“Face identity disentanglement via latent space mapping” by Nitzan, Bermano, Li and Cohen-Or
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Face identity disentanglement via latent space mapping
Session/Category Title:
- Image Synthesis with Generative Models
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
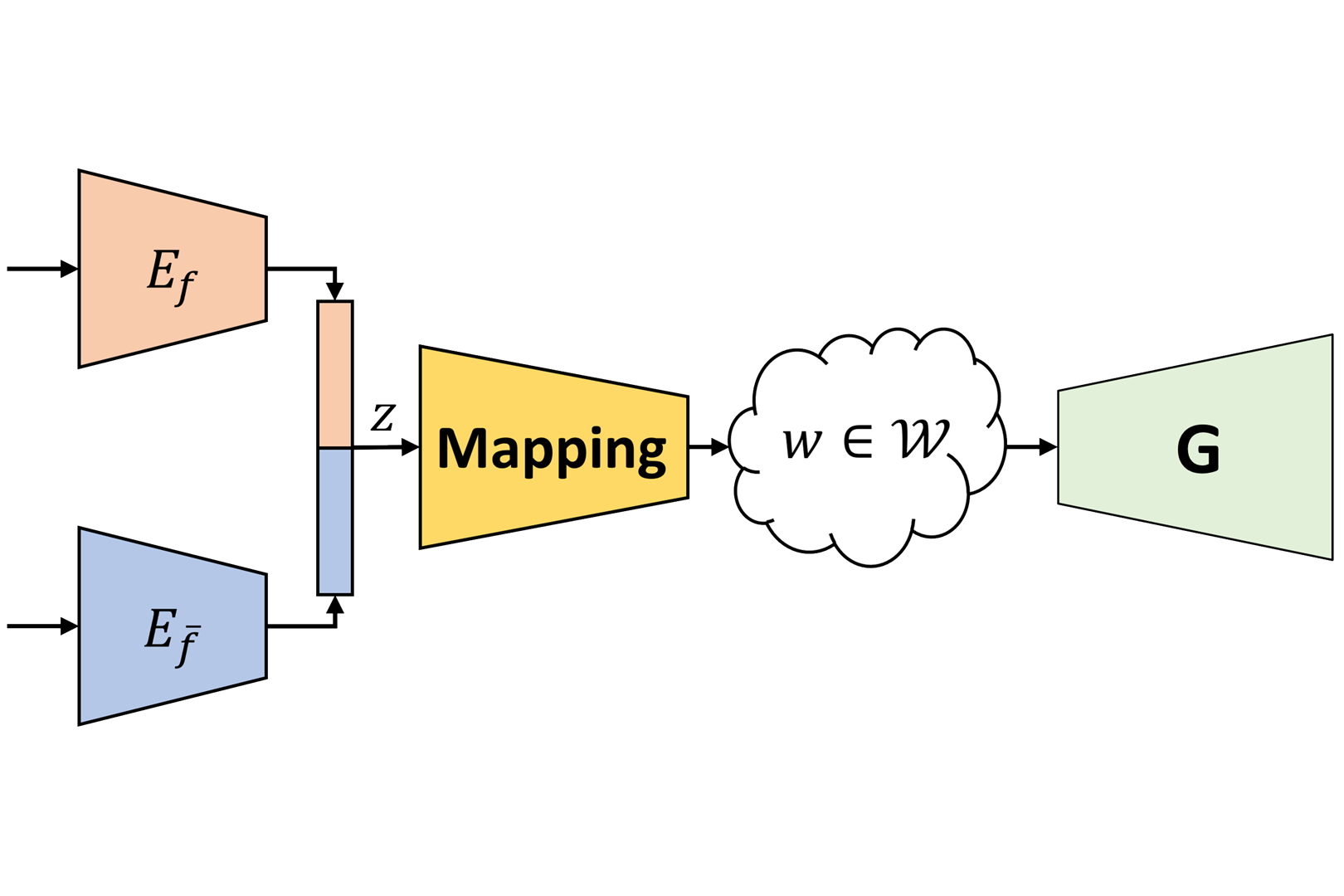
Learning disentangled representations of data is a fundamental problem in artificial intelligence. Specifically, disentangled latent representations allow generative models to control and compose the disentangled factors in the synthesis process. Current methods, however, require extensive supervision and training, or instead, noticeably compromise quality.In this paper, we present a method that learns how to represent data in a disentangled way, with minimal supervision, manifested solely using available pre-trained networks. Our key insight is to decouple the processes of disentanglement and synthesis, by employing a leading pre-trained unconditional image generator, such as StyleGAN. By learning to map into its latent space, we leverage both its state-of-the-art quality, and its rich and expressive latent space, without the burden of training it.We demonstrate our approach on the complex and high dimensional domain of human heads. We evaluate our method qualitatively and quantitatively, and exhibit its success with de-identification operations and with temporal identity coherency in image sequences. Through extensive experimentation, we show that our method successfully disentangles identity from other facial attributes, surpassing existing methods, even though they require more training and supervision.
