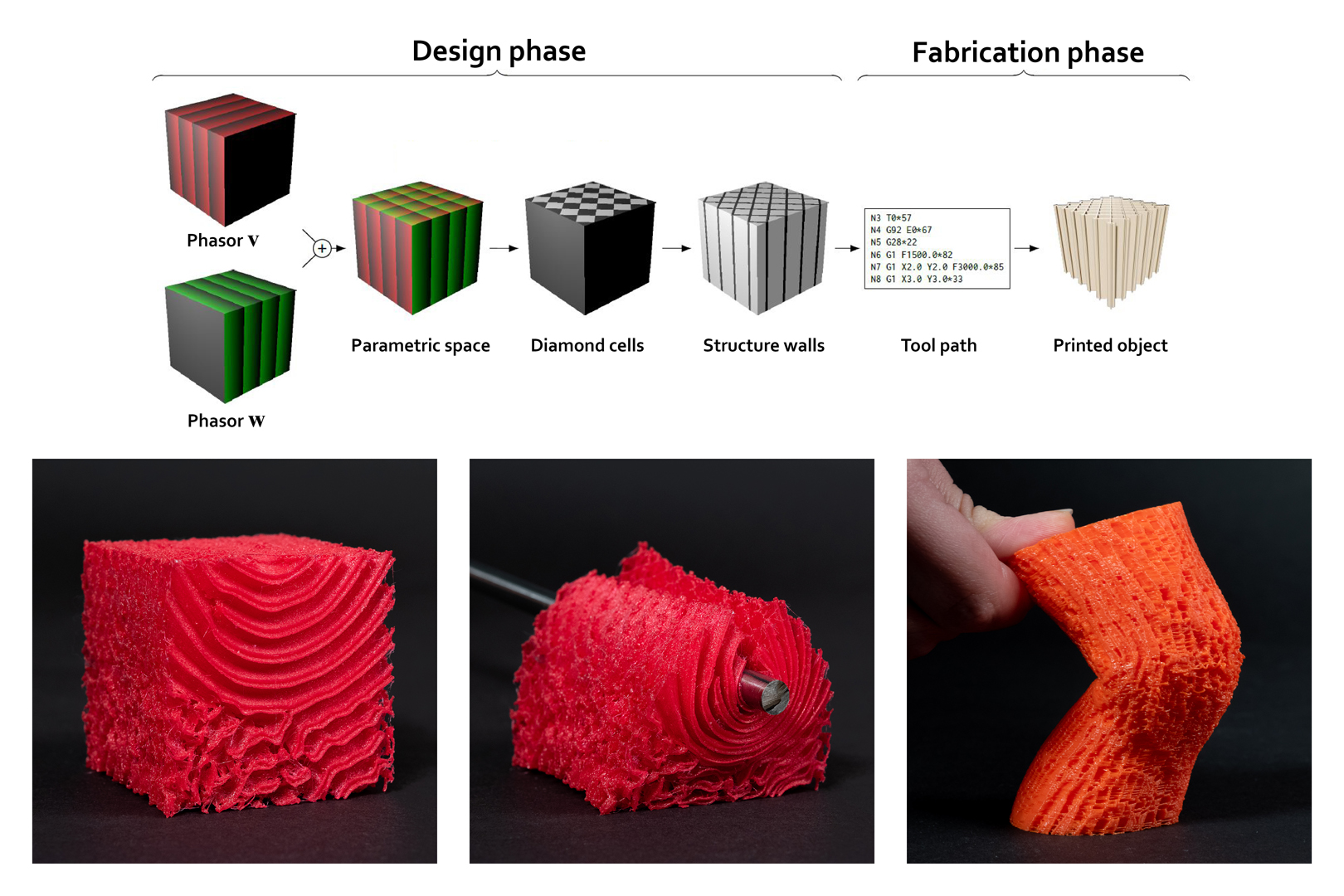
“Freely orientable microstructures for designing deformable 3D prints” by Tricard, Tavernier, Zanni, Martínez, Hugron, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Freely orientable microstructures for designing deformable 3D prints
Session/Category Title:
- Fabrication: Computational Design
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
Nature offers a marvel of astonishing and rich deformation behaviors. Yet, most of the objects we fabricate are comparatively rather inexpressive, either rigid or exhibiting simple homogeneous deformations when interacted with.We explore the synthesis and fabrication of novel microstructures that mimic the effects of having oriented rigid fibers in an otherwise flexible material: the result is extremely rigid along a transverse direction while being comparatively very flexible in the locally orthogonal plane. By allowing free gradation of the rigidity direction orientation within the object, the microstructures can be designed such that, under deformation, distances along fibers in the volume are preserved while others freely change. Through a simple painting tool, this allows a designer to influence the way the volume reshapes when deformed, and results in a wide range of novel possibilities. Many gradations are possible: local free orientation of the fibers; local control of the overall material rigidity (structure density); local canceling of the effect of the fibers, obtaining a more isotropic material.Our algorithm to synthesize the structures builds upon procedural texturing. It produces a cellular geometry that can be fabricated reliably despite 3D printing walls at a minimal thickness, allowing prints to be very flexible. The synthesis algorithm is efficient and scales to large volumes.
