“Deep point correlation design” by Leimkühler, Singh, Myszkowski, Seidel and Ritschel
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Deep point correlation design
Session/Category Title:
- Samples & Speckles
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
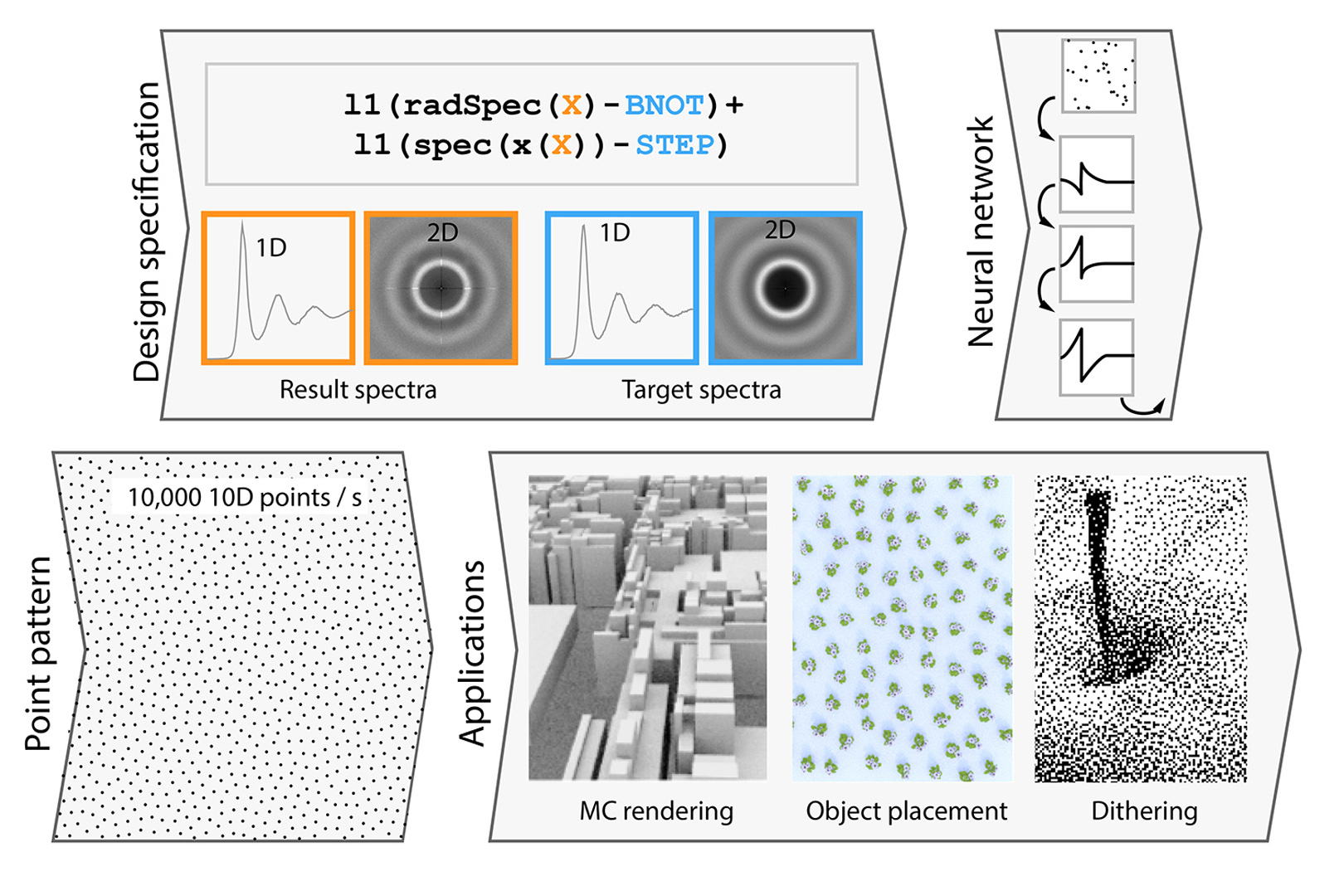
Designing point patterns with desired properties can require substantial effort, both in hand-crafting coding and mathematical derivation. Retaining these properties in multiple dimensions or for a substantial number of points can be challenging and computationally expensive. Tackling those two issues, we suggest to automatically generate scalable point patterns from design goals using deep learning. We phrase pattern generation as a deep composition of weighted distance-based unstructured filters. Deep point pattern design means to optimize over the space of all such compositions according to a user-provided point correlation loss, a small program which measures a pattern’s fidelity in respect to its spatial or spectral statistics, linear or non-linear (e. g., radial) projections, or any arbitrary combination thereof. Our analysis shows that we can emulate a large set of existing patterns (blue, green, step, projective, stair, etc.-noise), generalize them to countless new combinations in a systematic way and leverage existing error estimation formulations to generate novel point patterns for a user-provided class of integrand functions. Our point patterns scale favorably to multiple dimensions and numbers of points: we demonstrate nearly 10k points in 10-D produced in one second on one GPU. All the resources (source code and the pre-trained networks) can be found at https://sampling.mpi-inf.mpg.de/deepsampling.html.