References:
1. Rameen Abdal, Yipeng Qin, and Peter Wonka. 2019. Image2StyleGAN: How to Embed Images Into the StyleGAN Latent Space?. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 4432–4441.Google ScholarCross Ref
2. Kfir Aberman, Rundi Wu, Dani Lischinski, Baoquan Chen, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2019. Learning character-agnostic motion for motion retargeting in 2D. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.01680 (2019).Google Scholar
3. Naphtali Abudarham, Lior Shkiller, and Galit Yovel. 2019. Critical features for face recognition. Cognition 182 (2019), 73–83.Google ScholarCross Ref
4. Hadar Averbuch-Elor, Daniel Cohen-Or, Johannes Kopf, and Michael F. Cohen. 2017. Bringing Portraits to Life. ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceeding of SIGGRAPH Asia 2017) 36, 6 (2017), 196.Google Scholar
5. Jianmin Bao, Dong Chen, Fang Wen, Houqiang Li, and Gang Hua. 2018. Towards open-set identity preserving face synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 6713–6722.Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Baylies. 2019. stylegan-encoder. https://github.com/pbaylies/stylegan-encoder. Accessed: April 2020.Google Scholar
7. Yoshua Bengio, Aaron Courville, and Pascal Vincent. 2013. Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 35, 8 (2013), 1798–1828.Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Diane Bouchacourt, Ryota Tomioka, and Sebastian Nowozin. 2018. Multi-level variational autoencoder: Learning disentangled representations from grouped observations. In Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Google Scholar
9. Qiong Cao, Li Shen, Weidi Xie, Omkar M Parkhi, and Andrew Zisserman. 2018. Vggface2: A dataset for recognising faces across pose and age. In 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018). IEEE, 67–74.Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Xi Chen, Yan Duan, Rein Houthooft, John Schulman, Ilya Sutskever, and Pieter Abbeel. 2016. Infogan: Interpretable representation learning by information maximizing generative adversarial nets. In Advances in neural information processing systems. 2172–2180.Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Yunjey Choi, Minje Choi, Munyoung Kim, Jung-Woo Ha, Sunghun Kim, and Jaegul Choo. 2018. Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 8789–8797.Google ScholarCross Ref
12. Yunjey Choi, Youngjung Uh, Jaejun Yoo, and Jung-Woo Ha. 2019. StarGAN v2: Diverse Image Synthesis for Multiple Domains. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.01865 (2019).Google Scholar
13. Antonia Creswell and Anil Anthony Bharath. 2018. Inverting the generator of a generative adversarial network. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems 30, 7 (2018), 1967–1974.Google Scholar
14. deepfakes. 2019. faceswap. https://github.com/deepfakes/faceswap. Accessed: April 2020.Google Scholar
15. Jiankang Deng, Jia Guo, Niannan Xue, and Stefanos Zafeiriou. 2019. Arcface: Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 4690–4699.Google ScholarCross Ref
16. Emily Denton, Ben Hutchinson, Margaret Mitchell, and Timnit Gebru. 2019. Detecting bias with generative counterfactual face attribute augmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.06439 (2019).Google Scholar
17. Emily L Denton et al. 2017. Unsupervised learning of disentangled representations from video. In Advances in neural information processing systems. 4414–4423.Google Scholar
18. Zhen-Hua Feng, Josef Kittler, Muhammad Awais, Patrik Huber, and Xiao-Jun Wu. 2018. Wing loss for robust facial landmark localisation with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2235–2245.Google ScholarCross Ref
