of iterative PCA algorithms. Journal of Computational Biology 16, 11.Google ScholarCross Ref
2. Baraff, D. 1992. Dynamic Simulation of Non-Penetrating Rigid Bodies. PhD thesis, Cornell University. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Brown, S., 2008. The scalable city project. http://scalablecity.net.Google Scholar
4. Cohen, J., Lin, M., Manocha, D., and Ponamgi, M. 1995. I-COLLIDE: An interactive and exact collision detection system for large-scale environments. In Proc. of ACM Interactive 3D Graphics Conference, 189–196. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Coming, D. S., and Staadt, O. G. 2006. Kinetic sweep and prune for multi-body continuous motion. Computers and Graphics 30, 439–449. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Coming, D. S., and Staadt, O. G. 2008. Velocity-aligned discrete oriented polytopes for dynamic collision detection. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 14, 1. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Edelsbrunner, H., and Maurer, H. A. 1981. On the intersection of orthogonal objects. Inf. Process. Lett. 13, 177–181.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Ericson, C. 2005. Real-Time Collision Detection. Morgan Kaufmann.Google Scholar
9. Grand, S. L. 2008. GPU Gems 3. Addison-Wesley, ch. Broad-Phrase Collision Detection with CUDA, 697–721.Google Scholar
10. Harada, T., Koshizuka, S., and Kawaguchi, Y. 2007. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics on GPUs. In Computer Graphics International.Google Scholar
11. Harada, T. 2007. GPU Gems3. Addison-Wesley Pearson Education, ch. Real-time Rigid Body Simulation on GPUs.Google Scholar
12. Jolliffe, I. T. 2002. Principal Component Analysis. Springer.Google Scholar
13. Lauterbach, C., Garland, M., Sengupta, S., Luebke, D., and Manocha, D. 2009. Fast BVH construction on GPUs. In Eurographics.Google Scholar
14. Lauterbach, C., Mo, Q., and Manocha, D. 2010. gProximity: Hierarchical GPU-based operations for collision and distance queries. In Eurographics.Google Scholar
15. Lin, M., and Manocha, D. 2003. Collision and proximity queries. In Handbook of Discrete and Computational Geometry.Google Scholar
16. Lin, M. C. 1993. Efficient Collision Detection for Animation and Robotics. PhD thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Mazhar, H., Heyn, T., Tasora, A., and Negrut, D. 2009. Collision detection using spatial subdivision. In Multibody Dynamics.Google Scholar
18. Mirtich, B. V. 1996. Impulse-based Dynamic Simulation of Rigid Body Systems. PhD thesis, University of California, Berkeley. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. NVIDIA. 2010. NVIDIA CUDA Best Practice Guide.Google Scholar
20. Ponamgi, M., Manocha, D., and Lin, M. 1995. Incremental algorithms for collision detection between general solid models. In Proc. ACM Symposium on Solid Modeling and Applications, 293–304. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T., and Flannery, B. P. 1992. Numerical Recipes in C. Cambridge University Press.Google Scholar
22. Samet, H. 2006. Foundations of Multidimensional and Metric Data Structures. Morgan Kaufmann. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Seiler, L., Carmean, D., Sprangle, E., Forsyth, T., Abrash, M., Dubey, P., Junkins, S., Lake, A., Sugerman, J., Cavin, R., Espasa, R., Grochowski, E., Juan, T., and Hanrahan, P. 2008. Larrabee: a many-core x86 architecture for visual computing. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3, 1–15. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Sengupta, S., Harris, M., Zhang, Y., and Owens, J. D. 2007. Scan primitives for GPU computing. In Graphics Hardware, 97–106. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Tang, M., Curtis, S., Yoon, S.-E., and Manocha, D. 2009. ICCD: Interactive continuous collision detection between deformable models using connectivity-based culling. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 15, 544–557. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Tang, M., Manocha, D., and Tong, R. 2010. MCCD: Multicore collision detection between deformable models. Graphical Models 72, 2, 7–23. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Terdiman, P. 2007. Sweep-and-prune. http://www.codercorner.com/SAP.pdf.Google Scholar
28. Tracy, D. J., Buss, S. R., and Woods, B. M. 2009. Efficient large-scale sweep and prune methods with AABB insertion and removal. In Proc. IEEE Virtual Reality, 191–198. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Wald, I. 2007. On fast construction of SAH-based bounding volume hierarchies. In IEEE/EG Symposium on Interactive Ray Tracing, 33–40. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Woulfe, M., Dingliana, J., and Manzke, M. 2007. Hardware accelerated broad phase collision detection for realtime simulations. In Workshop in Virtual Reality Interactions and Physical Simulation.Google Scholar
31. Zerodin, 2010. Zerodin games. http://www.zerodingames.com.Google Scholar
32. Zhou, K., Hou, Q., Wang, R., and Gui, B. 2008. Real-time KD-tree construction on graphics hardware. ACM Transactions on Graphics. Google ScholarDigital Library