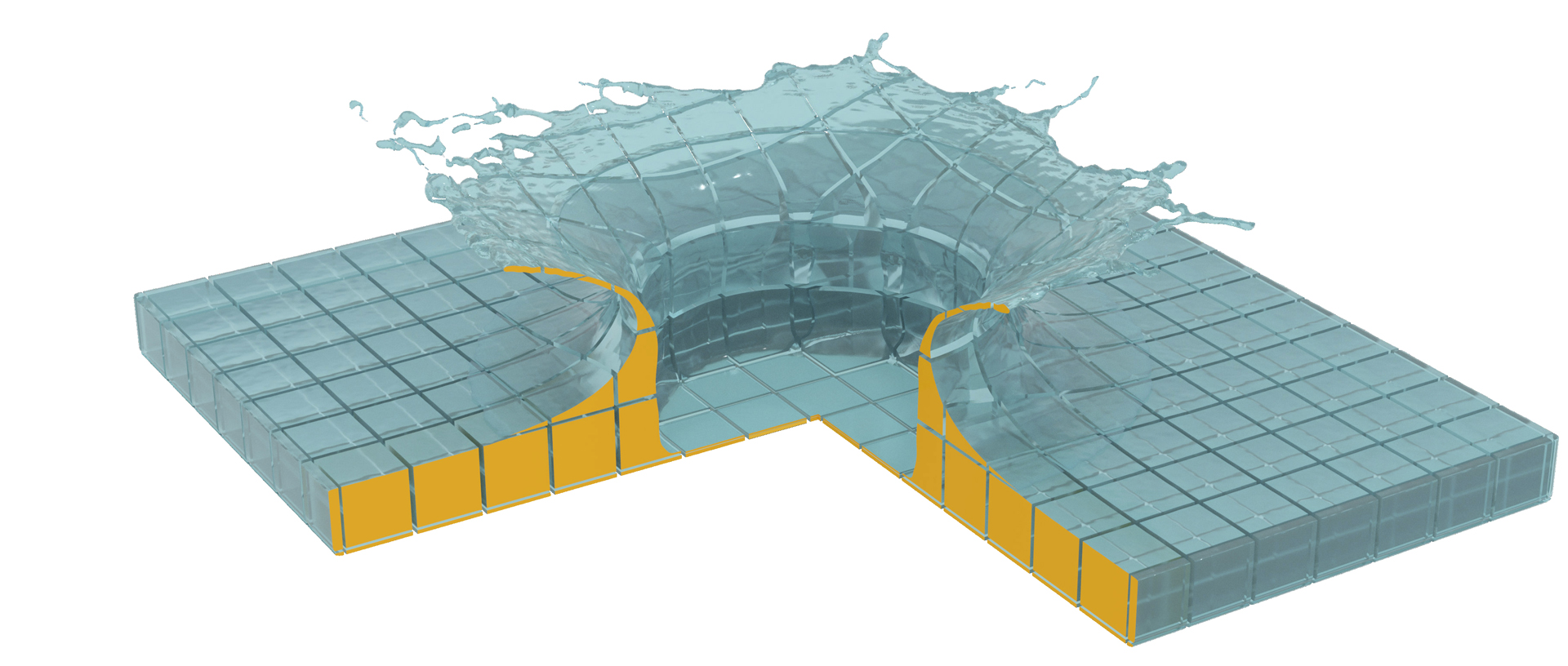
“Mandoline: robust cut-cell generation for arbitrary triangle meshes” by Tao, Batty, Fiume and Levin
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Mandoline: robust cut-cell generation for arbitrary triangle meshes
Session/Category Title:
- Composing & Decomposing Geometry
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
Although geometry arising “in the wild” most often comes in the form of a surface representation, a plethora of geometrical and physical applications require the construction of volumetric embeddings either of the geometry itself or the domain surrounding it. Cartesian cut-cell-based mesh generation provides an attractive solution in which volumetric elements are constructed from the intersection of the input surface geometry with a uniform or adaptive hexahedral grid. This choice, especially common in computational fluid dynamics, has the potential to efficiently generate accurate, surface-conforming cells; unfortunately, current solutions are often slow, fragile, or cannot handle many common topological situations. We therefore propose a novel, robust cut-cell construction technique for triangle surface meshes that explicitly computes the precise geometry of the intersection cells, even on meshes that are open or non-manifold. Its fundamental geometric primitive is the intersection of an arbitrary segment with an axis-aligned plane. Beginning from the set of intersection points between triangle mesh edges and grid planes, our bottom-up approach robustly determines cut-edges, cut-faces, and finally cut-cells, in a manner designed to guarantee topological correctness. We demonstrate its effectiveness and speed on a wide range of input meshes and grid resolutions, and make the code available as open source.
