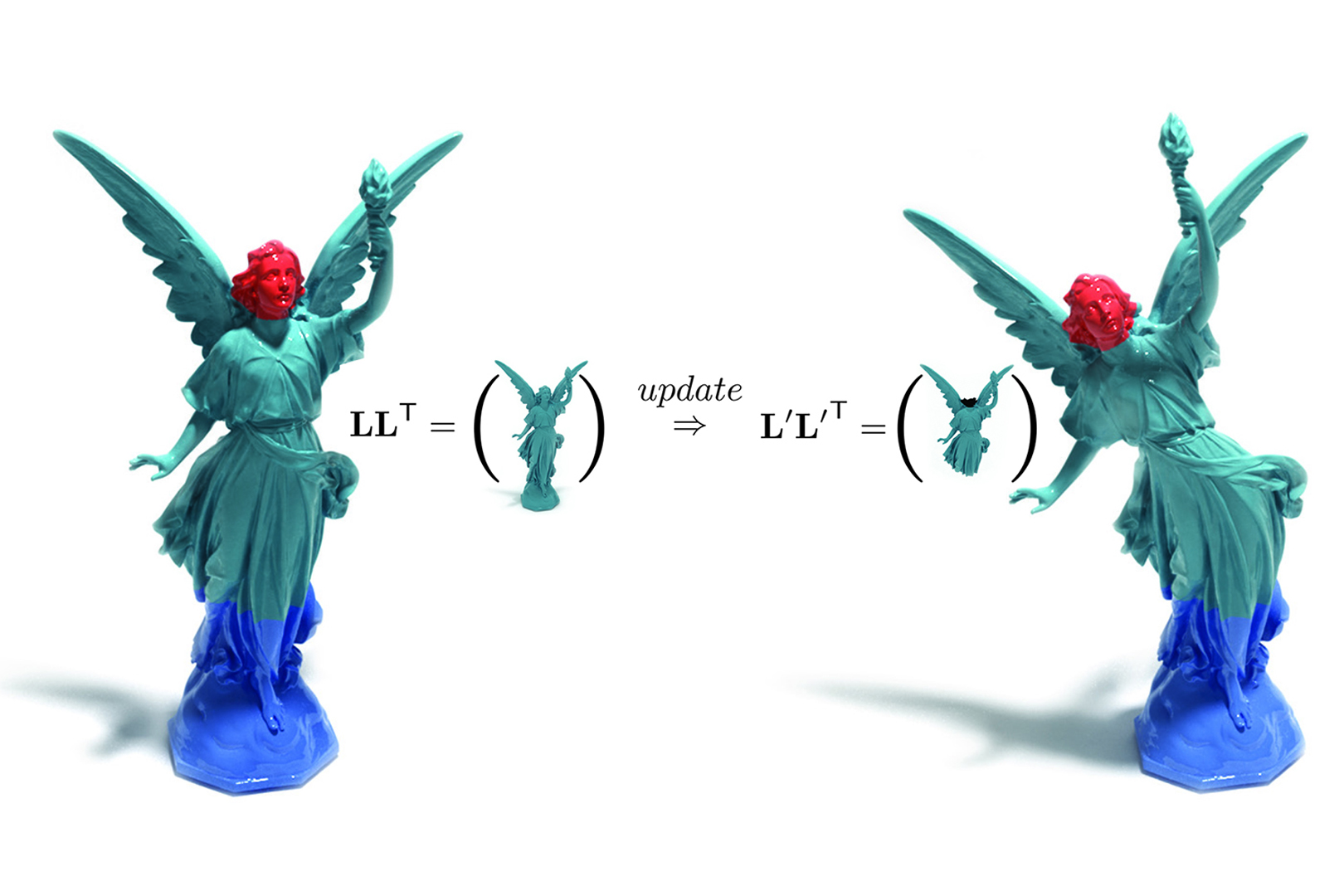
“Factor once: reusing cholesky factorizations on sub-meshes”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Factor once: reusing cholesky factorizations on sub-meshes
Session/Category Title:
- Nets, cages and meshes
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
A common operation in geometry processing is solving symmetric and positive semi-definite systems on a subset of a mesh, with conditions for the vertices at the boundary of the region. This is commonly done by setting up the linear system for the sub-mesh, factorizing the system (potentially applying preordering to improve sparseness of the factors), and then solving by back-substitution. This approach suffers from a comparably high setup cost for each local operation. We propose to reuse factorizations defined on the full mesh to solve linear problems on sub-meshes. We show how an update on sparse matrices can be performed in a particularly efficient way to obtain the factorization of the operator on a sun-mesh significantly outperforming general factor updates and complete refactorization. We analyze the resulting speedup for a variety of situations and demonstrate that our method outperforms factorization of a new matrix by a factor of up to 10 while never being slower in our experiments.
