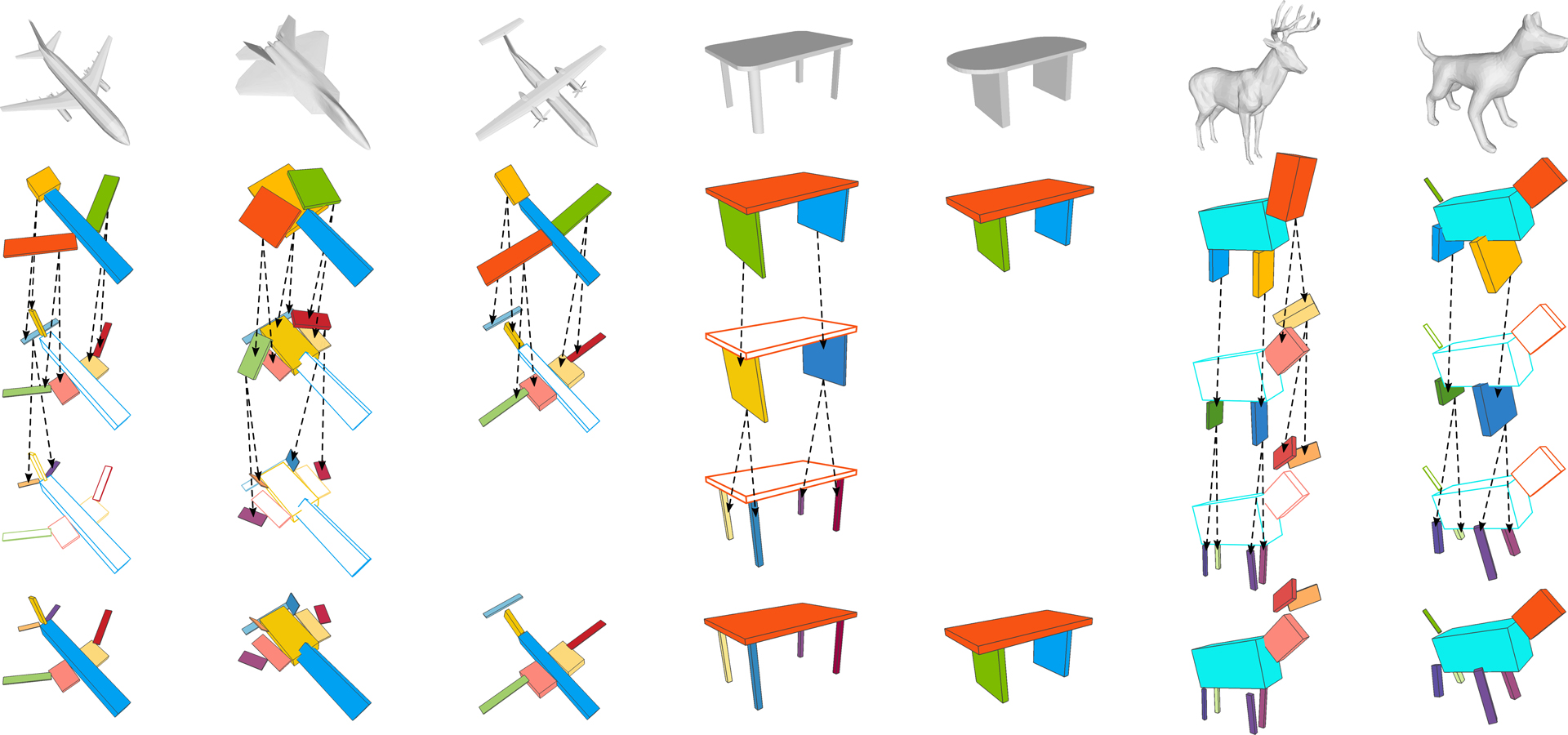
“Learning adaptive hierarchical cuboid abstractions of 3D shape collections” by Sun, Zou, Tong and Liu
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Learning adaptive hierarchical cuboid abstractions of 3D shape collections
Session/Category Title:
- Geometry Off the Deep End
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
Abstracting man-made 3D objects as assemblies of primitives, i.e., shape abstraction, is an important task in 3D shape understanding and analysis. In this paper, we propose an unsupervised learning method for automatically constructing compact and expressive shape abstractions of 3D objects in a class. The key idea of our approach is an adaptive hierarchical cuboid representation that abstracts a 3D shape with a set of parametric cuboids adaptively selected from a hierarchical and multi-level cuboid representation shared by all objects in the class. The adaptive hierarchical cuboid abstraction offers a compact representation for modeling the variant shape structures and their coherence at different abstraction levels. Based on this representation, we design a convolutional neural network (CNN) for predicting the parameters of each cuboid in the hierarchical cuboid representation and the adaptive selection mask of cuboids for each input 3D shape. For training the CNN from an unlabeled 3D shape collection, we propose a set of novel loss functions to maximize the approximation quality and compactness of the adaptive hierarchical cuboid abstraction and present a progressive training scheme to refine the cuboid parameters and the cuboid selection mask effectively.We evaluate the effectiveness of our approach on various 3D shape collections and demonstrate its advantages over the existing cuboid abstraction approach. We also illustrate applications of the resulting adaptive cuboid representations in various shape analysis and manipulation tasks.
