“Light reallocation for high contrast projection using an analog micromirror array”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Light reallocation for high contrast projection using an analog micromirror array
Session/Category Title:
- Imaging hardware
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
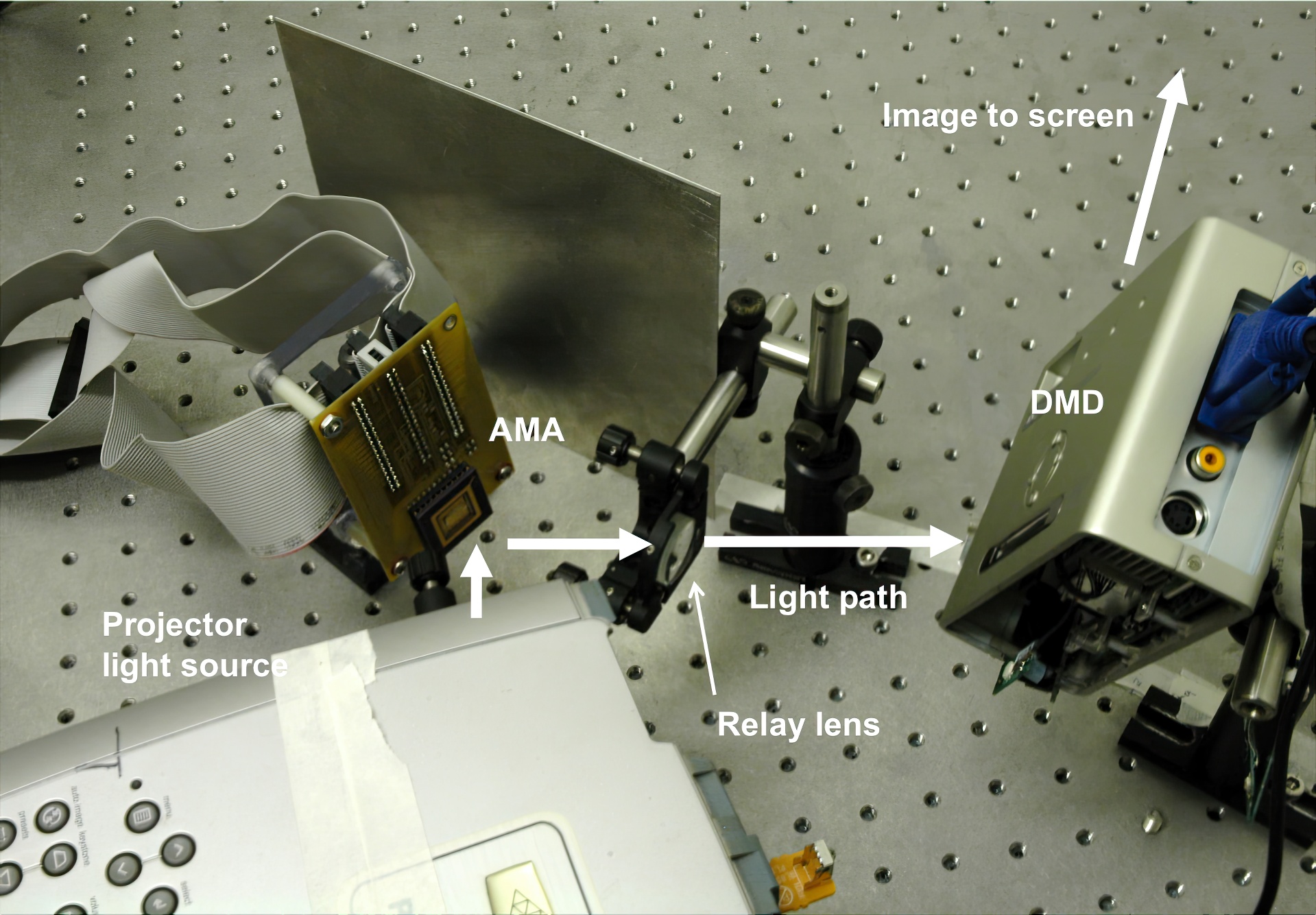
We demonstrate for the first time a proof of concept projector with a secondary array of individually controllable, analog micromirrors added to improve the contrast and peak brightness of conventional projectors. The micromirrors reallocate the light of the projector lamp from the dark parts towards the light parts of the image, before it reaches the primary image modulator. Each element of the analog micromirror array can be tipped/tilted to divert portions of the light from the lamp in two dimensions. By directing these mirrors on an image-dependent basis, we can increase both the peak intensity of the projected image as well as its contrast.In this paper, we describe and analyze the optical design for projectors using this light reallocation approach. We also discuss software algorithms to compute the best light reallocation pattern for a given input image, using the constraints of real hardware. We perform extensive simulations of this process to evaluate image quality and performance characteristics of this process. Finally, we present a first proof-of-concept implementation of this approach using a prototype analog micromirror device.