References:
1. 2009. Intel Math Kernel Library. Reference Manual. Intel Corporation.Google Scholar
2. Mario Botsch and Olga Sorkine. 2008. On Linear Variational Surface Deformation Methods. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 14, 1 (Jan 2008), 213–230. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Sofien Bouaziz, Mario Deuss, Yuliy Schwartzburg, Thibaut Weise, and Mark Pauly. 2012. Shape-Up: Shaping Discrete Geometry with Projections. Computer Graphics Forum 31, 5 (2012), 1657–1667. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Yanqing Chen, Timothy A Davis, William W Hager, and Sivasankaran Rajamanickam. 2008. Algorithm 887: CHOLMOD, supernodal sparse Cholesky factorization and update/downdate. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS) 35, 3 (2008), 22. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Keenan Crane, Clarisse Weischedel, and Max Wardetzky. 2013. Geodesics in Heat: A New Approach to Computing Distance Based on Heat Flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 5, Article 152 (Oct. 2013), 11 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. T. Davis and W. Hager. 1999. Modifying a Sparse Cholesky Factorization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 20, 3 (1999), 606–627. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. T. A. Davis. 2006. Direct Methods for Sparse Linear Systems. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA. Google Scholar
8. Timothy A. Davis and William W. Hager. 2000. Multiple-Rank Modifications of a Sparse Cholesky Factorization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 22, 4 (July 2000), 997–1013. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Timothy A. Davis and William W. Hager. 2009. Dynamic Supernodesin Sparse Cholesky Update/Downdate and Triangular Solves. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 35, 4, Article 27 (Feb. 2009), 23 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Mathieu Desbrun, Mark Meyer, and Pierre Alliez. 2002. Intrinsic Parameterizations of Surface Meshes. Computer Graphics Forum 21, 3 (2002), 209–218.Google ScholarCross Ref
11. Mathieu Desbrun, Mark Meyer, Peter Schröder, and Alan H. Barr. 1999. Implicit Fairing of Irregular Meshes Using Diffusion and Curvature Flow. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’99). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, 317–324. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Gaël Guennebaud, Benoît Jacob, et al. 2010. Eigen v3. http://eigen.tuxfamily.org.Google Scholar
13. Florian Hecht, Yeon Jin Lee, Jonathan R. Shewchuk, and James F. O’Brien. 2012. Updated Sparse Cholesky Factors for Corotational Elastodynamics. ACM Transactions on Graphics 31, 5 (oct 2012), 123:1–13. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Philipp Herholz, Timothy A. Davis, and Marc Alexa. 2017. Localized Solutions of Sparse Linear Systems for Geometry Processing. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6, Article 183 (Nov. 2017), 8 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. George Karypis and Vipin Kumar. 1998. A fast and high quality multilevel scheme for partitioning irregular graphs. SIAM Journal on scientific Computing 20, 1 (1998), 359–392. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Joseph W.H. Liu. 1990. The Role of Elimination Trees in Sparse Factorization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 11, 1 (1990), 134–172. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Mark Meyer, Mathieu Desbrun, Peter Schröder, and Alan H. Barr. 2003. Discrete Differential-Geometry Operators for Triangulated 2-Manifolds. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 35–57.Google Scholar
18. Patrick Mullen, Yiying Tong, Pierre Alliez, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2008. Spectral Conformal Parameterization. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Geometry Processing (SGP ’08). Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland, Switzerland, 1487–1494. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1731309.1731335 Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Ulrich Pinkall and Konrad Polthier. 1993. Computing discrete minimal surfaces and their conjugates. Experim. Math. 2 (1993), 15–36.Google ScholarCross Ref
20. Olga Sorkine and Marc Alexa. 2007. As-rigid-as-possible Surface Modeling. In Proceedings of the Fifth Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (SGP ’07). Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland, Switzerland, 109–116. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Olga Sorkine and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2004. Least-Squares Meshes. In Proceedings of the Shape Modeling International 2004 (SMI ’04). IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA, 191–199. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Olga Sorkine, Daniel Cohen-Or, Yaron Lipman, Marc Alexa, Christian Rössl, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2004. Laplacian Surface Editing. In Proceedings of the 2004 Eurographics/ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Geometry Processing (SGP ’04). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 175–184. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Yu-Hong Yeung, Jessica Crouch, and Alex Pothen. 2016. Interactively Cutting and Constraining Vertices in Meshes Using Augmented Matrices. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 2, Article 18 (Feb. 2016), 17 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library