References:
1. Abadi et al. 2016. TensorFlow: A System for Large-scale Machine Learning. In Proc. USENIX.Google Scholar
2. Pankaj K Agarwal, Jeff Erickson, et al. 1999. Geometric range searching and its relatives. Contemp. Math. 223 (1999).Google Scholar
3. Abdalla GM Ahmed, Hélène Perrier, David Coeurjolly, Victor Ostromoukhov, Jianwei Guo, Dong-Ming Yan, Hui Huang, and Oliver Deussen. 2016. Low-discrepancy blue noise sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 6 (2016).Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Luke Anderson, Tzu-Mao Li, Jaakko Lehtinen, and Frédo Durand. 2017. Aether: An Embedded Domain Specific Sampling Language for Monte Carlo Rendering. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Matan Atzmon, Haggai Maron, and Yaron Lipman. 2018. Point Convolutional Neural Networks by Extension Operators. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Steve Bako, Thijs Vogels, Brian Mcwilliams, Mark Meyer, Jan NováK, Alex Harvill, Pradeep Sen, Tony Derose, and Fabrice Rousselle. 2017. Kernel-predicting Convolutional Networks for Denoising Monte Carlo Renderings. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Michael Balzer, Thomas Schlömer, and Oliver Deussen. 2009. Capacity-constrained point distributions: a variant of Lloyd’s method. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3 (2009).Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Gilbert Louis Bernstein, Chinmayee Shah, Crystal Lemire, Zachary Devito, Matthew Fisher, Philip Levis, and Pat Hanrahan. 2016. Ebb: A DSL for Physical Simulation on CPUs and GPUs. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 2 (2016).Google ScholarDigital Library
9. John Bowers, Rui Wang, Li-Yi Wei, and David Maletz. 2010. Parallel Poisson disk sampling with spectrum analysis on surfaces. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 6 (2010).Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Luca Brandolini, Leonardo Colzani, and Andrea Torlaschi. 2001. Mean square decay of Fourier transforms in Euclidean and non Euclidean spaces. Tohoku Math J 53, 3 (2001).Google Scholar
11. Chakravarty R. Alla Chaitanya, Anton S. Kaplanyan, Christoph Schied, Marco Salvi, Aaron Lefohn, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Timo Aila. 2017. Interactive Reconstruction of Monte Carlo Image Sequences Using a Recurrent Denoising Autoencoder. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. SIGGRAPH) 36, 4 (2017).Google Scholar
12. Angel X. Chang, Thomas A. Funkhouser, Leonidas J. Guibas, Pat Hanrahan, Qi-Xing Huang, Zimo Li, Silvio Savarese, Manolis Savva, Shuran Song, Hao Su, Jianxiong Xiao, Li Yi, and Fisher Yu. 2015. ShapeNet: An Information-Rich 3D Model Repository. arxiv:1512.03012 (2015).Google Scholar
13. Zhonggui Chen, Zhan Yuan, Yi-King Choi, Ligang Liu, and Wenping Wang. 2012. Variational blue noise sampling. IEEE Trans. Vis Comp. Graph. 18, 10 (2012).Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Kenneth Chiu, Peter Shirley, and Changyaw Wang. 1994. Graphics Gems IV. Chapter Multi-jittered Sampling.Google Scholar
15. Per Christensen, Andrew Kensler, and Charlie Kilpatrick. 2018. Progressive multi-jittered sample sequences. Comp. Graph. Forum (Proc. EGSR) 37, 4 (2018).Google Scholar
16. Sebastian Claici, Edward Chien, and Justin Solomon. 2018. Stochastic Wasserstein Barycenters. arxiv:1802-05757 (2018).Google Scholar
