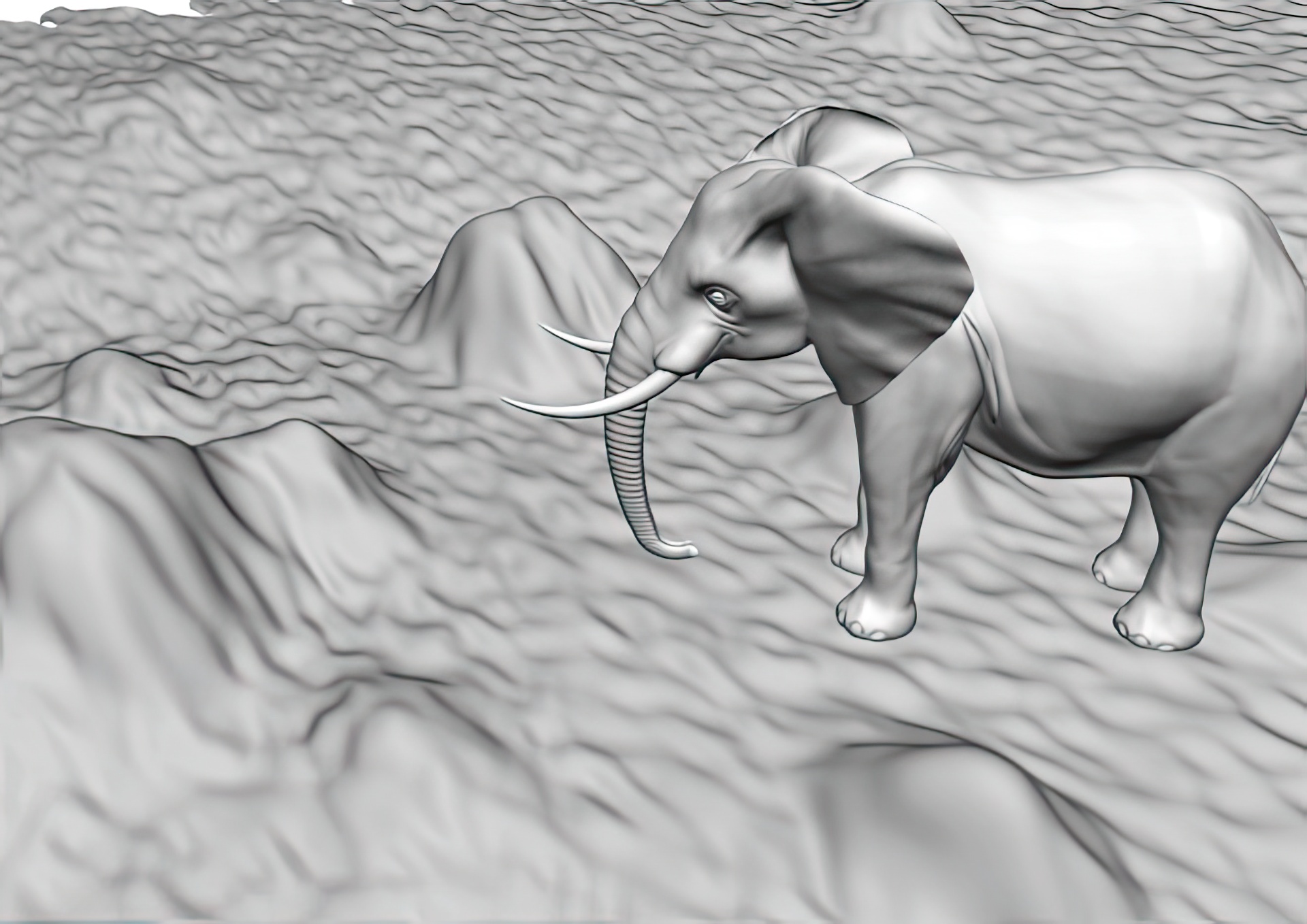
“Emerging images”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Emerging images
Session/Category Title: Perception
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
Emergence refers to the unique human ability to aggregate information from seemingly meaningless pieces, and to perceive a whole that is meaningful. This special skill of humans can constitute an effective scheme to tell humans and machines apart. This paper presents a synthesis technique to generate images of 3D objects that are detectable by humans, but difficult for an automatic algorithm to recognize. The technique allows generating an infinite number of images with emerging figures. Our algorithm is designed so that locally the synthesized images divulge little useful information or cues to assist any segmentation or recognition procedure. Therefore, as we demonstrate, computer vision algorithms are incapable of effectively processing such images. However, when a human observer is presented with an emergence image, synthesized using an object she is familiar with, the figure emerges when observed as a whole. We can control the difficulty level of perceiving the emergence effect through a limited set of parameters. A procedure that synthesizes emergence images can be an effective tool for exploring and understanding the factors affecting computer vision techniques.
