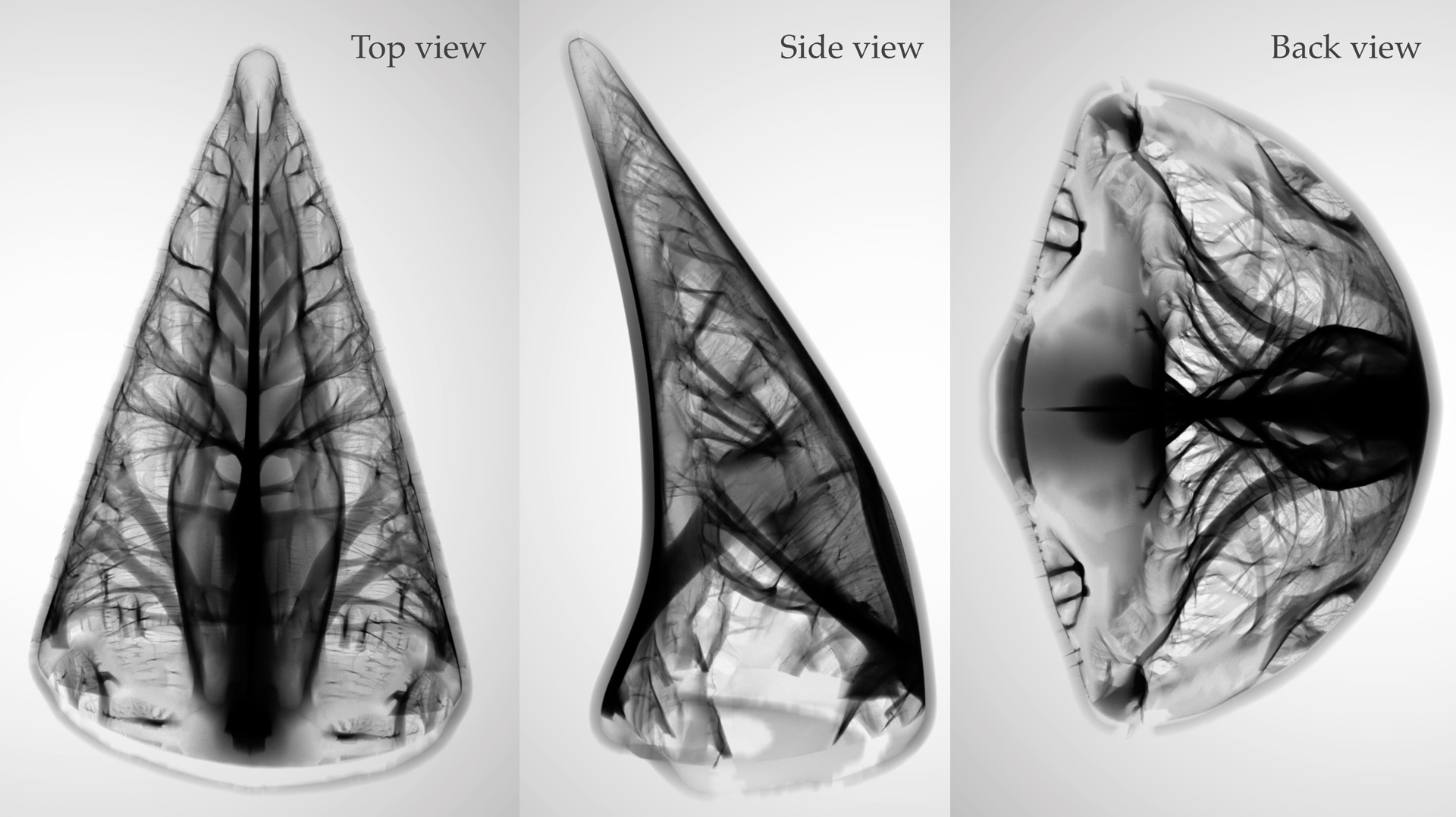
“Narrow-band topology optimization on a sparsely populated grid”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Narrow-band topology optimization on a sparsely populated grid
Session/Category Title:
- Optimizing structures & materials
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
A variety of structures in nature exhibit sparse, thin, and intricate features. It is challenging to investigate these structural characteristics using conventional numerical approaches since such features require highly refined spatial resolution to capture and therefore they incur a prohibitively high computational cost. We present a novel computational framework for high-resolution topology optimization that delivers leaps in simulation capabilities, by two orders of magnitude, from the state-of-the-art approaches. Our technique accommodates computational domains with over one billion grid voxels on a single shared-memory multiprocessor platform, allowing automated emergence of structures with both rich geometric features and exceptional mechanical performance. To achieve this, we track the evolution of thin structures and simulate its elastic deformation in a dynamic narrow-band region around high-density sites to avoid wasted computational effort on large void regions. We have also designed a mixed-precision multigrid-preconditioned iterative solver that keeps the memory footprint of the simulation to a compact size while maintaining double-precision accuracy. We have demonstrated the efficacy of the algorithm through optimizing a variety of complex structures from both natural and engineering systems.
