“Path tracing estimators for refractive radiative transfer” by Pediredla, Chalmiani, Scopelliti, Chamanzar, Narasimhan, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Path tracing estimators for refractive radiative transfer
Session/Category Title:
- Light Transport: Methods
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
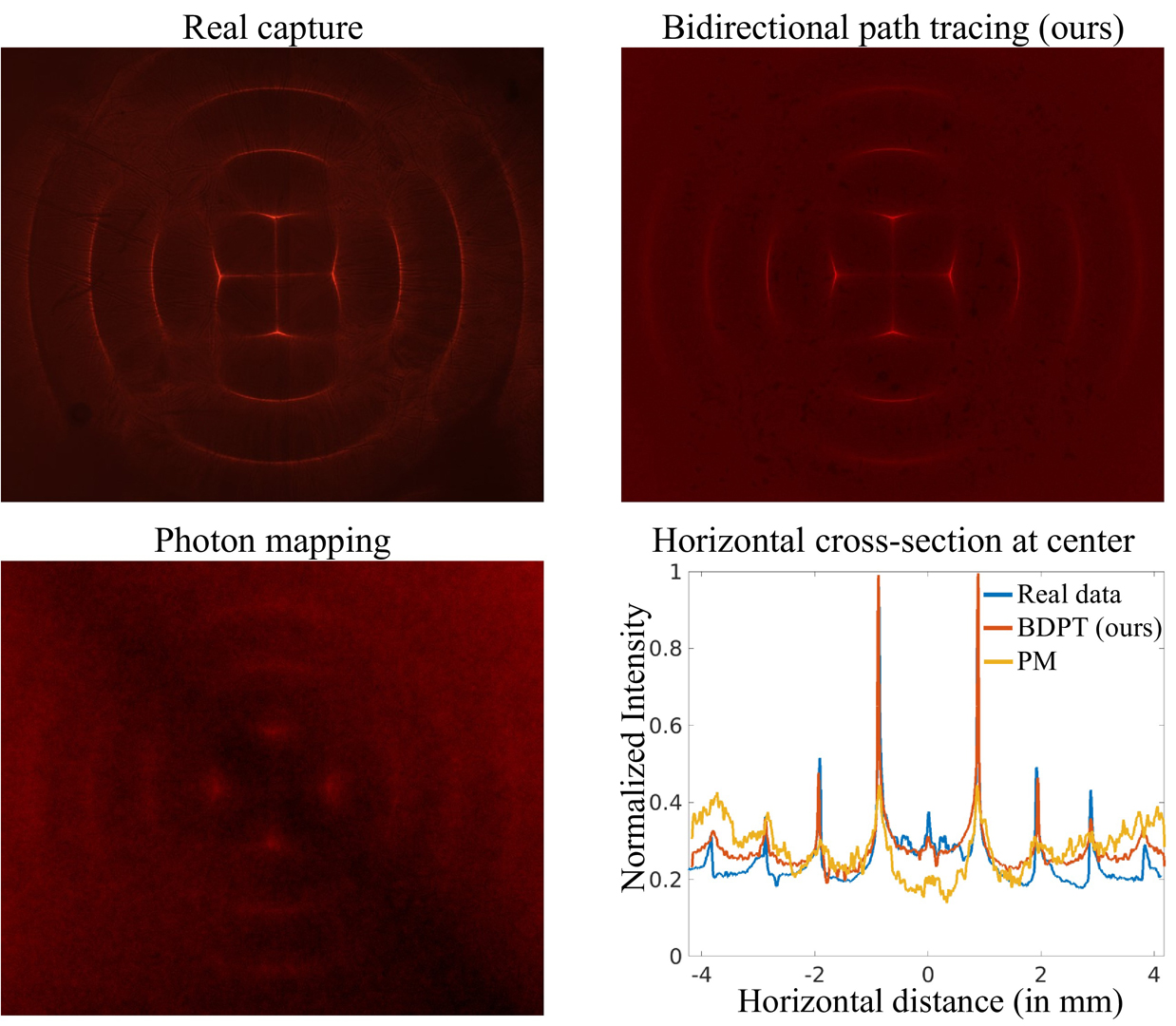
Rendering radiative transfer through media with a heterogeneous refractive index is challenging because the continuous refractive index variations result in light traveling along curved paths. Existing algorithms are based on photon mapping techniques, and thus are biased and result in strong artifacts. On the other hand, existing unbiased methods such as path tracing and bidirectional path tracing cannot be used in their current form to simulate media with a heterogeneous refractive index. We change this state of affairs by deriving unbiased path tracing estimators for this problem. Starting from the refractive radiative transfer equation (RRTE), we derive a path-integral formulation, which we use to generalize path tracing with next-event estimation and bidirectional path tracing to the heterogeneous refractive index setting. We then develop an optimization approach based on fast analytic derivative computations to produce the point-to-point connections required by these path tracing algorithms. We propose several acceleration techniques to handle complex scenes (surfaces and volumes) that include participating media with heterogeneous refractive fields. We use our algorithms to simulate a variety of scenes combining heterogeneous refraction and scattering, as well as tissue imaging techniques based on ultrasonic virtual waveguides and lenses. Our algorithms and publicly-available implementation can be used to characterize imaging systems such as refractive index microscopy, schlieren imaging, and acousto-optic imaging, and can facilitate the development of inverse rendering techniques for related applications.
References:
1. Sameer Agarwal, Keir Mierle, and Others. [n. d.]. Ceres Solver. http://ceres-solver.org.Google Scholar
2. Marco Ament, Christoph Bergmann, and Daniel Weiskopf. 2014. Refractive radiative transfer equation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 2 (2014), 17.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. James Arvo. 1995. Analytic methods for simulated light transport. Ph.D. Dissertation.Google Scholar
4. Bradley Atcheson, Ivo Ihrke, Wolfgang Heidrich, Art Tevs, Derek Bradley, Marcus Magnor, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2008. Time-resolved 3d capture of non-stationary gas flows. ACM transactions on graphics (TOG) 27, 5 (2008), 1–9.Google Scholar
5. Csaba Bálint and Gábor Valasek. 2018. Accelerating Sphere Tracing.. In Eurographics (Short Papers). 29–32.Google Scholar
6. Gavin Barill, Neil G Dickson, Ryan Schmidt, David IW Levin, and Alec Jacobson. 2018. Fast winding numbers for soups and clouds. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 43.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Fethallah Benmansour, Guillaume Carlier, Gabriel Peyré, and Filippo Santambrogio. 2010. Derivatives with respect to metrics and applications: subgradient marching algorithm. Numer. Math. 116, 3 (2010), 357–381.Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Benedikt Bitterli. 2016. Rendering resources. https://benedikt-bitterli.me/resources/.Google Scholar