References:
1. Michael J Aftosmis, Marsha J Berger, and John E Melton. 1998. Robust and efficient Cartesian mesh generation for component-based geometry. AIAA journal 36, 6 (1998), 952–960.Google ScholarCross Ref
2. PF Antonietti and I Mazzieri. 2018. High-order Discontinuous Galerkin methods for the elastodynamics equation on polygonal and polyhedral meshes. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 342 (2018), 414–437.Google ScholarCross Ref
3. Vinicius C. Azevedo, Christopher Batty, and Manuel M. Oliveira. 2016. Preserving Geometry and Topology for Fluid Flows with Thin Obstacles and Narrow Gaps. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, Article 97 (2016), 97:1–97:12 pages. Issue 4. Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2016.Google Scholar
4. M. Berger. 2017. Chapter 1 – Cut Cells: Meshes and Solvers. In Handbook of Numerical Methods for Hyperbolic Problems, Rémi Abgrall and Chi-Wang Shu (Eds.). Handbook of Numerical Analysis, Vol. 18. Elsevier, 1 — 22. Google ScholarCross Ref
5. P. Colella, D. T. Graves, T. J. Ligocki, G. Miller, D. Modiano, P. O. Schwartz, B. Van Straalen, J. Pilliod, D. Trebotich, M. Barad, B. Keen, A. Nonaka, and C. Shen. 2014. EBChombo software package for Cartesian grid, embedded boundary applications. Technical Report.Google Scholar
6. RK Crockett, Phillip Colella, and Daniel T Graves. 2011. A Cartesian grid embedded boundary method for solving the Poisson and heat equations with discontinuous coefficients in three dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 7 (2011), 2451–2469.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Christian Dick, Marcus Rogowsky, and Rüdiger Westermann. 2016. Solving the fluid pressure Poisson equation using multigrid—evaluation and improvements. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 22, 11 (2016), 2480–2492.Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Olivier Dionne and Martin de Lasa. 2013. Geodesic voxel binding for production character meshes. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. ACM, 173–180.Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Essex Edwards and Robert Bridson. 2014. Detailed water with coarse grids: combining surface meshes and adaptive discontinuous Galerkin. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 4 (2014), 136.Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Florian Ferstl, Rüdiger Westermann, and Christian Dick. 2014. Large-scale liquid simulation on adaptive hexahedral grids. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 20, 10 (2014), 1405–1417.Google ScholarCross Ref
11. Matthew Fisher, Boris Springborn, Peter Schröder, and Alexander I Bobenko. 2007. An algorithm for the construction of intrinsic delaunay triangulations with applications to digital geometry processing. Computing 81, 2–3 (2007), 199–213.Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Eitan Grinspun, Anil N. Hirani, Mathieu Desbrun, and Peter Schröder. 2003. Discrete Shells. In Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA ’03). Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland, Switzerland, 62–67. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=846276.846284Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Eran Guendelman, Andrew Selle, Frank Losasso, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2005. Coupling water and smoke to thin deformable and rigid shells. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 24. ACM, 973–981.Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Anil Nirmal Hirani. 2003. Discrete exterior calculus. Ph.D. Dissertation. California Institute of Technology.Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Yixin Hu, Qingnan Zhou, Xifeng Gao, Alec Jacobson, Denis Zorin, and Daniele Panozzo. 2018. Tetrahedral Meshing in the Wild. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 60 (July 2018), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Alec Jacobson, Daniele Panozzo, C Schüller, Olga Diamanti, Qingnan Zhou, N Pietroni, et al. 2016. libigl: A simple C++ geometry processing library.Google Scholar
17. Jan Jaśkowiec, Piotr Pluciński, and Anna Stankiewicz. 2016. Discontinuous Galerkin method with arbitrary polygonal finite elements. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design 120 (2016), 1–17.Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Hong-Jun Kim and Timothy J Tautges. 2010. EBMesh: An embedded boundary meshing tool. In Proceedings of the 19th International Meshing Roundtable. Springer, 227–242.Google ScholarCross Ref
