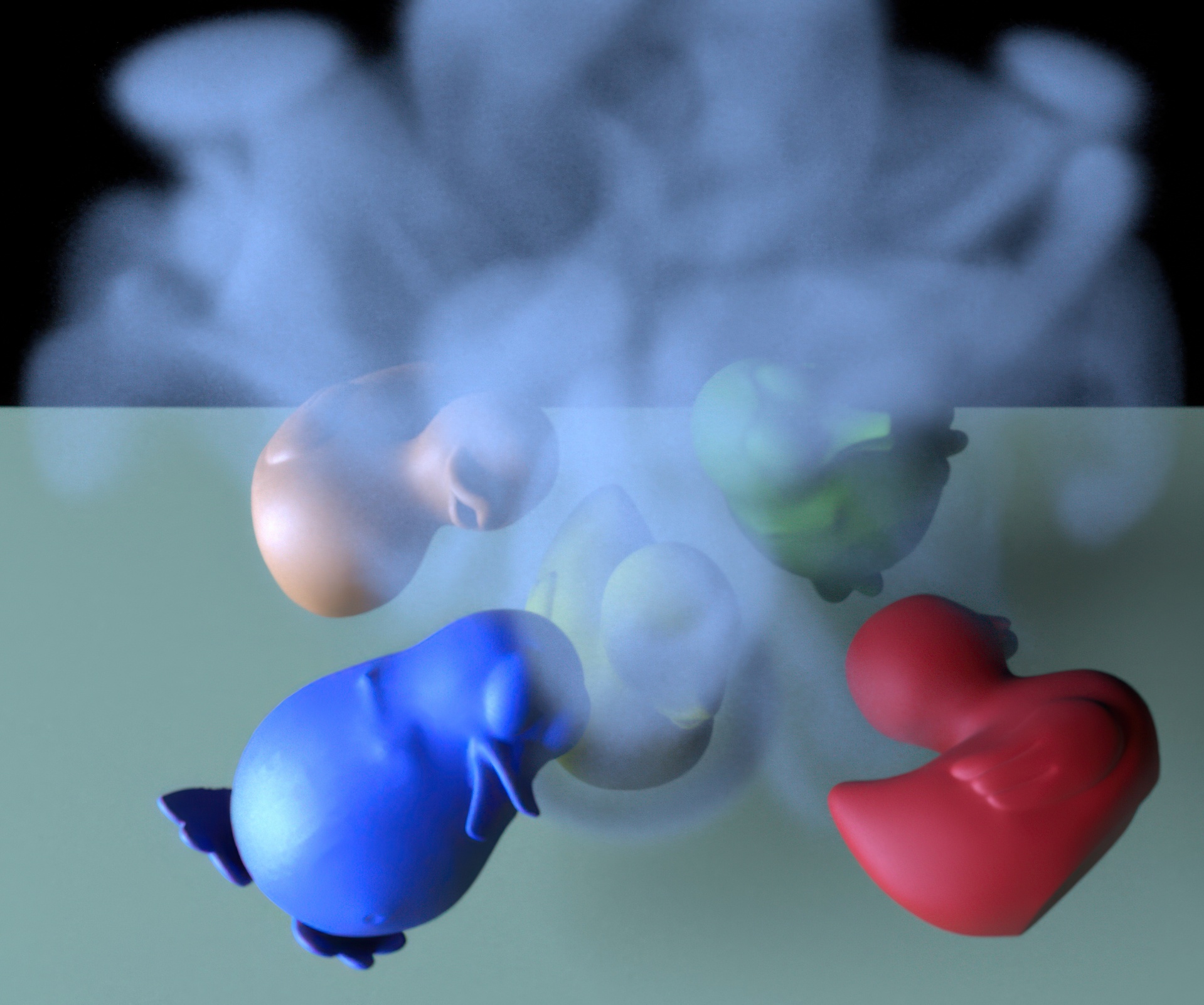
“Eulerian solid-fluid coupling” by Teng, Levin and Kim
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Eulerian solid-fluid coupling
Session/Category Title:
- Smash & Splash
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We present a new method that achieves a two-way coupling between deformable solids and an incompressible fluid where the underlying geometric representation is entirely Eulerian. Using the recently developed Eulerian Solids approach [Levin et al. 2011], we are able to simulate multiple solids undergoing complex, frictional contact while simultaneously interacting with a fluid. The complexity of the scenarios we are able to simulate surpasses those that we have seen from any previous method. Eulerian Solids have previously been integrated using explicit schemes, but we develop an implicit scheme that allows large time steps to be taken. The in-compressibility condition is satisfied in both the solid and the fluid, which has the added benefit of simplifying collision handling.
