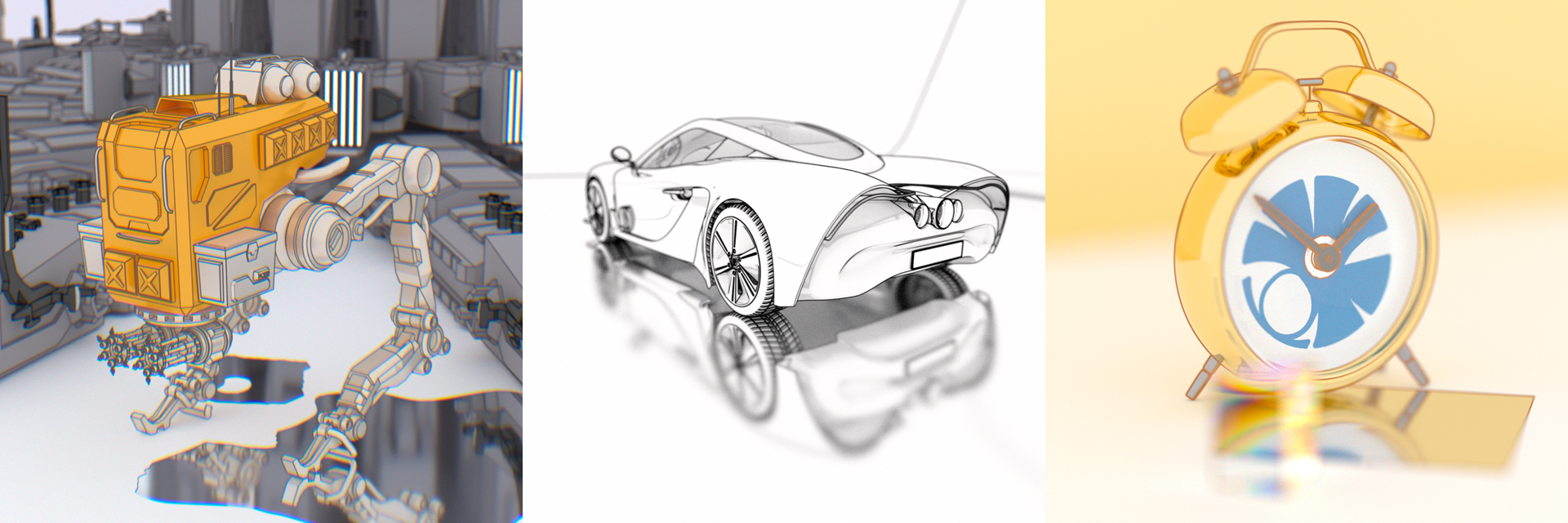
“Physically-based feature line rendering” by West
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Physically-based feature line rendering
Session/Category Title:
- NPR and Digital Art
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
Feature lines visualize the shape and structure of 3D objects, and are an essential component of many non-photorealistic rendering styles. Existing feature line rendering methods, however, are only able to render feature lines in limited contexts, such as on immediately visible surfaces or in specular reflections. We present a novel, path-based method for feature line rendering that allows for the accurate rendering of feature lines in the presence of complex physical phenomena such as glossy reflection, depth-of-field, and dispersion. Our key insight is that feature lines can be modeled as view-dependent light sources. These light sources can be sampled as a part of ordinary paths, and seamlessly integrate into existing physically-based rendering methods. We illustrate the effectiveness of our method in several real-world rendering scenarios with a variety of different physical phenomena.
References:
1. Andreas Bauer. 2017. A New Contour Method for Highly Detailed Geometry. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2017 Talks (Los Angeles, California) (SIGGRAPH ’17). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 71, 2 pages.
2. Dennis R. Bukenberger, Katharina Schwarz, and Hendrik P. A. Lensch. 2018. Stereo-Consistent Contours in Object Space. Computer Graphics Forum 37, 1 (2018), 301–312. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/cgf.13291
3. Pierre Bénard and Aaron Hertzmann. 2019. Line Drawings from 3D Models: A Tutorial. Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision 11, 1-2 (2019), 1–159.
4. A. N. M. Imroz Choudhury and Steven G. Parker. 2009. Ray Tracing NPR-Style Feature Lines. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering (New Orleans, Louisiana) (NPAR ’09). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 5–14.