19. Dan Koschier, Jan Bender, and Nils Thuerey. 2017. Robust eXtended finite elements for complex cutting of deformables. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 55.Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Long Lee and Randall J LeVeque. 2003. An immersed interface method for incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 25, 3 (2003), 832–856.Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Yijing Li and Jernej Barbič. 2018. Immersion of self-intersecting solids and surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 45.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Haojie Lian, Asger N Christiansen, Daniel A Tortorelli, Ole Sigmund, and Niels Aage. 2017. Combined shape and topology optimization for minimization of maximal von Mises stress. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 55, 5 (2017), 1541–1557.Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Konstantin Lipnikov, Gianmarco Manzini, and Mikhail Shashkov. 2014. Mimetic finite difference method. J. Comput. Phys. 257 (2014), 1163–1227.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Sebastian Martin, Peter Kaufmann, Mario Botsch, Martin Wicke, and Markus Gross. 2008. Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 27. Wiley Online Library, 1521–1529.Google Scholar
25. Matthias Meinke, Lennart Schneiders, Claudia Günther, and Wolfgang Schröder. 2013. A cut-cell method for sharp moving boundaries in Cartesian grids. Computers & Fluids 85 (2013), 135–142.Google ScholarCross Ref
26. Rajat Mittal and Gianluca Iaccarino. 2005. Immersed boundary methods. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 37 (2005), 239–261.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Neil Molino, Zhaosheng Bao, and Ron Fedkiw. 2004. A virtual node algorithm for changing mesh topology during simulation. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 23. ACM, 385–392.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Matthias Müller. 2009. Fast and robust tracking of fluid surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2009 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. ACM, 237–245.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Maks Ovsjanikov, Mirela Ben-Chen, Justin Solomon, Adrian Butscher, and Leonidas Guibas. 2012. Functional maps: a flexible representation of maps between shapes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4 (2012), 30.Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Taylor Patterson, Nathan Mitchell, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2012. Simulation of complex nonlinear elastic bodies using lattice deformers. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 6 (2012), 197.Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Glaucio H Paulino and Arun L Gain. 2015. Bridging art and engineering using Escher-based virtual elements. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 51, 4 (2015), 867–883.Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Nicholas Ray, Dmitry Sokolov, Maxence Reberol, Franck Ledoux, and Bruno Levy. 2018. Hex-dominant meshing: Mind the gap! Computer-Aided Design 102 (2018), 94–103.Google Scholar
33. Masoud Safdari, Ahmad R Najafi, Nancy R Sottos, and Philippe H Geubelle. 2016. A NURBS-based generalized finite element scheme for 3D simulation of heterogeneous materials. J. Comput. Phys. 318 (2016), 373–390.Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Nicholas Sharp, Yousuf Soliman, and Keenan Crane. 2019. Navigating intrinsic triangulations. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 4 (2019), 55.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Jonathan Richard Shewchuk. 1996. Triangle: Engineering a 2D Quality Mesh Generator and Delaunay Triangulator. In Applied Computational Geometry: Towards Geometric Engineering, Ming C. Lin and Dinesh Manocha (Eds.). Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 1148. Springer-Verlag, 203–222. From the First ACM Workshop on Applied Computational Geometry.Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Hang Si. 2015. TetGen, a Delaunay-based quality tetrahedral mesh generator. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS) 41, 2 (2015), 11.Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Eftychios Sifakis, Kevin G Der, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2007. Arbitrary cutting of deformable tetrahedralized objects. In Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. Eurographics Association, 73–80.Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Jeffrey Slotnick, Abdollah Khodadoust, Juan Alonso, David Darmofal, William Gropp, Elizabeth Lurie, and Dimitri Mavriplis. 2014. CFD vision 2030 study: a path to revolutionary computational aerosciences. (2014).Google Scholar
39. Maxime Theillard, Landry Fokoua Djodom, Jean-Léopold Vié, and Frédéric Gibou. 2013. A second-order sharp numerical method for solving the linear elasticity equations on irregular domains and adaptive grids-application to shape optimization. J. Comput. Phys. 233 (2013), 430–448.Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Chris Wojtan, Nils Thürey, Markus Gross, and Greg Turk. 2010. Physics-inspired topology changes for thin fluid features. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4 (2010), 1–8. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Qingnan Zhou, Eitan Grinspun, Denis Zorin, and Alec Jacobson. 2016. Mesh Arrangements for Solid Geometry. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 4 (2016).Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Qingnan Zhou and Alec Jacobson. 2016. Thingi10K: A Dataset of 10,000 3D-Printing Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.04797 (2016).Google Scholar