References:
1. Martín Abadi, Ashish Agarwal, Paul Barham, and etal. 2015. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems.Google Scholar
2. Gareth Bradshaw and Carol O’Sullivan. 2004. Adaptive medial-axis approximation for sphere-tree construction. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 1 (2004), 1–26.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Angel X. Chang, Thomas Funkhouser, and etal. 2015. ShapeNet: an information-rich 3D model repository. arXiv:1512.03012 [cs.GR].Google Scholar
4. David Cohen-Steiner, Pierre Alliez, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2004. Variational Shape Approximation. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 23, 3 (2004), 905–914.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Nicu D. Cornea, Deborah Silver, and Patrick Min. 2007. Curve-skeleton properties, applications, and algorithms. IEEE. T. Vis. Comput. Gr. 13, 3 (2007), 530–548.Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Fernando De Goes, Siome Goldenstein, Mathieu Desbrun, and Luiz Velho. 2011. Exoskeleton: Curve network abstraction for 3D shapes. Comput. Graph. 35, 1 (2011), 112–121.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Tao Du, Jeevana Priya Inala, Yewen Pu, Andrew Spielberg, Adriana Schulz, Daniela Rus, Armando Solar-Lezama, and Wojciech Matusik. 2018. InverseCSG: Automatic conversion of 3D models to CSG trees. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) (2018).Google Scholar
8. Noa Fish, Melinos Averkiou, Oliver van Kaick, Olga Sorkine-Hornung, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Niloy J. Mitra. 2014. Meta-representation of shape families. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) (2014), 34:1–34:11.Google Scholar
9. Qiang Fu, Xiaowu Chen, Xiaoyu Su, Jia Li, and Hongbo Fu. 2016. Structure-adaptive shape editing for man-made objects. Comput. Graph. Forum (EG) 35, 2 (2016), 27–36.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. Aleksey Golovinskiy and Thomas Funkhouser. 2009. Consistent segmentation of 3D models. Computers and Graphics 33, 3 (2009), 262–269.Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Giorgio Gori, Alla Sheffer, Nicholas Vining, Enrique Rosales, Nathan Carr, and Tao Ju. 2017. FlowRep: Descriptive curve networks for free-form design shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 36, 4 (2017), 59:1–59:14.Google ScholarDigital Library
12. M. S. Hassouna and A. A. Farag. 2009. Variational curve skeletons using gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31, 12 (2009), 2257–2274.Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Ruizhen Hu, Lubin Fan, and Ligang Liu. 2012. Co-segmentation of 3D shapes via subspace clustering. Comput. Graph. Forum (SGP) 31, 5 (2012), 1703–1713.Google ScholarDigital Library
14. R. Hu, M. Savva, and O. van Kaick. 2018. Functionality representations and applications for shape analysis. Comput. Graph. Forum 37, 2 (2018), 603–624.Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Qixing Huang, Vladlen Koltun, and Leonidas Guibas. 2011. Joint shape segmentation with linear programming. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) 30, 6 (2011), 125:1–125:12.Google Scholar
16. Evangelos Kalogerakis, Melinos Averkiou, Subhransu Maji, and Siddhartha Chaudhuri. 2017. 3D shape segmentation with projective convolutional networks. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Google Scholar
17. Evangelos Kalogerakis, Aaron Hertzmann, and Karan Singh. 2010. Learning 3D mesh segmentation and labeling. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 29, 4 (2010), 102:1–102:12.Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Jun Li, Kai Xu, Siddhartha Chaudhuri, Ersin Yumer, Hao Zhang, and Leonidas Guibas. 2017. GRASS: Generative recursive autoencoders for shape structures. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 36, 4 (2017), 52:1–52:14.Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Yangyan Li, Xiaokun Wu, Yiorgos Chrysathou, Andrei Sharf, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Niloy J. Mitra. 2011. GlobFit: Consistently fitting primitives by discovering global relations. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 30, 4 (2011), 52:1–52:12.Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Wallace Lira, Chi-Wing Fu, and Hao Zhang. 2018. Fabricable Eulerian wires for 3D shape abstraction. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) (2018), 240:1–240:13.Google Scholar