17. Richard Condit, Peter S. Ashton, Patrick Baker, Sarayudh Bunyavejchewin, Savithri Gunatilleke, Nimal Gunatilleke, Stephen P. Hubbell, Robin B. Foster, Akira Itoh, James V. LaFrankie, Hua Seng Lee, Elizabeth Losos, N. Manokaran, R. Sukumar, and Takuo Yamakura. 2000. Spatial Patterns in the Distribution of Tropical Tree Species. Science 288, 5470 (2000).Google Scholar
18. Robert L Cook. 1986. Stochastic sampling in computer graphics. ACM Trans. Graph. 5, 1 (1986).Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Ken Dahm and Alexander Keller. 2017. Learning Light Transport the Reinforced Way. arXiv:1701.07403 (2017).Google Scholar
20. Sabrina Dammertz and Alexander Keller. 2008. Image Synthesis by Rank-1 Lattices. In Monte Carlo and Quasi-Monte Carlo Methods 2006.Google Scholar
21. Fernando De Goes, Katherine Breeden, Victor Ostromoukhov, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2012. Blue noise through optimal transport. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6 (2012).Google Scholar
22. Zachary Devito, Michael Mara, Michael Zollhöfer, Gilbert Bernstein, Jonathan Ragan-Kelley, Christian Theobalt, Pat Hanrahan, Matthew Fisher, and Matthias Niessner. 2017. Opt: A Domain Specific Language for Non-Linear Least Squares Optimization in Graphics and Imaging. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 5 (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Laurent Dinh, Jascha Sohl-Dickstein, and Samy Bengio. 2017. Density estimation using Real NVP. In ICLR.Google Scholar
24. David P. Dobkin, David Eppstein, and Don P. Mitchell. 1996. Computing the Discrepancy with Applications to Supersampling Patterns. ACM Trans. Graph. 15, 4 (1996).Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Carola Doerr and François-Michel De Rainville. 2013. Constructing Low Star Discrepancy Point Sets with Genetic Algorithms. In Proc. GECCO.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Ron O Dror, Thomas K Leung, Edward H Adelson, and Alan S Willsky. 2001. Statistics of real-world illumination. In CVPR.Google Scholar
27. Raanan Fattal. 2011. Blue-noise point sampling using kernel density model. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (2011).Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Iliyan Georgiev and Marcos Fajardo. 2016. Blue-noise Dithered Sampling. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2016 Talks.Google Scholar
29. Ian Goodfellow, Jean Pouget-Abadie, Mehdi Mirza, Bing Xu, David Warde-Farley, Sherjil Ozair, Aaron Courville, and Yoshua Bengio. 2014. Generative adversarial nets. In NIPS.Google Scholar
30. John H. Halton. 1960. On the Efficiency of Certain Quasi-random Sequences of Points in Evaluating Multi-dimensional Integrals. Numer. Math. 2, 1 (1960).Google Scholar
31. Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In CVPR.Google Scholar
32. Daniel Heck, Thomas Schlömer, and Oliver Deussen. 2013. Blue noise sampling with controlled aliasing. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. SIGGRAPH) 32, 3 (2013).Google ScholarDigital Library
33. A.S. Hedayat, N.J.A. Sloane, and John Stufken. 1999. Orthogonal Arrays: Theory and Applications. Springer New York.Google ScholarCross Ref
34. Felix Heide, Steven Diamond, Matthias Niessner, Jonathan Ragan-Kelley, Wolfgang Heidrich, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2016. ProxImaL: Efficient Image Optimization Using Proximal Algorithms. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4 (2016).Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Pedro Hermosilla, Tobias Ritschel, Pere-Pau Vázquez, Àlvar Vinacua, and Timo Ropinski. 2018. Monte Carlo Convolution for Learning on Non-uniformly Sampled Point Clouds. ACM Trans. Graph (Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia) 37, 5 (2018).Google Scholar