References:
1. Niels Aage, Erik Andreassen, Boyan S Lazarov, and Ole Sigmund. 2017. Giga-voxel computational morphogenesis for structural design. Nature 550, 7674 (2017), 84. Google ScholarCross Ref
2. M.F Ashby. 2006. The properties of foams and lattices. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A 364, 1838 (2006), 15–30. Google ScholarCross Ref
3. David Bommes, Bruno Lévy, Nico Pietroni, Enrico Puppo, Claudio Silva, Marco Tarini, and Denis Zorin. 2013. Quad-Mesh Generation and Processing: A Survey. Comput. Graph. Forum 32, 6 (2013), 51–76. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. James Brennan-Craddock. 2011. The Investigation of a Method to Generate Conformal Lattice Structures for Additive Manufacturing. Ph.D. Dissertation. Loughborough Univ.Google Scholar
5. Yong Chen. 2007. 3D Texture Mapping for Rapid Manufacturing. Computer-Aided Design and Applications 4, 6 (2007), 761–771. Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Zuenko Evgeny and Matthias Harders. 2019. Wrinkles, Folds, Creases, Buckles: Small-Scale Surface Deformations as Periodic Functions on 3D Meshes. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. PP (05 2019), 1–1. Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Marc L.M. François, Letian Chen, and Michel Coret. 2017. Elasticity and symmetry of triangular lattice materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 129, Supplement C (2017), 18–27. Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Oleg Fryazinov, Turlif Vilbrandt, and Alexander Pasko. 2013. Multi-Scale Space-Variant FRep Cellular Structures. Computer-Aided Design 45, 1 (2013), 26–34. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Xifeng Gao, Wenzel Jakob, Marco Tarini, and Daniele Panozzo. 2017. Robust HexDominant Mesh Generation Using Field-Guided Polyhedral Agglomeration. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 4 (2017), 1–13. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Perle Geoffroy-Donders, Grégoire Allaire, and Olivier Pantz. 2020. 3-d topology optimization of modulated and oriented periodic microstructures by the homogenization method. J. Comput. Phys. 401 (2020), 108994. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Lorna J Gibson and Michael F Ashby. 1999. Cellular solids: structure and properties. Cambridge university press.Google Scholar
12. Alexander Goldberg, Matthias Zwicker, and Frédo Durand. 2008. Anisotropic Noise. ACM Transactions on Graphics 27, 3 (Aug. 2008), 1–8. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Jeroen P Groen, Florian C Stutz, Niels Aage, Jakob A Bærentzen, and Ole Sigmund. 2020. De-homogenization of optimal multi-scale 3D topologies. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 364 (2020), 112979.Google ScholarCross Ref
14. Alexandra Ion, Johannes Frohnhofen, Ludwig Wall, Robert Kovacs, Mirela Alistar, Jack Lindsay, Pedro Lopes, Hsiang-Ting Chen, and Patrick Baudisch. 2016. Metamaterial Mechanisms. In UIST ’16. 529–539.Google Scholar
15. Wenzel Jakob, Marco Tarini, Daniele Panozzo, and Olga Sorkine-Hornung. 2015. Instant Field-Aligned Meshes. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 6 (Nov. 2015), 1–15. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Robert M Jones. 1975. Mechanics of Composite Materials. Vol. 193. Scripta Book Company Washington, DC.Google Scholar
17. Felix Knöppel, Keenan Crane, Ulrich Pinkall, and Peter Schröder. 2015. Stripe Patterns on Surfaces. ACM Trans Graph. 34, 4 (2015). Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Tim Kuipers, Eugeni L. Doubrovski, Jun Wu, and Charlie C. L. Wang. 2020. A framework for adaptive width control of dense contour-parallel toolpaths in fused deposition modeling. arXiv:cs.GR/2004.13497Google Scholar
19. Tim Kuipers, Jun Wu, and Charlie C.L. Wang. 2019. CrossFill: Foam Structures with Graded Density for Continuous Material Extrusion. Computer-Aided Design 114 (2019), 37 — 50. Google ScholarCross Ref