References:
1. Niels Aage, Erik Andreassen, and Boyan Stefanov Lazarov. 2015. Topology optimization using PETSc: An easy-to-use, fully parallel, open source topology optimization framework. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 51, 3 (2015), 565–572. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Niels Aage, Erik Andreassen, Boyan S. Lazarov, and Ole Sigmund. 2017. Giga-voxel computational morphogenesis for structural design. Nature 550 7674 (2017), 84–86.Google Scholar
3. Martin P Bendsøe and Ole Sigmund. 2009. Topology Optimization. (2009).Google Scholar
4. Emmanuel Brun, Arthur Guittet, and Frédéric Gibou. 2012. A local level-set method using a hash table data structure. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 6 (2012), 2528–2536. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Tyler E Bruns and Daniel A Tortorelli. 2003. An element removal and reintroduction strategy for the topology optimization of structures and compliant mechanisms. International journal for numerical methods in engineering 57, 10 (2003), 1413–1430.Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Vivien J Challis, Anthony P Roberts, and Joseph F Grotowski. 2014. High resolution topology optimization using graphics processing units (GPUs). Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 49, 2 (2014), 315–325. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Asger Nyman Christiansen, J Andreas Bærentzen, Morten Nobel-Jørgensen, Niels Aage, and Ole Sigmund. 2015. Combined shape and topology optimization of 3D structures. Computers & Graphics 46 (2015), 25–35. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Asger Nyman Christiansen, Morten Nobel-Jørgensen, Niels Aage, Ole Sigmund, and Jakob Andreas Bærentzen. 2014. Topology optimization using an explicit interface representation. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 49, 3 (2014), 387–399. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Joshua D Deaton and Ramana V Grandhi. 2014. A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: post 2000. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 49, 1 (2014), 1–38. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Christian Dick, Joachim Georgii, and Rüdiger Westermann. 2011. A real-time multigrid finite hexahedra method for elasticity simulation using CUDA. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory 19, 2 (2011).Google Scholar
11. Christopher Dileo and Xinyan Deng. 2009. Design of and experiments on a dragonfly-inspired robot. Advanced Robotics 23, 7–8 (2009), 1003–1021.Google ScholarCross Ref
12. Jean Donea, S Giuliani, and Jean-Pierre Halleux. 1982. An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian finite element method for transient dynamic fluid-structure interactions. Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering 33, 1–3 (1982), 689–723.Google Scholar
13. R Elliot English, Linhai Qiu, Yue Yu, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2013. Chimera grids for water simulation. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. ACM, 85–94. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Douglas Enright, Ronald Fedkiw, Joel Ferziger, and Ian Mitchell. 2002. A hybrid particle level set method for improved interface capturing. J. Comput. Phys. 183, 1 (2002), 83–116. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. H. A. Eschenauer, V. V. Kobelev, and A. Schumacher. 1994. Bubble method for topology and shape optimization of structures. Structural optimization 8, 1 (1994).Google Scholar
16. Florian Ferstl, Ryoichi Ando, Chris Wojtan, Rüdiger Westermann, and Nils Thuerey. 2016. Narrow band FLIP for liquid simulations. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 35. Wiley Online Library, 225–232.Google Scholar
17. Florian Ferstl, Rüdiger Westermann, and Christian Dick. 2014. Large-scale liquid simulation on adaptive hexahedral grids. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 20, 10 (2014), 1405–1417.Google ScholarCross Ref
18. Sarah F. Frisken, Ronald N. Perry, Alyn P. Rockwood, and Thouis R. Jones. 2000. Adaptively Sampled Distance Fields: A General Representation of Shape for Computer Graphics. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’00). 249–254. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Yuanming Hu. 2018. Taichi: An Open-Source Computer Graphics Library. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.09293 (2018).Google Scholar