References:
1. Akinci, N., Cornelis, J., Akinci, G., and Teschner, M. 2013. Coupling elastic solids with smoothed particle hydrodynamics fluids. Comp. Anim. and Virtual Worlds, 195–203.
2. Baaijens, F. P. T. 2001. A fictitious domain mortar element method for fluid/structure interaction. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 35, 7, 743–761. Cross Ref
3. Bargteil, A. W., Wojtan, C., Hodgins, J. K., and Turk, G. 2007. A finite element method for animating large viscoplastic flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3.
4. Batty, C., Bertails, F., and Bridson, R. 2007. A fast variational framework for accurate solid-fluid coupling. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 26, ACM, 100.
5. Belytschko, T., Liu, W. K., Moran, B., and Elkhodary, K. 2013. Nonlinear finite elements for continua and structures. John Wiley & Sons.
6. Bouaziz, S., Martin, S., Liu, T., Kavan, L., and Pauly, M. 2014. Projective dynamics: Fusing constraint projections for fast simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July), 154:1–154:11.
7. Brackbill, J., and Ruppel, H. 1986. Flip: A method for adaptively zoned, particle-in-cell calculations of fluid flows in two dimensions. J. of Comp. Phys. 65, 2, 314–343.
8. Bridson, R., Fedkiw, R., and Anderson, J. 2002. Robust treatment of collisions, contact and friction for cloth animation. In ACM Trans. Graph., 594–603.
9. Bridson, R. 2008. Fluid Simulation for Computer Graphics. AK Peters.
10. Carlson, M., Mucha, P. J., and Turk, G. 2004. Rigid fluid: Animating the interplay between rigid bodies and fluid. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug.), 377–384.
11. Chentanez, N., Goktekin, T. G., Feldman, B. E., and O’Brien, J. F. 2006. Simultaneous coupling of fluids and deformable bodies. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. Comp. Anim., 83–89.
12. Clausen, P., Wicke, M., Shewchuk, J. R., and O’Brien, J. F. 2013. Simulating liquids and solid-liquid interactions with lagrangian meshes. ACM Trans. Graph., 17:1–15.
13. Fan, Y., Litven, J., Levin, D. I., and Pai, D. K. 2013. Eulerian-on-lagrangian simulation. ACM Trans. Graph..
14. Fedkiw, R., Stam, J., and Jensen, H. W. 2001. Visual simulation of smoke. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH, 15–22.
15. Guendelman, E., Selle, A., Losasso, F., and Fedkiw, R. 2005. Coupling water and smoke to thin deformable and rigid shells. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (July), 973–981.
16. Guennebaud, G., Jacob, B., et al., 2010. Eigen v3. http://eigen.tuxfamily.org.
17. He, X., Liu, N., Wang, G., Zhang, F., Li, S., Shao, S., and Wang, H. 2012. Staggered meshless solid-fluid coupling. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6 (Nov.), 149:1–149:12.
18. Heo, N., and Ko, H.-S. 2010. Detail-preserving fully-eulerian interface tracking framework. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 6 (Dec.).
19. Ihmsen, M., Orthmann, J., Solenthaler, B., Kolb, A., and Teschner, M. 2014. SPH Fluids in Computer Graphics. In Eurographics State of the Art Reports.
20. Irving, G., Schroeder, C., and Fedkiw, R. 2007. Volume conserving finite element simulations of deformable models. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 26.
21. Jiang, C., Schroeder, C., Selle, A., Teran, J., and Stomakhin, A. 2015. The affine particle-in-cell method. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (July), 51:1–51:10.
22. Jiang, C., Schroeder, C., Teran, J., Stomakhin, A., and Selle, A. 2016. The material point method for simulating continuum materials. In ACM SIGGRAPH Courses.
23. Kamrin, K., Rycroft, C. H., and Nave, J.-C. 2012. Reference map technique for finite-strain elasticity and fluid-solid interaction. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 60, 11 (Nov.), 1952–1969. Cross Ref
24. Kaufmann, P., Martin, S., Botsch, M., Grinspun, E., and Gross, M. 2009. Enrichment textures for detailed cutting of shells. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3 (July), 50:1–50:10.
25. Kim, T., and Delaney, J. 2013. Subspace fluid re-simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (July), 62:1–62:9.
26. Klingner, B. M., Feldman, B. E., Chentanez, N., and O’Brien, J. F. 2006. Fluid animation with dynamic meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3 (July), 820–825.
27. Lenaerts, T., Adams, B., and Dutré, P. 2008. Porous flow in particle-based fluid simulations. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 27, 49:1–49:8.