References:
1. Agarwal, P., and Varadarajan, K. 2004. A near-linear constant-factor approximation for euclidean bipartite matching? In Proceedings of the twentieth annual symposium on Computational geometry, ACM New York, NY, USA, 247–252. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Bimber, O., and Iwai, D. 2008. Superimposing dynamic range. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. Siggraph Asia) 27, 5, 1–8. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Bloom, D., 1997. The grating light valve: revolutionizing display technology.Google Scholar
4. Brennesholtz, M. S., and Stupp, E. H. 2008. Projection Displays, 2nd ed. Wiley. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Damberg, G., Seetzen, H., Ward, G., Heidrich, W., and Whitehead, L. 2007. High Dynamic Range Projection Systems. Proceedings of the 2006 Society for Information Display Annual Symposium.Google Scholar
6. Debevec, P. 2005. A median cut algorithm for light probe sampling. In SIGGRAPH ’05: ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Posters, ACM, New York, NY, USA, 66. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Derra, G., Moench, H., Fischer, E., Giese, H., Hechtfischer, U., Heusler, G., Koerber, A., Niemann, U., Noertemann, F., Pekarski, P., et al. 2005. UHP lamp systems for projection applications. JOURNAL OF PHYSICS-LONDON-D APPLIED PHYSICS 38, 17, 2995.Google Scholar
8. Dewald, D., Segler, D., and Penn, S. 2004. Advances in contrast enhancement for DLP projection displays. Journal of the Society for Information Display 11, 177–181.Google ScholarCross Ref
9. Halbach, K. 1964. Matrix representation of Gaussian optics. American Journal of Physics 32, 90.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. Hecht, E. 2002. Optics, 4th ed. Addison Wesley, San Francisco, CA, USA.Google Scholar
11. Heckbert, P. 1982. Color image quantization for frame buffer display. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics 16, 3, 297–307. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Hoskinson, R., and Stoeber, B. 2008. High-dynamic range image projection using an auxiliary mems mirror array. Optics Express 16, 7361–7368.Google ScholarCross Ref
13. Hoskinson, R., Buescher, D., Hampl, S., Holle, M., and Stoeber, B. 2010. Arrays of large-area, large-angle tip/tilt micromirrors for use in a high-contrast projector. In submission.Google Scholar
14. Iisaka, H., Toyooka, T., Yoshida, S., and Nagata, M. 2003. Novel Projection System Based on an Adaptive Dynamic Range Control Concept. In Procoeedings Int Disp Workshops, vol. 10, 1553–1556.Google Scholar
15. Kuhn, H. 1955. The Hungarian method for the assignment and transportation problems. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly 2, 83–97.Google ScholarCross Ref
16. Kusakabe, Y., Kanazawa, M., Nojiri, Y., Furuya, M., and Yoshimura, M. 2009. A high-dynamic-range and high-resolution projector with dual modulation. In Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 7241.Google Scholar
17. Mantiuk, R., Daly, S., Myszkowski, K., and Seidel, H.-P. 2005. Predicting visible differences in high dynamic range images – model and its calibration. In Human Vision and Electronic Imaging X, IS&T/SPIE’s 17th Annual Symposium on Electronic Imaging (2005), B. E. Rogowitz, T. N. Pappas, and S. J. Daly, Eds., vol. 5666, 204–214.Google Scholar
18. Nagahara, H., Kuthirummal, S., Zhou, C., and Nayar, S. 2008. Flexible Depth of Field Photography. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Pavlovych, A., and Stuerzlinger, W. 2005. A High-Dynamic Range Projection System. Progress in biomedical optics and imaging 6, 39.Google Scholar
20. Seetzen, H., Heidrich, W., Stuerzlinger, W., Ward, G., Whitehead, L., Trentacoste, M., Ghosh, A., and Vorozcovs, A. 2004. High dynamic range display systems. ACM Transactions on Graphics (Siggraph 2004) 23, 3, 760–768. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Seetzen, H. 2009. High Dynamic Range Display and Projection Systems. PhD thesis, University of British Columbia.Google Scholar
22. Texas Instruments. 2005. DMD 0.7 XGA 12 DDR DMD Discovery.Google Scholar
23. Toyooka, T., Yoshida, S., and Iisaka, H. 2005. Illumination control system for adaptive dynamic range control. Journal of the Society for Information Display 13, 105.Google ScholarCross Ref
24. Tsai, J., Chiou, S., Hsieh, T., Sun, C., Hah, D., and Wu, M. 2008. Two-axis MEMS scanners with radial vertical combdrive actuators—design, theoretical analysis, and fabrication. Journal of Optics A: Pure and Applied Optics 10, 044006.Google ScholarCross Ref