19. Aviv Gabbay and Yedid Hoshen. 2019. Demystifying Inter-Class Disentanglement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.11796 (2019).Google Scholar
20. Oran Gafni, Lior Wolf, and Yaniv Taigman. 2019. Live Face De-Identification in Video. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 9378–9387.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. Lore Goetschalckx, Alex Andonian, Aude Oliva, and Phillip Isola. 2019. GANalyze: Toward Visual Definitions of Cognitive Image Properties. arXiv:cs.CV/1906.10112Google Scholar
22. Ian Goodfellow, Jean Pouget-Abadie, Mehdi Mirza, Bing Xu, David Warde-Farley, Sherjil Ozair, Aaron Courville, and Yoshua Bengio. 2014. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27, Z. Ghahramani, M. Welling, C. Cortes, N. D. Lawrence, and K. Q. Weinberger (Eds.). Curran Associates, Inc., 2672–2680. http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5423-generative-adversarial-nets.pdfGoogle ScholarDigital Library
23. Naama Hadad, Lior Wolf, and Moni Shahar. 2018. A two-step disentanglement method. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 772–780.Google ScholarCross Ref
24. Erik Härkönen, Aaron Hertzmann, Jaakko Lehtinen, and Sylvain Paris. 2020. GANSpace: Discovering Interpretable GAN Controls. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.02546 (2020).Google Scholar
25. Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. 2015. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 1026–1034.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 770–778.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Martin Heusel, Hubert Ramsauer, Thomas Unterthiner, Bernhard Nessler, and Sepp Hochreiter. 2017. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In Advances in neural information processing systems. 6626–6637.Google Scholar
28. Irina Higgins, Loic Matthey, Arka Pal, Christopher Burgess, Xavier Glorot, Matthew Botvinick, Shakir Mohamed, and Alexander Lerchner. 2017. beta-VAE: Learning Basic Visual Concepts with a Constrained Variational Framework. Iclr 2, 5 (2017), 6.Google Scholar
29. Huaibo Huang, Ran He, Zhenan Sun, Tieniu Tan, et al. 2018. Introvae: Introspective variational autoencoders for photographic image synthesis. In Advances in neural information processing systems. 52–63.Google Scholar
30. Xun Huang and Serge Belongie. 2017. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 1501–1510.Google ScholarCross Ref
31. Ali Jahanian, Lucy Chai, and Phillip Isola. 2019. On the “steerability” of generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.07171 (2019).Google Scholar
32. Justin Johnson, Alexandre Alahi, and Li Fei-Fei. 2016. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In European conference on computer vision. Springer, 694–711.Google ScholarCross Ref
33. Tero Karras, Timo Aila, Samuli Laine, and Jaakko Lehtinen. 2017. Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196 (2017).Google Scholar
34. Tero Karras, Samuli Laine, and Timo Aila. 2019b. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 4401–4410.Google ScholarCross Ref
35. Tero Karras, Samuli Laine, Miika Aittala, Janne Hellsten, Jaakko Lehtinen, and Timo Aila. 2019a. Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.04958 (2019).Google Scholar
36. Hyeongwoo Kim, Pablo Garrido, Ayush Tewari, Weipeng Xu, Justus Thies, Matthias Nießner, Patrick Pérez, Christian Richardt, Michael Zollhöfer, and Christian Theobalt. 2018. Deep video portraits. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 1–14.Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Hyunjik Kim and Andriy Mnih. 2018. Disentangling by factorising. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.05983 (2018).Google Scholar