28. Lentine, M., Cong, M., Patkar, S., and Fedkiw, R. 2012. Simulating free surface flow with very large time steps. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. Comp. Anim., 107–116.
29. Levin, D. I., Litven, J., Jones, G. L., Sueda, S., and Pai, D. K. 2011. Eulerian solid simulation with contact. In ACM Trans. Graph., vol. 30.
30. Liu, B., Mason, G., Hodgson, J., Tong, Y., and Desbrun, M. 2015. Model-reduced variational fluid simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6 (Oct.), 244:1–244:12.
31. Macklin, M., and Müller, M. 2013. Position based fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, 104.
32. Macklin, M., Müller, M., Chentanez, N., and Kim, T.-Y. 2014. Unified particle physics for real-time applications. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July), 153:1–153:12.
33. McAdams, A., Selle, A., Ward, K., Sifakis, E., and Teran, J. 2009. Detail preserving continuum simulation of straight hair. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, 62:1–62:6.
34. McAdams, A., Zhu, Y., Selle, A., Empey, M., Tamstorf, R., Teran, J., and Sifakis, E. 2011. Efficient elasticity for character skinning with contact and collisions. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (July), 37:1–37:12.
35. Mullen, P., Crane, K., Pavlov, D., Tong, Y., and Desbrun, M. 2009. Energy-preserving integrators for fluid animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3 (July), 38:1–38:8.
36. Müller, M., and Chentanez, N. 2011. Solid simulation with oriented particles. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (July), 92:1–92:10.
37. Peskin, C. S. 1972. The immersed boundary method. Acta Numerica 11 (1), 479–517.
38. Robinson-Mosher, A., Shinar, T., Gretarsson, J., Su, J., and Fedkiw, R. 2008. Two-way coupling of fluids to rigid and deformable solids and shells. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3.
39. Robinson-Mosher, A., English, R. E., and Fedkiw, R. 2009. Accurate tangential velocities for solid fluid coupling. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. Comp. Anim., 227–236.
40. Selle, A., Fedkiw, R., Kim, B., Liu, Y., and Rossignac, J. 2008. An unconditionally stable maccormack method. J. Sci. Comput. 35, 2-3 (June), 350–371.
41. Sifakis, E., Marino, S., and Teran, J. 2008. Globally coupled collision handling using volume preserving impulses. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. Comp. Anim., 147–153.
42. Sin, F. S., Schroeder, D., and Barbic, J. 2013. Vega: Nonlinear fem deformable object simulator. Computer Graphics Forum 32, 1, 36–48. Cross Ref
43. Solenthaler, B., Schläfli, J., and Pajarola, R. 2007. A unified particle model for fluid-solid interactions. Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds 18, 1, 69–82.
44. Souli, M., and Benson, D. J. 2013. Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian and Fluid-Structure Interaction: Numerical Simulation. John Wiley & Sons.
45. Stam, J. 1999. Stable fluids. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH, 121–128.
46. Stomakhin, A., Howes, R., Schroeder, C., and Teran, J. M. 2012. Energetically consistent invertible elasticity. In ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. Comp. Anim., 25–32.
47. Stomakhin, A., Schroeder, C., Chai, L., Teran, J., and Selle, A. 2013. A material point method for snow simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4, 102.
48. Stomakhin, A., Schroeder, C., Jiang, C., Chai, L., Teran, J., and Selle, A. 2014. Augmented mpm for phase-change and varied materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July), 138:1–138:11.
49. Takahashi, T., Ueki, H., Kunimatsu, A., and Fujii, H. 2002. The simulation of fluid-rigid body interaction. In ACM SIGGRAPH Abstracts and Applications, 266–266.
50. Valkov, B., Rycroft, C. H., and Kamrin, K. 2015. Eulerian method for multiphase interactions of soft solid bodies in fluids. Journal of Applied Mechanics 82, 4. Cross Ref
51. Wang, H., O’Brien, J., and Ramamoorthi, R. 2010. Multi-resolution isotropic strain limiting. ACM Transactions on Graphics 29, 6, 156:1–156:10.
52. Wick, T. 2013. Coupling of fully eulerian and arbitrary lagrangian-eulerian methods for fluid-structure interaction computations. Computational Mechanics 52, 5, 1113–1124.
53. Zhang, X., Bridson, R., and Greif, C. 2015. Restoring the missing vorticity in advection-projection fluid solvers. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, 52:1–52:8.
54. Zhu, Y., and Bridson, R. 2005. Animating sand as a fluid. ACM Trans. Graph. 24 (July), 965–972.
55. Zhu, B., Lu, W., Cong, M., Kim, B., and Fedkiw, R. 2013. A new grid structure for domain extension. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, 63:1–63:12.