9. Thomas E Booth. 2007. Unbiased Monte Carlo estimation of the reciprocal of an integral. Nuclear science and engineering 156, 3 (2007), 403–407.Google Scholar
10. Max Born and Emil Wolf. 2013. Principles of optics: electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light. Elsevier.Google Scholar
11. Mike Cammarano and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2002. Time Dependent Photon Mapping. In EGWR, Paul Debevec and Simon Gibson (Eds.). 135–144. https://doi.org/10/c54tGoogle Scholar
12. Chen Cao, Zhong Ren, Baining Guo, and Kun Zhou. 2010. Interactive Rendering of Non-Constant, Refractive Media Using the Ray Equations of Gradient-Index Optics. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 29. Wiley Online Library, 1375–1382.Google Scholar
13. Maysamreza Chamanzar, Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti, Julien Bloch, Ninh Do, Minyoung Huh, Dongjin Seo, Jillian Iafrati, Vikaas S Sohal, Mohammad-Reza Alam, and Michel M Maharbiz. 2019. Ultrasonic sculpting of virtual optical waveguides in tissue. Nature communications 10, 1 (2019), 1–10.Google Scholar
14. Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. 2013. Radiative transfer. Courier Corporation.Google Scholar
15. Min Chen and James Arvo. 2000a. Perturbation methods for interactive specular reflections. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 6, 3 (2000), 253–264.Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Min Chen and James Arvo. 2000b. Theory and application of specular path perturbation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 19, 4 (2000), 246–278.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. SB Dalziel, Graham O Hughes, and Bruce R Sutherland. 2000. Whole-field density measurements by ‘synthetic schlieren’. Experiments in fluids 28, 4 (2000), 322–335.Google Scholar
18. Cornelius Gillen. 2012. Metamorphic geology: an introduction to tectonic and metamorphic processes. Springer Science & Business Media.Google Scholar
19. Eduard Gröller. 1995. Nonlinear ray tracing: Visualizing strange worlds. The Visual Computer 11, 5 (1995), 263–274.Google ScholarCross Ref
20. Diego Gutierrez, Adolfo Munoz, Oscar Anson, and Francisco J Seron. 2005. Non-linear Volume Photon Mapping.. In Rendering Techniques. 291–300.Google Scholar
21. Diego Gutierrez, Francisco J Seron, Adolfo Munoz, and Oscar Anson. 2006. Simulation of atmospheric phenomena. Computers & Graphics 30, 6 (2006), 994–1010.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Jörg Haber, Marcus Magnor, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2005. Physically-based simulation of twilight phenomena. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 24, 4 (2005), 1353–1373.Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Toshiya Hachisuka and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2009. Stochastic progressive photon mapping. In ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2009 papers. 1–8.Google Scholar
24. Toshiya Hachisuka, Shinji Ogaki, and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2008. Progressive photon mapping. In ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2008 papers. 1–8.Google Scholar
25. Johannes Hanika, Marc Droske, and Luca Fascione. 2015. Manifold next event estimation. In Computer graphics forum, Vol. 34. Wiley Online Library, 87–97.Google Scholar