21. Chen Liu, Jimei Yang, Duygu Ceylan, Ersin Yumer, and Yasutaka Furukawa. 2018. PlaneNet: piece-wise planar reconstruction from a single RGB image. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Google Scholar
22. Lin Lu, Yi-King Choi, Wenping Wang, and Myung-Soo Kim. 2007. Variational 3D shape segmentation for bounding volume computation. Comput. Graph. Forum 26, 3 (2007), 329–338.Google ScholarCross Ref
23. Ravish Mehra, Qingnan Zhou, Jeremy Long, Alla Sheffer, Amy Gooch, and Niloy J. Mitra. 2009. Abstraction of man-made shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) 28, 5 (2009), 137:1–137:10.Google Scholar
24. Niloy Mitra, Michael Wand, Hao Zhang, Daniel Cohen-Or, Vladimir Kim, and Qi-Xing Huang. 2014. Structure-aware shape processing. In SIGGRAPH 2014 Courses. 1:1–1:22.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Kaichun Mo, Shilin Zhu, Angel X. Chang, Li Yi, Subarna Tripathi, Leonidas J. Guibas, and Hao Su. 2019. PartNet: A large-scale benchmark for fine-grained and hierarchical part-level 3D object understanding. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Google Scholar
26. Chengjie Niu, Jun Li, and Kai Xu. 2018. Im2Struct: Recovering 3D shape structure from a single RGB image. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Google Scholar
27. Zhenyu Shu, Chengwu Qi, Shiqing Xin, Chao Hu, Li Wang, Yu Zhang, and Ligang Liu. 2016. Unsupervised 3D shape segmentation and co-segmentation via deep learning. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 43 (2016), 39 — 52.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Oana Sidi, Oliver van Kaick, Yanir Kleiman, Hao Zhang, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2011. Unsupervised co-segmentation of a set of shapes via descriptor-space spectral clustering. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) 30, 6 (2011), 126:1–126:10.Google Scholar
29. Shubham Tulsiani,, Hao Su, Leonidas J. Guibas, Alexei A. Efros, and Jitendra Malik. 2017. Learning shape abstractions by assembling volumetric primitives. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Google Scholar
30. Oliver van Kaick, Kai Xu, Hao Zhang, Yanzhen Wang, Shuyang Sun, Ariel Shamir, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2013. Co-hierarchical analysis of shape structures. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 32, 4 (2013), 69:1–69:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Peng-Shuai Wang, Yang Liu, Yu-Xiao Guo, Chun-Yu Sun, and Xin Tong. 2017. O-CNN: Octree-based convolutional neural networks for 3D shape analysis. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 36, 4 (2017), 72:1–72:11.Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Peng-Shuai Wang, Chun-Yu Sun, Yang Liu, and Xin Tong. 2018. Adaptive O-CNN: A patch-based deep representation of 3D shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) (2018).Google Scholar
33. Jianhua Wu and Leif Kobbelt. 2005. Structure recovery via hybrid variational surface approximation. Comput. Graph. Forum (EG) 24, 3 (2005), 277–284.Google ScholarCross Ref
34. Q. Wu, K. Xu, and J. Wang. 2018. Constructing 3D CSG models from 3D raw point clouds. Comput. Graph. Forum 37, 5 (2018), 221–232.Google ScholarCross Ref
35. Kai Xu, Vladimir G. Kim, Qixing Huang, and Evangelos Kalogerakis. 2015. Data-Driven Shape Analysis and Processing. Comput. Graph. Forum 36, 1 (2015), 101–132.Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Dong-Ming Yan, Yang Liu, and Wenping Wang. 2006. Quadric Surface Extraction by Variational Shape Approximation. In Geometric Modeling and Processing – GMP. 73–86.Google Scholar
37. Li Yi, Leonidas Guibas, Aaron Hertzmann, Vladimir G. Kim, Hao Su, and Ersin Yumer. 2017. Learning hierarchical shape segmentation and labeling from online repositories. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 36, 4 (2017), 70:1–70:12.Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Fenggen Yu, Kun Liu, Yan Zhang, Chenyang Zhu, and Kai Xu. 2019. PartNet: A recursive part decomposition network for fine-grained and hierarchical shape segmentation. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Google Scholar
39. Mehmet Ersin Yumer and Levent Burak Kara. 2012. Co-abstraction of shape collections. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) 31, 6 (2012), 166:1–166:11.Google Scholar
40. Chuhang Zou, Ersin Yumer, Jimei Yang, Duygu Ceylan, and Derek Hoiem. 2017. 3D-PRNN: Generating shape primitives with recurrent neural networks. In International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).Google ScholarCross Ref