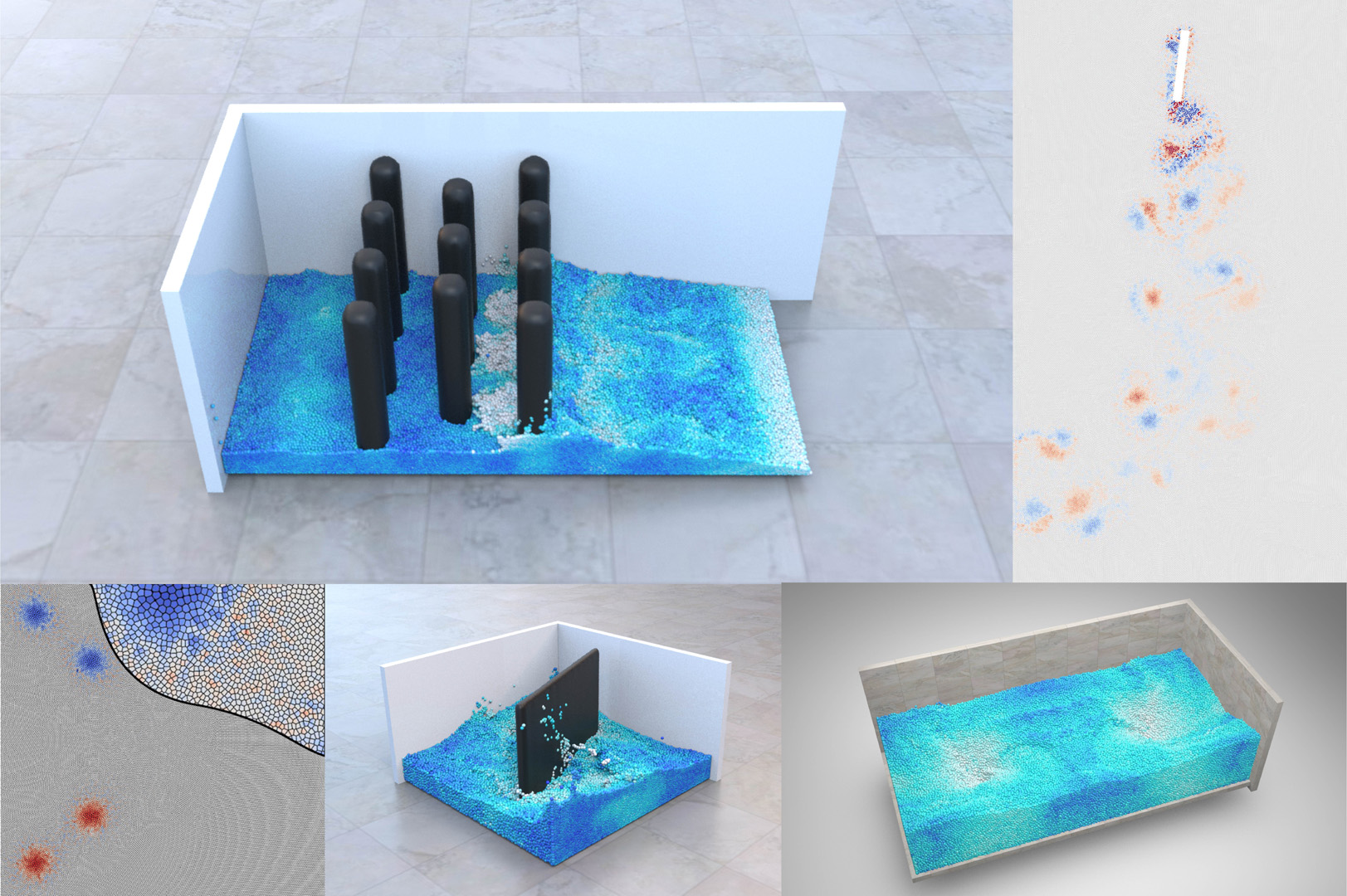
“Lagrangian Covector Fluid With Free Surface”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Lagrangian Covector Fluid With Free Surface
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We present a novel Lagrangian solver for incompressible flows, leveraging flow-maps to simulate vortical evolution with particles. Our approach focuses on using particle trajectories as flow maps, tailoring path integrals along trajectories for complex boundary conditions, and computing physical quantities on particles with a Voronoi-based Poisson solver to avoid interpolation.