26. John C Hart. 1996. Sphere tracing: A geometric method for the antialiased ray tracing of implicit surfaces. The Visual Computer 12, 10 (1996), 527–545.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Walton L Howes. 1984. Rainbow schlieren and its applications. Applied Optics 23, 14 (1984), 2449–2460.Google ScholarCross Ref
28. Ivo Ihrke, Gernot Ziegler, Art Tevs, Christian Theobalt, Marcus Magnor, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2007. Eikonal rendering: Efficient light transport in refractive objects. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 26, 3 (2007), 59.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. David S Immel, Michael F Cohen, and Donald P Greenberg. 1986. A radiosity method for non-diffuse environments. Acm Siggraph Computer Graphics 20, 4 (1986), 133–142.Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Akira Ishimaru. 1978. Wave propagation and scattering in random media. Vol. 2. Academic press New York.Google Scholar
31. Wenzel Jakob. 2010. Mitsuba renderer. http://www.mitsuba-renderer.org.Google Scholar
32. Wenzel Jakob. 2016. Path Space Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods in Computer Graphics. In Monte Carlo and Quasi-Monte Carlo Methods. Springer, 107–141.Google Scholar
33. Wenzel Jakob and Steve Marschner. 2012. Manifold exploration: a Markov Chain Monte Carlo technique for rendering scenes with difficult specular transport. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4 (2012), 1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Adrian Jarabo, Julio Marco, Adolfo Muñoz, Raul Buisan, Wojciech Jarosz, and Diego Gutierrez. 2014. A framework for transient rendering. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 33, 6 (2014), 1–10.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Adrian Jarabo, Belen Masia, Julio Marco, and Diego Gutierrez. 2017. Recent advances in transient imaging: A computer graphics and vision perspective. Visual Informatics 1, 1 (2017), 65–79.Google ScholarCross Ref
36. Yu Ji, Jinwei Ye, and Jingyi Yu. 2013. Reconstructing gas flows using light-path approximation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2507–2514.Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Peter B Johnson and R-WJPrB Christy. 1972. Optical constants of the noble metals. Physical review B 6, 12 (1972), 4370.Google Scholar
38. James T Kajiya. 1986. The rendering equation. In ACM SIGGRAPH computer graphics, Vol. 20. ACM, 143–150.Google Scholar
39. Anton S Kaplanyan, Johannes Hanika, and Carsten Dachsbacher. 2014. The natural-constraint representation of the path space for efficient light transport simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 4 (2014), 1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Felix P Kapron. 1970. Geometrical optics of parabolic index-gradient cylindrical lenses. JOSA 60, 11 (1970), 1433–1436.Google ScholarCross Ref
41. Yasin Karimi, Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti, Ninh Do, Mohammad-Reza Alam, and Maysamreza Chamanzar. 2019. In situ 3D reconfigurable ultrasonically sculpted optical beam paths. Optics express 27, 5 (2019), 7249–7265.Google Scholar
42. Yu A Kravtsov and Yu I Orlov. 1990. Geometrical optics of inhomogeneous media. Springer-Verlag.Google Scholar
43. P Krehl and S Engemann. 1995. August Toepler—the first who visualized shock waves. Shock Waves 5, 1–2 (1995), 1–18.Google ScholarCross Ref
44. Eric P Lafortune and Yves D Willems. 1996. Rendering participating media with bidirectional path tracing. In Rendering techniques’ 96. Springer, 91–100.Google ScholarDigital Library