References:
1. Barlow, H., and Tripathy, S. P. 1997. Corresp. noise and signal pooling in the detection of coherent visual motion. J. Neurosci. 17, 20.Google ScholarCross Ref
2. Cortes, C., and Vapnik, V. 1995. Support vector networks. In Machine Learning, 273–297. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Deussen, O., Hiller, S., Overveld, C. V., and Strothotte, T. 2000. Floating points: A method for computing stipple drawings. Computer Graphics Forum 19, 40–51.Google ScholarCross Ref
4. Elson, J., Douceur, J. R., Howel, J., and Saul, J. 2007. Asirra: a captcha that exploits interest-aligned manual image categorization. In ACM Conf. on CCS, 366–374. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Epshtein, B., and Ullman, S. 2005. Feature hierarchies for object classification. In IEEE ICCV, vol. 1, 220–227. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Epshtein, B., Lifshitz, I., and Ullman, S. 2008. Image interpretation by a single bottom-up top-down cycle. Proc. of the National Acad. of Sc. 105, 38, 14298–14303.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Gal, R., Sorkine, O., Popa, T., Sheffer, A., and Cohen-Or, D. 2007. 3D collage: Expressive non-realistic modeling. In Proc. of NPAR, ACM Press, 7–14. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Golle, P. 2008. Machine learning attacks against the asirra captcha. In ACM Conf. on CCS, 535–542. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Kanizsa, G. 1979. Organization in Vision: Essays on Gestalt Perception. Praeger New York.Google Scholar
10. Kim, J., and Pellacini, F. 2002. Jigsaw image mosaics. In ACM SIGGRAPH Trans. Graph., 657–664. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Kim, B. 2000. Perceptual Org. for Artificial Vision Sys. Springer.Google Scholar
12. Lee, C. H., Varshney, A., and Jacobs, D. W. 2005. Mesh saliency. In ACM SIGGRAPH Trans. Graph., 659–666. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Lobay, A., and Forsyth, D. A. 2006. Shape from texture without boundaries. Int. J. of Computer Vision 67, 1, 71–91. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Lowe, D. G. 2004. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. Journal of Computer Vision 60, 91–110. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Massot, C., and Herault, J. 2008. Model of frequency analysis in the visual cortex and the shape from texture problem. Int. Journal of Computer Vision 76, 2 (February), 165–182. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Mori, G., and Malik, J. 2003. Recognizing objects in adversarial clutter: Breaking a visual captcha. In IEEE CVPR, 134–141. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Nister, D., and Stewenius, H. 2006. Scalable recognition with a vocabulary tree. In IEEE CVPR, 2161–2168. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Orchard, J., and Kaplan, C. S. 2008. Cut-out image mosaics. In Proc. of NPAR, 79–87. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Ostromoukhov, V., Donohue, C., and Jodoin, P.-M. 2004. Fast hierarchical importance sampling with blue noise properties. ACM SIGGRAPH Trans. Graph. 23, 3, 488–495. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Schmidt, R., Grimm, C., and Wyvill, B. 2006. Interactive decal compositing with discrete exponential maps. In ACM SIGGRAPH Trans. Graph., 605–613. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Serre, T., Wolf, L., Bileschi, S., Riesenhuber, M., and Poggio, T. 2007. Robust object recognition with cortex-like mechanisms. Trans. on PAMI 29, 3 (March), 411–426. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Serre, T., Oliva, A., and Poggio, T. 2007. A feedforward architecture accounts for rapid categorization. PNAS 104, 15 (April), 6424–6429.Google ScholarCross Ref
23. Shlizerman, I. K., Basri, R., and Nadler, B. 2008. 3D shape reconstruction of Mooney faces. In IEEE CVPR, 1–8.Google Scholar
24. Stauffer, C., and Grimson, W. E. L. 2000. Learning patterns of activity using real-time tracking. Trans. on PAMI 22, 8, 747–757. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Tsotsos, J. 1992. On the relative complexity of active vs. passive visual search. Int. Journal of Computer Vision 7, 2, 127–141. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Ullman, S. 2000. High Level Vision: Object Recognition and Visual Cognition. MIT Press.Google Scholar
27. von Ahn, L., Blum, M., and Langford, J. 2004. Telling humans and computers apart automatically. Commun. ACM 47, 2, 56–60. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Watson, B., Friedman, A., and McGaffey, A. 2001. Measuring and predicting visual fidelity. In ACM SIGGRAPH Trans. Graph., ACM, 213–220. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Yan, J., and Ahmad, A. S. E. 2008. A low-cost attack on a microsoft captcha. In ACM Conf. on CCS, 543–554. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Yang, C., and Yang, H.-L. 2008. Realization of seurat’s pointillism via non-photorealistic rendering. The Visual Computer 24, 5, 303–322. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Yoon, J., Lee, I., and Kang, H. 2008. A hidden picture puzzles generator. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 27, 1869–1877.Google ScholarCross Ref
32. Zakia, R. D. 2001. Perception and Imaging. Focal Press.Google Scholar