38. Davis E. King. 2009. Dlib-ml: A Machine Learning Toolkit. Journal of Machine Learning Research 10 (2009), 1755–1758.Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Diederik P. Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2015. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, May 7–9, 2015, Conference Track Proceedings, Yoshua Bengio and Yann LeCun (Eds.). http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980Google Scholar
40. Lingzhi Li, Jianmin Bao, Hao Yang, Dong Chen, and Fang Wen. 2019. FaceShifter: Towards High Fidelity And Occlusion Aware Face Swapping. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.13457 (2019).Google Scholar
41. Zachary C Lipton and Subarna Tripathi. 2017. Precise recovery of latent vectors from generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.04782 (2017).Google Scholar
42. Ming-Yu Liu, Thomas Breuel, and Jan Kautz. 2017. Unsupervised image-to-image translation networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems. 700–708.Google Scholar
43. Yu Liu, Fangyin Wei, Jing Shao, Lu Sheng, Junjie Yan, and Xiaogang Wang. 2018. Exploring disentangled feature representation beyond face identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2080–2089.Google ScholarCross Ref
44. Francesco Locatello, Stefan Bauer, Mario Lucic, Gunnar Rätsch, Sylvain Gelly, Bernhard Schölkopf, and Olivier Bachem. 2018. Challenging common assumptions in the un-supervised learning of disentangled representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.12359 (2018).Google Scholar
45. Junyu Luo, Yong Xu, Chenwei Tang, and Jiancheng Lv. 2017. Learning inverse mapping by autoencoder based generative adversarial nets. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Springer, 207–216.Google ScholarCross Ref
46. Emile Mathieu, Tom Rainforth, N. Siddharth, and Yee Whye Teh. 2018. Disentangling Disentanglement in Variational Autoencoders. arXiv:stat.ML/1812.02833Google Scholar
47. Lars Mescheder, Andreas Geiger, and Sebastian Nowozin. 2018. Which training methods for GANs do actually converge? arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.04406 (2018).Google Scholar
48. Masahiro Mori et al. 1970. The uncanny valley. Energy 7, 4 (1970), 33–35.Google Scholar
49. Yuval Nirkin, Yosi Keller, and Tal Hassner. 2019. Fsgan: Subject agnostic face swapping and reenactment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 7184–7193.Google ScholarCross Ref
50. Guim Perarnau, Joost Van De Weijer, Bogdan Raducanu, and Jose M Álvarez. 2016. Invertible conditional gans for image editing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.06355 (2016).Google Scholar
51. Stanislav Pidhorskyi, Donald A Adjeroh, and Gianfranco Doretto. 2020. Adversarial Latent Autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). [to appear].Google ScholarCross Ref
52. Albert Pumarola, Antonio Agudo, Aleix M Martinez, Alberto Sanfeliu, and Francesc Moreno-Noguer. 2018. Ganimation: Anatomically-aware facial animation from a single image. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). 818–833.Google ScholarCross Ref
53. Scott E Reed, Yi Zhang, Yuting Zhang, and Honglak Lee. 2015. Deep visual analogy-making. In Advances in neural information processing systems. 1252–1260.Google Scholar
54. Elad Richardson, Yuval Alaluf, Or Patashnik, Yotam Nitzan, Yaniv Azar, Stav Shapiro, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2020. Encoding in Style: a StyleGAN Encoder for Image-to-Image Translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.00951 (2020).Google Scholar
55. Omry Sendik, Dani Lischinski, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2019. What’s in a Face? Metric Learning for Face Characterization. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 38. Wiley Online Library, 405–416.Google Scholar