45. Shingyu Leung, Jianliang Qian, et al. 2006. An adjoint state method for three-dimensional transmission traveltime tomography using first-arrivals. Communications in Mathematical Sciences 4, 1 (2006), 249–266.Google ScholarCross Ref
46. Rudolf Karl Luneburg. 1966. Mathematical theory of optics. Univ of California Press.Google Scholar
47. Chenguang Ma, Xing Lin, Jinli Suo, Qionghai Dai, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2014. Transparent object reconstruction via coded transport of intensity. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 3238–3245.Google ScholarDigital Library
48. Euan McLeod, Adam B Hopkins, and Craig B Arnold. 2006. Multiscale Bessel beams generated by a tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction lens. Optics letters 31, 21 (2006), 3155–3157.Google Scholar
49. Roberto Merlin. 2011. Maxwell’s fish-eye lens and the mirage of perfect imaging. Journal of Optics 13, 2 (2011), 024017.Google ScholarCross Ref
50. Alexandre Mermillod-Blondin, Euan McLeod, and Craig B Arnold. 2008. High-speed varifocal imaging with a tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction lens. Optics letters 33, 18 (2008), 2146–2148.Google Scholar
51. Don Mitchell and Pat Hanrahan. 1992. Illumination from curved reflectors. In Proceedings of the 19th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 283–291.Google ScholarDigital Library
52. Qi Mo, Hengchin Yeh, and Dinesh Manocha. 2015. Tracing analytic ray curves for light and sound propagation in non-linear media. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 22, 11 (2015), 2493–2506.Google Scholar
53. Adolfo Muñoz. 2014. Higher order ray marching. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 33. Wiley Online Library, 167–176.Google Scholar
54. Jan Novák, Iliyan Georgiev, Johannes Hanika, and Wojciech Jarosz. 2018. Monte carlo methods for volumetric light transport simulation. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. Wiley Online Library, 551–576.Google Scholar
55. Jan Novak, Iliyan Georgiev, Johannes Hanika, and Wojciech Jarosz. 2018. Monte Carlo Methods for Volumetric Light Transport Simulation. Computer Graphics Forum (2018).Google Scholar
56. Adithya Pediredla, Yasin Karimi Chalamiani, Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti, Maysam Chamanzar, Srinivasa Narasimhan, and Gkioulekas Ioannis. 2020. Mitsuba Eikonal Renderer. https://github.com/cmu-ci-lab/MitsubaER.Google Scholar
57. Adithya Pediredla, Ashok Veeraraghavan, and Ioannis Gkioulekas. 2019. Ellipsoidal path connections for time-gated rendering. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 4 (2019), 1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
58. Etienne Robein. 2010. Seismic imaging: a review of the techniques, their principles, merits and limitations. EAGE publications.Google Scholar
59. Jesus M Sanz-Serna. 1992. Symplectic integrators for Hamiltonian problems: an overview. Acta numerica 1 (1992), 243–286.Google Scholar
60. Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti and Maysamreza Chamanzar. 2019. Ultrasonically sculpted virtual relay lens for in situ microimaging. Light: Science & Applications 8, 1 (2019), 1–15.Google ScholarCross Ref
61. James Albert Sethian. 1996. Level set methods: Evolving interfaces in geometry, fluid mechanics, computer vision, and materials science. Vol. 1999. Cambridge University Press Cambridge.Google Scholar