20. Ares Lagae, Sylvain Lefebvre, Rob Cook, Tony Derose, George Drettakis, David S. Ebert, J.P. Lewis, Ken Perlin, and Matthias Zwicker. 2010a. A Survey of Procedural Noise Functions. Computer Graphics Forum 29, 8 (2010), 2579–2600.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. Ares Lagae, Sylvain Lefebvre, Rob Cook, Tony DeRose, George Drettakis, D. S. Ebert, J. P. Lewis, Ken Perlin, and Matthias Zwicker. 2010b. A Survey of Procedural Noise Functions. Computer Graphics Forum 29, 8 (2010), 2579–2600. Google ScholarCross Ref
22. Ares Lagae, Sylvain Lefebvre, George Drettakis, and Philip Dutré. 2009. Procedural Noise using Sparse Gabor Convolution. ACM Transactions on Graphics 28, 3 (2009), 54–64. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. J. P. Lewis. 1989. Algorithms for Solid Noise Synthesis. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. 263–270. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Dawei Li, Ning Dai, Xiaotong Jiang, and Xiaosheng Chen. 2015. Interior Structural Optimization Based on the Density-Variable Shape Modeling of 3D Printed Objects. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 83, 9 (2015), 1627–1635. Google ScholarCross Ref
25. Nils Lichtenberg, Noeska Smit, Christian Hansen, and Kai Lawonn. 2018. Real-time field aligned stripe patterns. Computers & Graphics 74 (Aug. 2018), 137–149. Google ScholarCross Ref
26. Marco Livesu, Stefano Ellero, Jonàs Martínez, Sylvain Lefebvre, and Marco Attene. 2017. From 3D Models to 3D Prints: An Overview of the Processing Pipeline. Computer Graphics Forum 36 (2017), 537–564. Google ScholarCross Ref
27. S.K. Maiti, M.F. Ashby, and L.J. Gibson. 1984. Fracture toughness of brittle cellular solids. Scripta Metallurgica 18, 3 (1984), 213 — 217. Google ScholarCross Ref
28. Jonàs Martínez, Jérémie Dumas, and Sylvain Lefebvre. 2016. Procedural Voronoi Foams for Additive Manufacturing. ACM Transactions on Graphics 35, 4 (2016), 44:1–44:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Jonàs Martínez, Samuel Hornus, Haichuan Song, and Sylvain Lefebvre. 2018. Polyhedral Voronoi diagrams for additive manufacturing. ACM Transactions on Graphics 37, 4 (2018), 15. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Jonàs Martínez, Haichuan Song, Jérémie Dumas, and Sylvain Lefebvre. 2017. Orthotropic k-nearest foams for additive manufacturing. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 4 (2017), 1–12. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Asla Medeiros e Sá, Vinícius Moreira Mello, Karina Rodriguez Echavarria, and Derek Covill. 2015. Adaptive voids. The Visual Computer 31, 6 (2015), 799–808.Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Jean-Claude Michel, Hervé Moulinec, and P Suquet. 1999. Effective properties of composite materials with periodic microstructure: a computational approach. Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering 172, 1–4 (1999), 109–143. Google ScholarCross Ref
33. Fabrice Neyret and Eric Heitz. 2016. Understanding and controlling contrast oscillations in stochastic texture algorithms using Spectrum of Variance. Research Report. LJK / Grenoble University – INRIA. 8 pages.Google Scholar
34. nTopology. 2019. nTop design platform. https://ntopology.com.Google Scholar
35. Julian Panetta, Abtin Rahimian, and Denis Zorin. 2017. Worst-case Stress Relief for Microstructures. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 4 (2017), 122:1–122:16. Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Julian Panetta, Qingnan Zhou, Luigi Malomo, Nico Pietroni, Paolo Cignoni, and Denis Zorin. 2015. Elastic Textures for Additive Fabrication. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 4 (2015), 135:1–135:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Olivier Pantz and Karim Trabelsi. 2008. A Post-Treatment of the Homogenization Method for Shape Optimization. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 47, 3 (2008), 1380–1398. Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Alexander Pasko, Oleg Fryazinov, Turlif Vilbrandt, Pierre-Alain Fayolle, and Valery Adzhiev. 2011. Procedural function-based modelling of volumetric microstructures. Graphical Models 73, 5 (2011), 165–181. Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Minh-Son Pham, Chen Liu, Iain Todd, and Jedsada Lertthanasarn. 2019. Damage-tolerant architected materials inspired by crystal microstructure. Nature 565, 7739 (2019), 305. Google ScholarCross Ref
