“DiagSplit: parallel, crack-free, adaptive tessellation for micropolygon rendering”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- DiagSplit: parallel, crack-free, adaptive tessellation for micropolygon rendering
Session/Category Title: Geometry: interaction & subdivision
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
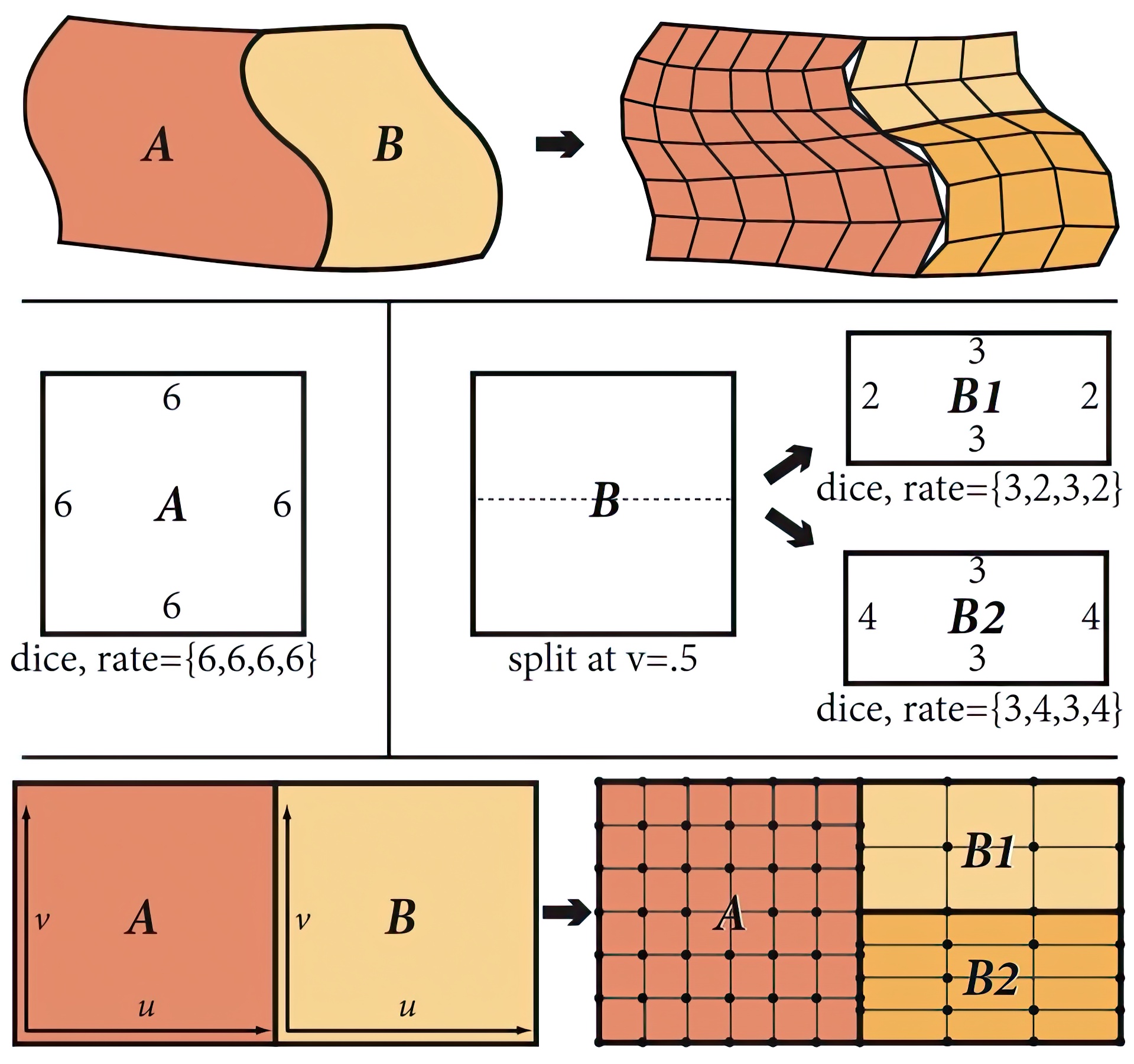
We present DiagSplit, a parallel algorithm for adaptively tessellating displaced parametric surfaces into high-quality, crack-free micropolygon meshes. DiagSplit modifies the split-dice tessellation algorithm to allow splits along non-isoparametric directions in the surface’s parametric domain, and uses a dicing scheme that supports unique tessellation factors for each subpatch edge. Edge tessellation factors are computed using only information local to subpatch edges. These modifications allow all subpatches generated by DiagSplit to be processed independently without introducing T-junctions or mesh cracks and without incurring the tessellation overhead of binary dicing. We demonstrate that DiagSplit produces output that is better (in terms of image quality and number of micropolygons produced) than existing parallel tessellation schemes, and as good as highly adaptive split-dice implementations that are less amenable to parallelization.