20. Haixiang Liu, Nathan Mitchell, Mridul Aanjaneya, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2016. A scalable schur-complement fluids solver for heterogeneous compute platforms. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 6 (2016), 201. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Frank Losasso, Frédéric Gibou, and Ron Fedkiw. 2004. Simulating water and smoke with an octree data structure. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 23. ACM, 457–462. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Aleka McAdams, Yongning Zhu, Andrew Selle, Mark Empey, Rasmus Tamstorf, Joseph Teran, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2011. Efficient elasticity for character skinning with contact and collisions. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 30, 4 (2011), 37. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Ken Museth. 2013. VDB: High-resolution sparse volumes with dynamic topology. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 3 (2013), 27. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. George IN Rozvany. 2009. A critical review of established methods of structural topology optimization. Structural and multidisciplinary optimization 37, 3 (2009), 217–237.Google Scholar
25. Stephan Schmidt and Volker Schulz. 2011. A 2589 line topology optimization code written for the graphics card. Computing and Visualization in Science (2011), 1–8. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Rajsekhar Setaluri, Mridul Aanjaneya, Sean Bauer, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2014. SPGrid: A sparse paged grid structure applied to adaptive smoke simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 6 (2014), 205. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Ole Sigmund. 2001. A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 21, 2 (2001), 120–127. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Ole Sigmund, Niels Aage, and Erik Andreassen. 2016. On the (non-) optimality of Michell structures. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 54, 2 (2016), 361–373. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Ole Sigmund and Kurt Maute. 2013. Topology optimization approaches. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 48, 6 (2013), 1031–1055.Google ScholarCross Ref
30. Ole Sigmund and S Torquato. 1999. Design of smart composite materials using topology optimization. Smart Materials and Structures 8, 3 (1999), 365.Google ScholarCross Ref
31. J. Sokolowski and A. Zochowski. 1999. On the Topological Derivative in Shape Optimization. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 37, 4 (1999). Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Eddie Wadbro and Martin Berggren. 2009. Megapixel topology optimization on a graphics processing unit. SIAM review 51, 4 (2009), 707–721. Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Jun Wu, Niels Aage, Ruediger Westermann, and Ole Sigmund. 2017. Infill Optimization for Additive Manufacturing-Approaching Bone-like Porous Structures. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (2017).Google Scholar
34. Jun Wu, Christian Dick, and Rüdiger Westermann. 2016a. A system for high-resolution topology optimization. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 22, 3 (2016), 1195–1208. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Jun Wu, Christian Dick, and Rüdiger Westermann. 2016b. A System for High-Resolution Topology Optimization. IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Computer Graphics 22, 3 (2016). Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Praveen Yadav and Krishnan Suresh. 2014. Large scale finite element analysis via assembly-free deflated conjugate gradient. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 14, 4 (2014), 041008.Google ScholarCross Ref
37. Wen Zheng, Bo Zhu, Byungmoon Kim, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2015. A new incompressibility discretization for a hybrid particle MAC grid representation with surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 280 (2015), 96–142. Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Bo Zhu, Wenlong Lu, Matthew Cong, Byungmoon Kim, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2013. A new grid structure for domain extension. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4 (2013), 63. Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Y Zhu, E Sifakis, J Teran, and A Brandt. 2010. An efficient and parallelizable multigrid framework for the simulation of elastic solids. ACM Trans. Graph 29, 16 (2010), 1–16. Google ScholarDigital Library