56. Yujun Shen, Jinjin Gu, Xiaoou Tang, and Bolei Zhou. 2019. Interpreting the latent space of gans for semantic face editing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.10786 (2019).Google Scholar
57. Yujun Shen, Ping Luo, Junjie Yan, Xiaogang Wang, and Xiaoou Tang. 2018. Faceidgan: Learning a symmetry three-player gan for identity-preserving face synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 821–830.Google ScholarCross Ref
58. Pawan Sinha and Tomaso Poggio. 1996. I think I know that face… Nature 384, 6608 (1996), 404–404.Google ScholarCross Ref
59. Qianru Sun, Ayush Tewari, Weipeng Xu, Mario Fritz, Christian Theobalt, and Bernt Schiele. 2018. A hybrid model for identity obfuscation by face replacement. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). 553–569.Google ScholarDigital Library
60. Christian Szegedy, Vincent Vanhoucke, Sergey Ioffe, Jon Shlens, and Zbigniew Wojna. 2016. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2818–2826.Google ScholarCross Ref
61. Ayush Tewari, Mohamed Elgharib, Gaurav Bharaj, Florian Bernard, Hans-Peter Seidel, Patrick Pérez, Michael Zollhöfer, and Christian Theobalt. 2020. StyleRig: Rigging StyleGAN for 3D Control over Portrait Images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.00121 (2020).Google Scholar
62. Justus Thies, Michael Zollhofer, Marc Stamminger, Christian Theobalt, and Matthias Nießner. 2016. Face2face: Real-time face capture and reenactment of rgb videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2387–2395.Google ScholarDigital Library
63. Justus Thies, Michael Zollhöfer, Christian Theobalt, Marc Stamminger, and Matthias Nießner. 2018. Headon: Real-time reenactment of human portrait videos. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4 (2018), 1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
64. Yu Tian, Xi Peng, Long Zhao, Shaoting Zhang, and Dimitris N Metaxas. 2018. CRGAN: learning complete representations for multi-view generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.11191 (2018).Google Scholar
65. Umar Toseeb, David RT Keeble, and Eleanor J Bryant. 2012. The significance of hair for face recognition. PloS one 7, 3 (2012).Google Scholar
66. Michael Tschannen, Olivier Bachem, and Mario Lucic. 2018. Recent advances in autoencoder-based representation learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.05069 (2018).Google Scholar
67. Yifan Wu, Fan Yang, and Haibin Ling. 2018. Privacy-protective-gan for face deidentification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.08906 (2018).Google Scholar
68. Fanyi Xiao, Haotian Liu, and Yong Jae Lee. 2019. Identity from here, Pose from there: Self-supervised Disentanglement and Generation of Objects using Unlabeled Videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 7013–7022.Google ScholarCross Ref
69. Egor Zakharov, Aliaksandra Shysheya, Egor Burkov, and Victor Lempitsky. 2019. Few-shot adversarial learning of realistic neural talking head models. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 9459–9468.Google ScholarCross Ref
70. Kaipeng Zhang, Zhanpeng Zhang, Zhifeng Li, and Yu Qiao. 2016. Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 23, 10 (2016), 1499–1503.Google Scholar
71. Hang Zhao, Orazio Gallo, Iuri Frosio, and Jan Kautz. 2016. Loss functions for image restoration with neural networks. IEEE Transactions on computational imaging 3, 1 (2016), 47–57.Google ScholarCross Ref
72. Jiapeng Zhu, Yujun Shen, Deli Zhao, and Bolei Zhou. 2020. In-Domain GAN Inversion for Real Image Editing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.00049 (2020).Google Scholar
73. Jun-Yan Zhu, Philipp Krähenbühl, Eli Shechtman, and Alexei A Efros. 2016. Generative visual manipulation on the natural image manifold. In European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 597–613.Google ScholarCross Ref