“Hyperbolic orbifold tutte embeddings” by Aigerman and Lipman
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Hyperbolic orbifold tutte embeddings
Session/Category Title:
- Parameterization & Remeshing
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
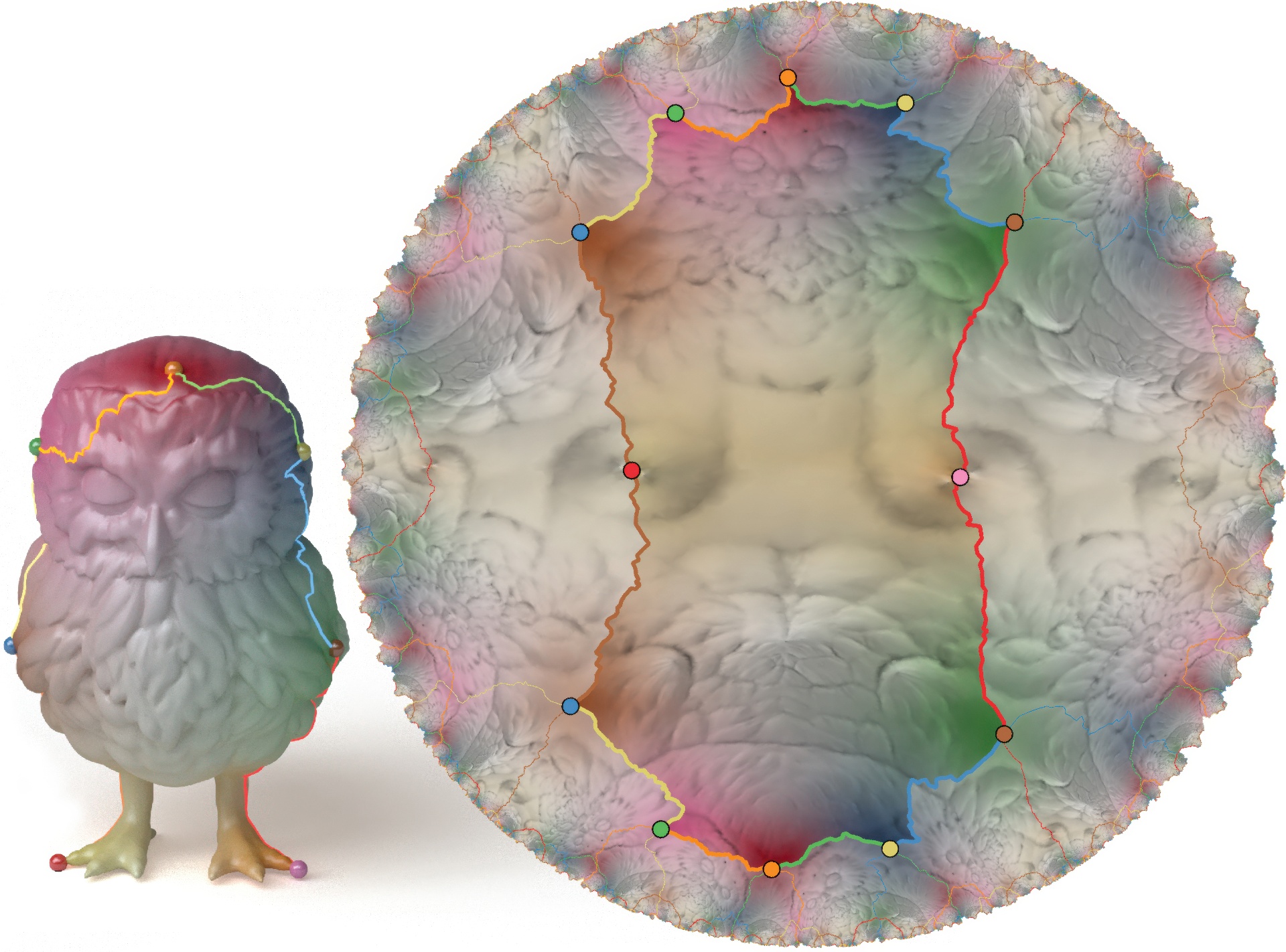
Tutte’s embedding is one of the most popular approaches for computing parameterizations of surface meshes in computer graphics and geometry processing. Its popularity can be attributed to its simplicity, the guaranteed bijectivity of the embedding, and its relation to continuous harmonic mappings.In this work we extend Tutte’s embedding into hyperbolic cone-surfaces called orbifolds. Hyperbolic orbifolds are simple surfaces exhibiting different topologies and cone singularities and therefore provide a flexible and useful family of target domains. The hyperbolic Orbifold Tutte embedding is defined as a critical point of a Dirichlet energy with special boundary constraints and is proved to be bijective, while also satisfying a set of points-constraints. An efficient algorithm for computing these embeddings is developed.We demonstrate a powerful application of the hyperbolic Tutte embedding for computing a consistent set of bijective, seamless maps between all pairs in a collection of shapes, interpolating a set of user-prescribed landmarks, in a fast and robust manner.