References:
[1]
C.B. Barber, D.P. Dobkin, and H.T. Huhdanpaa. 1996. The Quickhull algorithm for convex hulls. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS) 22, 4 (Dec 1996), 469?483. http://www.qhull.org
[2]
TF Buttke. 1992. Lagrangian numerical methods which preserve the Hamiltonian structure of incompressible fluid flow. (1992).
[3]
Tomas F Buttke. 1993. Velicity methods: Lagrangian numerical methods which preserve the Hamiltonian structure of incompressible fluid flow. In Vortex flows and related numerical methods. Springer, 39?57.
[4]
Thomas F Buttke and Alexandre J Chorin. 1993. Turbulence calculations in magnetization variables. Applied numerical mathematics 12, 1-3 (1993), 47?54.
[5]
Ricardo Cortez. 1996. An impulse-based approximation of fluid motion due to boundary forces. J. Comput. Phys. 123, 2 (1996), 341?353.
[6]
Keenan Crane, Fernando de Goes, Mathieu Desbrun, and Peter Schr?der. 2013. Digital geometry processing with discrete exterior calculus. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2013 Courses (Anaheim, California) (SIGGRAPH ?13). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 7, 126 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/2504435.2504442
[7]
Fernando De Goes, Corentin Wallez, Jin Huang, Dmitry Pavlov, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2015. Power particles: an incompressible fluid solver based on power diagrams.ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (2015), 50?1.
[8]
Yitong Deng, Hong-Xing Yu, Diyang Zhang, Jiajun Wu, and Bo Zhu. 2023. Fluid Simulation on Neural Flow Maps. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 42, 6 (2023), 1?21.
[9]
Daniel Duque. 2023. A unified derivation of Voronoi, power, and finite-element Lagrangian computational fluid dynamics. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids 98 (2023), 268?278.
[10]
Fan Feng, Jinyuan Liu, Shiying Xiong, Shuqi Yang, Yaorui Zhang, and Bo Zhu. 2022. Impulse fluid simulation. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (2022).
[11]
Toshiya Hachisuka. 2005. Combined Lagrangian-Eulerian approach for accurate advection. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Posters. 114?es.
[12]
Yuanming Hu, Tzu-Mao Li, Luke Anderson, Jonathan Ragan-Kelley, and Fr?do Durand. 2019. Taichi: a language for high-performance computation on spatially sparse data structures. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6 (2019), 201.
[13]
Bruno L?vy. 2022. Partial optimal transport for a constant-volume Lagrangian mesh with free boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 451 (2022), 110838.
[14]
Olivier Mercier, Xi-Yuan Yin, and Jean-Christophe Nave. 2020. The characteristic mapping method for the linear advection of arbitrary sets. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 42, 3 (2020), A1663?A1685.
[15]
Mohammad Sina Nabizadeh, Stephanie Wang, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Albert Chern. 2022. Covector fluids. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 41, 4 (2022), 1?16.
[16]
Valery Iustinovich Oseledets. 1989. On a new way of writing the Navier-Stokes equation. The Hamiltonian formalism. Russ. Math. Surveys 44 (1989), 210?211.
[17]
Ziyin Qu, Xinxin Zhang, Ming Gao, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Baoquan Chen. 2019. Efficient and conservative fluids using bidirectional mapping. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 4 (2019), 1?12.
[18]
PH Roberts. 1972. A Hamiltonian theory for weakly interacting vortices. Mathematika 19, 2 (1972), 169?179.