36. JS Hicks and RF Wheeling. 1959. An efficient method for generating uniformly distributed points on the surface of an n-dimensional sphere. Comm. ACM 2, 4 (1959).Google Scholar
37. Wojciech Jarosz, Afnan Enayet, Andrew Kensler, Charlie Kilpatrick, and Per Christensen. 2019. Orthogonal array sampling for Monte Carlo rendering. Computer Graphics Forum (Proceedings of EGSR) 38, 4 (2019).Google Scholar
38. Min Jiang, Yahan Zhou, Rui Wang, Richard Southern, and Jian Jun Zhang. 2015. Blue noise sampling using an SPH-based method. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6 (2015).Google ScholarDigital Library
39. S. Joe and F. Kuo. 2008. Constructing Sobol Sequences with Better Two-Dimensional Projections. SIAM J Scientific Comp. 30, 5 (2008).Google Scholar
40. Bhavya Kailkhura, Jayaraman J Thiagarajan, Peer-Timo Bremer, and Pramod K Varshney. 2016. Stair blue noise sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 6 (2016).Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Nima Khademi Kalantari, Steve Bako, and Pradeep Sen. 2015. A Machine Learning Approach for Filtering Monte Carlo Noise. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (2015).Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Simon Kallweit, Thomas Müller, Brian Mcwilliams, Markus Gross, and Jan Novák. 2017. Deep Scattering: Rendering Atmospheric Clouds with Radiance-predicting Neural Networks. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia) 36, 6 (2017).Google Scholar
43. Alexander Keller, Simon Premoze, and Matthias Raab. 2012. Advanced (Quasi) Monte Carlo Methods for Image Synthesis. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2012 Courses. Article 21.Google Scholar
44. Diederik P. Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2014. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arxiv:1412.6980 (2014).Google Scholar
45. Diederik P Kingma and Max Welling. 2013. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. arXiv:1312.6114 (2013).Google Scholar
46. Johannes Kopf, Daniel Cohen-Or, Oliver Deussen, and Dani Lischinski. 2006. Recursive Wang tiles for real-time blue noise. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. SIGGRAPH) 25, 3 (2006).Google ScholarDigital Library
47. Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. 2012. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In NIPS.Google ScholarDigital Library
48. Christopher Kulla, Alejandro Conty, Clifford Stein, and Larry Gritz. 2018. Sony Pictures Imageworks Arnold. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 3 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
49. Frances Kuo. 2007. Lattice rule generating vectors. web.maths.unsw.edu.au/~fkuo. Accessed: 2019-07-12.Google Scholar
50. Ares Lagae and Philip Dutre. 2008. A Comparison of Methods for Generating Poisson Disk Distributions. Comp. Graph. Forum 27, 1 (2008).Google Scholar
51. Tzu-Mao Li, Michaël Gharbi, Andrew Adams, Frédo Durand, and Jonathan Ragan-Kelley. 2018. Differentiable Programming for Image Processing and Deep Learning in Halide. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
52. Stuart Lloyd. 1982. Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans Inform. Theory 28, 2 (1982).Google ScholarDigital Library
53. Benoit B Mandelbrot. 1983. The fractal geometry of nature. WH Freeman New York.Google Scholar
54. Michael McCool and Eugene Fiume. 1992. Hierarchical Poisson disk sampling distributions. In Proc. Graphics interface.Google Scholar