40. Carlos M Portela, A Vidyasagar, Sebastian Krödel, Tamara Weissenbach, Daryl W Yee, Julia R Greer, and Dennis M Kochmann. 2020. Extreme mechanical resilience of self-assembled nanolabyrinthine materials. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117, 11 (2020), 5686–5693. Google ScholarCross Ref
41. Nicolas Ray, Wan Chiu Li, Bruno Lévy, Alla Sheffer, and Pierre Alliez. 2006. Periodic Global Parameterization. ACM Trans. Graph. 25 (2006), 1460–1485. Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Christian Schumacher, Bernd Bickel, Jan Rys, Steve Marschner, Chiara Daraio, and Markus Gross. 2015. Microstructures to Control Elasticity in 3D Printing. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 4 (2015), 136:1–136:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
43. Christian Schumacher, Steve Marschner, Markus Cross, and Bernhard Thomaszewski. 2018. Mechanical Characterization of Structured Sheet Materials. ACM Transactions on Graphics 37, 4, Article 148 (July 2018), 15 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
44. Lucas A. Shaw, Frederick Sun, Carlos M. Portela, Rodolfo I. Barranco, Julia R. Greer, and Jonathan B. Hopkins. 2019. Computationally efficient design of directionally compliant metamaterials. Nature Communications 10 (2019). Google ScholarCross Ref
45. Kumar Siddhant, Stephanie Tan, Zheng Li, and Dennis M Kochmann. 2020. Inverse-designed spinodoid metamaterials. npj Computational Materials 6, 1 (2020). Google ScholarCross Ref
46. Emmanuel Siéfert, Etienne Reyssat, José Bico, and Benoît Roman. 2019. Bio-inspired pneumatic shape-morphing elastomers. Nature Materials 18 (01 2019). Google ScholarCross Ref
47. M.G. Tarantino, O. Zerhouni, and K. Danas. 2019. Random 3D-printed isotropic composites with high volume fraction of pore-like polydisperse inclusions and near-optimal elastic stiffness. Acta Materialia 175 (2019), 331 — 340. Google ScholarCross Ref
48. Thibault Tricard, Semyon Efremov, Cédric Zanni, Fabrice Neyret, Jonàs Martínez, and Sylvain Lefebvre. 2019. Procedural Phasor Noise. ACM Transactions on Graphics 38, 4 (July 2019), 57:1–13. Google ScholarDigital Library
49. Kiril Vidimče, Szu-Po Wang, Jonathan Ragan-Kelley, and Wojciech Matusik. 2013. Open-Fab: A Programmable Pipeline for Multi-material Fabrication. ACM Transactions on Graphics 32, 4 (2013), 136:1–136:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
50. Hongqing Wang, Yong Chen, and David W Rosen. 2005. A hybrid geometric modeling method for large scale conformal cellular structures. In ASME 2005 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. 421–427.Google ScholarCross Ref
51. Jun Wu, Niels Aage, Rüdiger Westermann, and Ole Sigmund. 2018. Infill Optimization for Additive Manufacturing-Approaching Bone-Like Porous Structures. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 24, 2 (2018), 1127–1140. Google ScholarCross Ref
52. Jun Wu, Charlie C.L. Wang, Xiaoting Zhang, and Rüdiger Westermann. 2016. Self-supporting rhombic infill structures for additive manufacturing. Computer-Aided Design 80 (2016), 32–42. Google ScholarCross Ref
53. Jun Wu, Weiming Wang, and Xifeng Gao. 2019. Design and Optimization of Conforming Lattice Structures. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. (2019), 1–1. Google ScholarDigital Library
54. Bo Zhu, Mélina Skouras, Desai Chen, and Wojciech Matusik. 2017. Two-Scale Topology Optimization with Microstructures. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 5 (2017), 1. Google ScholarDigital Library