[19]
Takahiro Sato, Christopher Batty, Takeo Igarashi, and Ryoichi Ando. 2018. Spatially adaptive long-term semi-Lagrangian method for accurate velocity advection. Computational Visual Media 4, 3 (2018), 6.
[20]
Takahiro Sato, Takeo Igarashi, Christopher Batty, and Ryoichi Ando. 2017. A long-term semi-lagrangian method for accurate velocity advection. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2017 Technical Briefs. 1?4.
[21]
Robert Saye. 2016. Interfacial gauge methods for incompressible fluid dynamics. Science advances 2, 6 (2016), e1501869.
[22]
Robert Saye. 2017. Implicit mesh discontinuous Galerkin methods and interfacial gauge methods for high-order accurate interface dynamics, with applications to surface tension dynamics, rigid body fluid?structure interaction, and free surface flow: Part I. J. Comput. Phys. 344 (2017), 647?682.
[23]
Hagit Schechter and Robert Bridson. 2012. Ghost SPH for animating water. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4 (2012), 1?8.
[24]
DM Summers. 2000. A representation of bounded viscous flow based on Hodge decomposition of wall impulse. J. Comput. Phys. 158, 1 (2000), 28?50.
[25]
Jerry Tessendorf. 2015. Advection Solver Performance with Long Time Steps, and Strategies for Fast and Accurate Numerical Implementation. (2015).
[26]
Jerry Tessendorf and Brandon Pelfrey. 2011. The characteristic map for fast and efficient vfx fluid simulations. In Computer Graphics International Workshop on VFX, Computer Animation, and Stereo Movies. Ottawa, Canada.
[27]
Pauli Virtanen, Ralf Gommers, Travis E. Oliphant, Matt Haberland, Tyler Reddy, David Cournapeau, Evgeni Burovski, Pearu Peterson, Warren Weckesser, Jonathan Bright, St?fan J. van der Walt, Matthew Brett, Joshua Wilson, K. Jarrod Millman, Nikolay Mayorov, Andrew R. J. Nelson, Eric Jones, Robert Kern, Eric Larson, C J Carey, ?lhan Polat, Yu Feng, Eric W. Moore, Jake VanderPlas, Denis Laxalde, Josef Perktold, Robert Cimrman, Ian Henriksen, E. A. Quintero, Charles R. Harris, Anne M. Archibald, Ant?nio H. Ribeiro, Fabian Pedregosa, Paul van Mulbregt, and SciPy 1.0 Contributors. 2020. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nature Methods 17 (2020), 261?272. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0686-2
[28]
E Weinan and Jian-Guo Liu. 2003. Gauge method for viscous incompressible flows. Communications in Mathematical Sciences 1, 2 (2003), 317?332.
[29]
DC Wiggert and EB Wylie. 1976. Numerical predictions of two-dimensional transient groundwater flow by the method of characteristics. Water Resources Research 12, 5 (1976), 971?977.
[30]
S. Xiong, Z. Wang, M. Wang, and B. Zhu. 2022. A Clebsch method for free-surface vortical flow simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 41, 4 (2022).
[31]
Shuqi Yang, Shiying Xiong, Yaorui Zhang, Fan Feng, Jinyuan Liu, and Bo Zhu. 2021. Clebsch gauge fluid. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 40, 4 (2021), 1?11.
[32]
Xi-Yuan Yin, Olivier Mercier, Badal Yadav, Kai Schneider, and Jean-Christophe Nave. 2021. A Characteristic Mapping method for the two-dimensional incompressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 424 (2021), 109781.
[33]
Xi-Yuan Yin, Kai Schneider, and Jean-Christophe Nave. 2023. A Characteristic Mapping Method for the three-dimensional incompressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. (2023), 111876.
[34]
Xiao Zhai, Fei Hou, Hong Qin, and Aimin Hao. 2018. Fluid simulation with adaptive staggered power particles on gpus. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 26, 6 (2018), 2234?2246.