References:
1. Aigerman, N., and Lipman, Y. 2015. Orbifold tutte embeddings. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6 (Oct.), 190:1–190:12.
2. Aigerman, N., Poranne, R., and Lipman, Y. 2014. Lifted bijections for low distortion surface mappings. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July), 69:1–69:12.
3. Aigerman, N., Poranne, R., and Lipman, Y. 2015. Seamless surface mappings. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4, 72.
4. Bogo, F., Romero, J., Loper, M., and Black, M. J. 2014. FAUST: Dataset and evaluation for 3D mesh registration. In Proceedings IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, Piscataway, NJ, USA.
5. Bommes, D., Zimmer, H., and Kobbelt, L. 2009. Mixedinteger quadrangulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3 (July), 77:1–77:10.
6. Bradley, D., Popa, T., Sheffer, A., Heidrich, W., and Boubekeur, T. 2008. Markerless garment capture. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug.), 99:1–99:9.
7. Campen, M., Bommes, D., and Kobbelt, L. 2015. Quantized global parametrization. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 6, 192.
8. Cannon, J. W., Floyd, W. J., Kenyon, R., Parry, W. R., et al. 1997. Hyperbolic geometry. Flavors of geometry 31, 59–115.
9. Conway, J. H., Burgiel, H., and Goodman-Strauss, C. 2008. The symmetries of things. A.K. Peters, Wellesley (Mass.).
10. Desbrun, M., Meyer, M., and Alliez, P. 2002. Intrinsic parameterizations of surface meshes. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 21, Wiley Online Library, 209–218.
11. Fisher, M., Springborn, B., Schröder, P., and Bobenko, A. I. 2007. An algorithm for the construction of intrinsic delaunay triangulations with applications to digital geometry processing. Computing 81, 2-3, 199–213.
12. Floater, M. 2003. One-to-one piecewise linear mappings over triangulations. Mathematics of Computation 72, 242, 685–696.
13. Floater, M. S. 2003. Mean value coordinates. Computer Aided Geometric Design 20, 1, 19–27.
14. Giorgi, D., Biasotti, S., and Paraboschi, L. 2007. SHREC: SHape REtrieval Contest: Watertight models track. http://watertight.ge.imati.cnr.it/.
15. Gortler, S. J., Gotsman, C., and Thurston, D. 2006. Discrete one-forms on meshes and applications to 3d mesh parameterization. Computer Aided Geometric Design 23, 2, 83–112.
16. Hormann, K., and Greiner, G. 2000. MIPS: An efficient global parametrization method. In Curve and Surface Design: Saint-Malo 1999, P.-J. Laurent, P. Sablonnière, and L. L. Schumaker, Eds., Innovations in Applied Mathematics. Vanderbilt University Press, Nashville, TN, 153–162.
17. Hormann, K., Lévy, B., and Sheffer, A. 2007. Mesh parameterization: Theory and practice video files associated with this course are available from the citation page. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Courses, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH ’07.