55. Don P. Mitchell. 1992. Ray Tracing and Irregularities of Distribution. In In Third Eurographics Workshop on Rendering.Google Scholar
56. Scott A. Mitchell, Mohamed S. Ebeida, Muhammad A. Awad, Chonhyon Park, Anjul Patney, Ahmad A. Rushdi, Laura P. Swiler, Dinesh Manocha, and Li-Yi Wei. 2018. Spoke-Darts for High-Dimensional Blue-Noise Sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 2 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
57. Thomas Müller, Brian McWilliams, Fabrice Rousselle, Markus Gross, and Jan Nov’ak. 2018. Neural Importance Sampling. arXiv:1808.03856 (2018).Google Scholar
58. Jeffrey B Mulligan and Albert J Ahumada. 1992. Principled halftoning based on human vision models. In Human Vision, Visual Processing, and Digital Display III, Vol. 1666.Google Scholar
59. Oliver Nalbach, Elena Arabadzhiyska, Dushyant Mehta, Hans-Peter Seidel, and Tobias Ritschel. 2017. Deep Shading: Convolutional Neural Networks for Screen-Space Shading. Comp. Graph. Forum (Proc. EGSR) 36, 4 (2017).Google Scholar
60. Harald Niederreiter. 1978. Quasi-Monte Carlo methods and pseudo-random numbers. Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 84, 6 (1978).Google Scholar
61. H. Niederreiter. 1992. Random Number Generation and Quasi-Monte-Carlo Methods. SIAM.Google Scholar
62. Dirk Nuyens. 2013. The construction of good lattice rules and polynomial lattice rules. arXiv:1308.3601 (2013).Google Scholar
63. Deussen Oliver, Hiller Stefan, Van Overveld Cornelius, and Strothotte Thomas. 2001. Floating Points: A Method for Computing Stipple Drawings. Computer Graphics Forum 19, 3 (2001).Google Scholar
64. Victor Ostromoukhov, Charles Donohue, and Pierre-Marc Jodoin. 2004. Fast hierarchical importance sampling with blue noise properties. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (2004).Google ScholarDigital Library
65. Art B. Owen. 1997. Monte Carlo Variance of Scrambled Net Quadrature. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 34, 5 (1997), 27.Google ScholarDigital Library
66. A Cengiz Öztireli. 2016. Integration with stochastic point processes. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 5 (2016).Google ScholarDigital Library
67. A Cengiz Öztireli and Markus Gross. 2012. Analysis and synthesis of point distributions based on pair correlation. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6 (2012).Google Scholar
68. Hélène Perrier, David Coeurjolly, Feng Xie, Matt Pharr, Pat Hanrahan, and Victor Ostromoukhov. 2018. Sequences with Low-Discrepancy Blue-Noise 2-D Projections. Comp. Graph. Forum (Proc. Eurographics) 37, 2 (2018).Google Scholar
69. Matt Pharr, Wenzel Jakob, and Greg Humphreys. 2016. Physically Based Rendering: From Theory To Implementation (3rd ed.). Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA.Google ScholarDigital Library
70. Adrien Pilleboue, Gurprit Singh, David Coeurjolly, Michael Kazhdan, and Victor Ostromoukhov. 2015. Variance analysis for Monte Carlo integration. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (2015).Google ScholarDigital Library
71. Charles R Qi, Hao Su, Kaichun Mo, and Leonidas J Guibas. 2017. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. CVPR (2017).Google Scholar
72. Hongxing Qin, Yi Chen, Jinlong He, and Baoquan Chen. 2017. Wasserstein Blue Noise Sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 5 (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
73. Bernhard Reinert, Tobias Ritschel, Hans-Peter Seidel, and Iliyan Georgiev. 2016. Projective Blue-Noise Sampling. Comp. Graph. Forum 35, 1 (2016).Google Scholar