62. Gary S Settles and Michael J Hargather. 2017. A review of recent developments in schlieren and shadowgraph techniques. Measurement Science and Technology 28, 4 (2017), 042001.Google ScholarCross Ref
63. Dario Seyb, Alec Jacobson, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Wojciech Jarosz. 2019. Nonlinear sphere tracing for rendering deformed signed distance fields. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6 (2019), 1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
64. VD Shargorodsky, VP Vasiliev, NM Soyuzova, VB Burmistrov, IS Gashkin, MS Belov, TI Khorosheva, and E Nikolaev. 2000. Experimental spherical retroreflector on board of the meteor-3M satellite. In Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Laser Ranging. 1–5.Google Scholar
65. Anurag Sharma and AK Ghatak. 1981. A variational analysis of single mode graded-index fibers. Optics Communications 36, 1 (1981), 22–24.Google ScholarCross Ref
66. Jos Stam and Eric Languénou. 1996. Ray tracing in non-constant media. In Rendering Techniques’ 96. Springer, 225–234.Google Scholar
67. Shlomi Steinberg. 2020. Accurate Rendering of Liquid-Crystals and Inhomogeneous Optically Anisotropic Media. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 39, 3 (2020), 1–23.Google ScholarDigital Library
68. Teng-Qian Sun, Qing Ye, Xiao-Wan Wang, Jin Wang, Zhi-Chao Deng, Jian-Chun Mei, Wen-Yuan Zhou, Chun-Ping Zhang, and Jian-Guo Tian. 2014. Scanning focused refractive-index microscopy. Scientific reports 4 (2014), 5647.Google Scholar
69. Michael Unser. 1999. Splines: A perfect fit for signal and image processing. IEEE Signal processing magazine (1999).Google Scholar
70. Eric Veach. 1997. Robust Monte Carlo methods for light transport simulation. Vol. 1610. Stanford University PhD thesis.Google ScholarDigital Library
71. Eric Veach and Leonidas Guibas. 1995. Bidirectional estimators for light transport. In Photorealistic Rendering Techniques. Springer, 145–167.Google Scholar
72. Eric Veach and Leonidas J Guibas. 1997. Metropolis light transport. In Proceedings of the 24th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 65–76.Google ScholarDigital Library
73. Bruce Walter, Shuang Zhao, Nicolas Holzschuch, and Kavita Bala. 2009. Single scattering in refractive media with triangle mesh boundaries. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 28. ACM, 92.Google ScholarDigital Library
74. Daniel Weiskopf, Tobias Schafhitzel, and Thomas Ertl. 2004. GPU-based nonlinear ray tracing. In Computer graphics forum, Vol. 23. Wiley Online Library, 625–633.Google Scholar
75. Gordon Wetzstein, Ramesh Raskar, and Wolfgang Heidrich. 2011. Hand-held schlieren photography with light field probes. In 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP). IEEE, 1–8.Google ScholarCross Ref
76. Tianfan Xue, Michael Rubinstein, Neal Wadhwa, Anat Levin, Fredo Durand, and William T Freeman. 2014. Refraction wiggles for measuring fluid depth and velocity from video. In European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 767–782.Google ScholarCross Ref
77. Tizian Zeltner, Iliyan Georgiev, and Wenzel Jakob. 2020. Specular manifold sampling for rendering high-frequency caustics and glints. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 39, 4 (2020), 149–1.Google ScholarDigital Library
78. Yuan-Yuan Zhao, Yong-Liang Zhang, Mei-Ling Zheng, Xian-Zi Dong, Xuan-Ming Duan, and Zhen-Sheng Zhao. 2016. Three-dimensional Luneburg lens at optical frequencies. Laser & Photonics Reviews 10, 4 (2016), 665–672.Google ScholarCross Ref