18. Jin, M., Kim, J., Luo, F., and Gu, X. 2008. Discrete surface ricci flow. Visualization and Computer Graphics, IEEE Transactions on 14, 5, 1030–1043.
19. Karcher, H. 1977. Riemannian center of mass and mollifier smoothing. Communications on pure and applied mathematics 30, 5, 509–541.
20. Kharevych, L., Springborn, B., and Schröder, P. 2006. Discrete conformal mappings via circle patterns. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 25, 2, 412–438.
21. Kim, V. G., Lipman, Y., and Funkhouser, T. 2011. Blended intrinsic maps. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (July), 79:1–79:12.
22. Kraevoy, V., and Sheffer, A. 2004. Cross-parameterization and compatible remeshing of 3d models. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug.), 861–869.
23. Lee, A. W. F., Dobkin, D., Sweldens, W., and Schröder, P. 1999. Multiresolution mesh morphing. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH ’99, 343–350.
24. Lipman, Y. 2012. Bounded distortion mapping spaces for triangular meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (July), 108:1–108:13.
25. Liu, Y.-J., Xu, C.-X., Fan, D., and He, Y. 2015. Efficient construction and simplification of delaunay meshes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 6, 174.
26. Lovász, L. 2004. Discrete analytic functions: an exposition. Surveys in differential geometry 9, 241–273.
27. Miller, C. E., Tucker, A. W., and Zemlin, R. A. 1960. Integer programming formulation of traveling salesman problems. Journal of the ACM (JACM) 7, 4, 326–329.
28. Myles, A., and Zorin, D. 2013. Controlled-distortion constrained global parametrization. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (July), 105:1–105:14.
29. Nguyen, A., Ben-Chen, M., Welnicka, K., Ye, Y., and Guibas, L. 2011. An optimization approach to improving collections of shape maps. Computer Graphics Forum 30, 5, 1481–1491. Cross Ref
30. Pinkall, U., and Polthier, K. 1993. Computing discrete minimal surfaces and their conjugates. Experimental Mathematics 2, 15–36. Cross Ref
31. Schreiner, J., Asirvatham, A., Praun, E., and Hoppe, H. 2004. Inter-surface mapping. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug.), 870–877.
32. Schüller, C., Kavan, L., Panozzo, D., and Sorkine-Hornung, O. 2013. Locally injective mappings. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 32, Wiley Online Library, 125–135.
33. Sheffer, A., Lévy, B., Mogilnitsky, M., and Bogomyakov, A. 2005. Abf++: fast and robust angle based flattening. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 24, 2, 311–330.
34. Sheffer, A., Praun, E., and Rose, K. 2006. Mesh parameterization methods and their applications. Found. Trends. Comput. Graph. Vis. 2, 2 (Jan.), 105–171.
35. Shi, R., Zeng, W., Su, Z., Damasio, H., Lu, Z., Wang, Y., Yau, S.-T., and Gu, X. 2013. Hyperbolic harmonic mapping for constrained brain surface registration. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2013 IEEE Conference on, 2531–2538.
36. Smith, J., and Schaefer, S. 2015. Bijective parameterization with free boundaries. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (July), 70:1–70:9.
37. Springborn, B., Schröder, P., and Pinkall, U. 2008. Conformal equivalence of triangle meshes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 27, 3, 77.
38. Stephenson, K. 2005. Introduction to circle packing: The theory of discrete analytic functions. Cambridge University Press.
39. Tsui, A., Fenton, D., Vuong, P., Hass, J., Koehl, P., Amenta, N., Coeurjolly, D., DeCarli, C., and Carmichael, O. 2013. Globally optimal cortical surface matching with exact landmark correspondence. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, IPMI’13, 487–498.
40. Tutte, W. T. 1963. How to draw a graph. Proc. London Math. Soc 13, 3, 743–768. Cross Ref
41. Weber, O., and Zorin, D. 2014. Locally injective parametrization with arbitrary fixed boundaries. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 4, 75.