References:
1. Apodaca, A. A., and Gritz, L. 2000. Advanced RenderMan: Creating CGI for Motion Pictures. Morgan Kaufmann. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Blinn, J. F. 1978. Computer display of curved surfaces. PhD thesis, The University of Utah. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Burley, B., and Lacewell, D. 2008. Ptex: Per-face texture mapping for production rendering. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 27, Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 1155–1164. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Catmull, E. E. 1974. A subdivision algorithm for computer display of curved surfaces. PhD thesis, The University of Utah. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Clark, J. H. 1979. A fast scan-line algorithm for rendering parametric surfaces. In Computer Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH ’79), ACM, 174. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Cook, R., Carpenter, L., and Catmull, E. 2008. The Reyes image rendering architecture. In Computer Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH ’87), vol. 27, 1–11. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Eisenacher, C., Meyer, Q., and Loop, C. 2009. Real-time view-dependent rendering of parametric surfaces. In I3D ’09: Proceedings of the 2009 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, ACM, 137–143. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Fatahalian, K., Luong, E., Boulos, S., Akeley, K., Mark, W. R., and Hanrahan, P. 2009. Data-parallel rasterization of micropolygons with defocus and motion blur. In HPG ’09: Proceedings of the Conference on High Performance Graphics 2009, ACM, 59–68. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Foster, C., 2009. Aqsis renderer. http://aqsis.org/.Google Scholar
10. Kovacs, D., Mitchell, J., Drone, S., and Zorin, D. 2009. Real-time creased approximate subdivision surfaces. In I3D ’09: Proceedings of the 2009 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games, ACM, 155–160. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Lane, J. M., Carpenter, L. C., Whitted, T., and Blinn, J. F. 1980. Scan line methods for displaying parametrically defined surfaces. Communications of the ACM 23, 1, 23–34. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Lien, S., Shantz, M., and Pratt, V. 1987. Adaptive forward differencing for rendering curves and surfaces. Computer Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH ’87) 21, 4, 111–118. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Loop, C., and Schaefer, S. 2008. Approximating Catmull-Clark subdivision surfaces with bicubic patches. In ACM Transactions on Graphics, vol. 27, 1–11. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Microsoft, 2009. DirectX 11 SDK: August 2009. msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/directx/.Google Scholar
15. Moreton, H. 2001. Watertight tessellation using forward differencing. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Workshop on Graphics Hardware, ACM, 25–32. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Moule, K., and McCool, M. 2002. Efficient bounded adaptive tessellation of displacement maps. In Graphics Interface, 171–180.Google Scholar
17. Patney, A., and Owens, J. D. 2008. Real-time Reyes-style adaptive surface subdivision. ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH Asia) 27, 5. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Patney, A., Ebeida, M. S., and Owens, J. D. 2009. Parallel view-dependent tessellation of Catmull-Clark subdivision surfaces. In Proceedings of High Performance Graphics 2009, 99–108. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Purnomo, B., Cohen, J. D., and Kumar, S. 2004. Seamless texture atlases. In SGP ’04: Proceedings of the 2004 Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing, ACM, 65–74. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Rockwood, A. P., Heaton, K., and Davis, T. 1989. Real-time rendering of trimmed surfaces. In Computer Graphics (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’89), 107–116. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Schwarz, M., and Stamminger, M. 2009. Fast GPU-based adaptive tessellation with CUDA. In Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 28, Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 365–374.Google Scholar
22. Stam, J. 1998. Exact evaluation of Catmull-Clark subdivision surfaces at arbitrary parameter values. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH ’98, ACM, 395–404. Google ScholarDigital Library