5. Forrester Cole, Douglas DeCarlo, Adam Finkelstein, Kenrick Kin, R. Morley, and Anthony Santella. 2006. Directing Gaze in 3D Models with Stylized Focus. 377–387.
6. Forrester Cole, Aleksey Golovinskiy, Alex Limpaecher, Heather Stoddart Barros, Adam Finkelstein, Thomas Funkhouser, and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2008. Where Do People Draw Lines? ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug. 2008), 1–11.
7. Doug DeCarlo. 2012. Depicting 3D shape using lines. In Human Vision and Electronic Imaging XVII, Bernice E. Rogowitz, Thrasyvoulos N. Pappas, and Huib de Ridder (Eds.), Vol. 8291. International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE, 361 — 376.
8. Doug DeCarlo, Adam Finkelstein, and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2004. Interactive Rendering of Suggestive Contours with Temporal Coherence. In Third International Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering (NPAR). 15–24.
9. Doug DeCarlo, Adam Finkelstein, Szymon Rusinkiewicz, and Anthony Santella. 2003. Suggestive Contours for Conveying Shape. ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proc. SIGGRAPH) 22, 3 (July 2003), 848–855.
10. Aaron Hertzmann. 2020. Why Do Line Drawings Work? A Realism Hypothesis. Perception 49, 4 (2020), 439–451. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1177/0301006620908207 PMID: 32126897.
11. Aaron Hertzmann. 2021. The Role of Edges in Line Drawing Perception. Perception 50, 3 (2021), 266–275. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1177/0301006621994407 PMID: 33706622.
12. Wenzel Jakob and Johannes Hanika. 2019. A Low-Dimensional Function Space for Efficient Spectral Upsampling. Computer Graphics Forum (Proceedings of Eurographics) 38, 2 (March 2019).
13. Tilke Judd, Frédo Durand, and Edward H. Adelson. 2007. Apparent ridges for line drawing. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (2007), 19.
14. James T. Kajiya. 1986. The Rendering Equation. 20, 4 (Aug. 1986), 143–150. https://doi.org/10/cvf53j
15. Yongjin Kim, Jingyi Yu, Xuan Yu, and Seungyong Lee. 2008. Line-Art Illustration of Dynamic and Specular Surfaces. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 5, Article 156 (Dec. 2008), 10 pages.
16. Yunjin Lee, Lee Markosian, Seungyong Lee, and John F. Hughes. 2007. Line Drawings via Abstracted Shading. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Papers (San Diego, California) (SIGGRAPH ’07). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 18–es.
17. Difan Liu, Mohamed Nabail, Aaron Hertzmann, and Evangelos Kalogerakis. 2020. Neural Contours: Learning to Draw Lines From 3D Shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
18. Shinji Ogaki and Iliyan Georgiev. 2018. Production Ray Tracing of Feature Lines. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2018 Technical Briefs (Tokyo, Japan) (SA ’18). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 15, 4 pages.
19. Yutaka Ohtake, Alexander Belyaev, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2004. Ridge-Valley Lines on Meshes via Implicit Surface Fitting. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug. 2004), 609–612.
20. Matt Pharr, Brent Burley, Per Christensen, Marcos Fajardo, Luca Fascione, and Christopher Kulla. 2018. Design and Implementation of Modern Production Renderers. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2018 Panels (Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada) (SIGGRAPH ’18). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 4, 2 pages.
21. Matt Pharr, Wenzel Jakob, and Greg Humphreys. Physically Based Rendering: From Theory to Implementation (3 ed.). San Francisco, CA, USA.
22. Takafumi Saito and Tokiichiro Takahashi. 1990. Comprehensible Rendering of 3-D Shapes. ACM Siggraph Computer Graphics 24, 197–206.
23. Eric Veach. 1997. Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Light Transport Simulation. Ph.D. Thesis. Stanford University, United States – California.
24. Rex West, Iliyan Georgiev, Adrien Gruson, and Toshiya Hachisuka. 2020. Continuous Multiple Importance Sampling. ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH) 39, 4 (July 2020).
25. Roman Wiche and David Kuri. 2020. Performance Evaluation of Acceleration Structures for Cone-tracing Traversal. Journal of Computer Graphics Techniques Vol 9, 1 (2020).
26. Alexander Wilkie, Sehera Nawaz, Marc Droske, Andrea Weidlich, and Johannes Hanika. 2014. Hero Wavelength Spectral Sampling. 33, 4 (June 2014), 123–131. https://doi.org/10/f6fgb4