74. Peiran Ren, Yue Dong, Stephen Lin, Xin Tong, and Baining Guo. 2015. Image Based Relighting Using Neural Networks. ACM Trans. Graph. 34 (2015).Google Scholar
75. Danilo Jimenez Rezende and Shakir Mohamed. 2015. Variational inference with normalizing flows. arXiv:1505.05770 (2015).Google Scholar
76. Christian Schmaltz, Pascal Gwosdek, Andres Bruhn, and Joachim Weickert. 2010. Electrostatic Halftoning. Comp. Graph. Forum (2010).Google Scholar
77. David W Scott. 1979. On optimal and data-based histograms. Biometrika 66, 3 (1979).Google Scholar
78. Adrian Secord. 2002. Weighted Voronoi stippling. In Proc. NPAR.Google ScholarDigital Library
79. Peter Shirley. 1991. Discrepancy as a quality measure for sample distributions. In Proc. Eurographics.Google Scholar
80. Eero P Simoncelli and Bruno A Olshausen. 2001. Natural image statistics and neural representation. Ann. Review Neuroscience 24, 1 (2001).Google ScholarCross Ref
81. Gurprit Singh and Wojciech Jarosz. 2017. Convergence Analysis for Anisotropic Monte Carlo Sampling Spectra. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. SIGGRAPH) 36, 4 (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
82. Gurprit Singh, Cengiz Oztireli, Abdalla G.M. Ahmed, David Coeurjolly, Kartic Subr, Oliver Deussen, Victor Ostromoukhov, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Wojciech Jarosz. 2019a. Analysis of Sample Correlations for Monte Carlo Rendering. Comp. Graph Form. (Proc. EGSR) 38, 2 (2019).Google Scholar
83. Gurprit Singh, Kartic Subr, David Coeurjolly, Victor Ostromoukhov, and Wojciech Jarosz. 2019b. Fourier Analysis of Correlated Monte Carlo Importance Sampling. Comp. Graph. Forum 38, 1 (2019).Google Scholar
84. I.H. Sloan and S. Joe. 1994. Lattice methods for multiple integration. Clarendon Press.Google Scholar
85. I. M. Sobol. 1967. The distribution of points in a cube and the approximate evaluation of integrals. U. S. S. R. Comput. Math. and Math. Phys. 7 (1967).Google Scholar
86. Kartic Subr and Jan Kautz. 2013. Fourier analysis of stochastic sampling strategies for assessing bias and variance in integration. ACM Trans. Graph. 32 (2013).Google Scholar
87. Robert A Ulichney. 1988. Dithering with blue noise. Proc. IEEE 76, 1 (1988).Google ScholarCross Ref
88. Florent Wachtel, Adrien Pilleboue, David Coeurjolly, Katherine Breeden, Gurprit Singh, Gaël Cathelin, Fernando De Goes, Mathieu Desbrun, and Victor Ostromoukhov. 2014. Fast tile-based adaptive sampling with user-specified Fourier spectra. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (2014).Google ScholarDigital Library
89. Shenlong Wang, Simon Suo, Wei-Chiu Ma, Andrei Pokrovsky, and Raquel Urtasun. 2018b. Deep parametric continuous convolutional neural networks. In CVPR.Google Scholar
90. Yue Wang, Yongbin Sun, Ziwei Liu, Sanjay E. Sarma, Michael M. Bronstein, and Justin M. Solomon. 2018a. Dynamic Graph CNN for Learning on Point Clouds. arxiv:1801.07829 (2018).Google Scholar
91. Li-Yi Wei and Rui Wang. 2011. Differential domain analysis for non-uniform sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (2011).Google ScholarDigital Library
92. Dong-Ming Yan, Jian-Wei Guo, Bin Wang, Xiao-Peng Zhang, and Peter Wonka. 2015. A survey of blue-noise sampling and its applications. J Comp. Sci. and Tech. 30, 3 (2015).Google Scholar
93. John I Yellott. 1983. Spectral consequences of photoreceptor sampling in the rhesus retina. Science 221, 4608 (1983).Google Scholar
94. Quan Zheng and Matthias Zwicker. 2018. Learning to Importance Sample in Primary Sample Space. arxiv:1808.07840 (2018).Google Scholar
95. Yahan Zhou, Haibin Huang, Li-Yi Wei, and Rui Wang. 2012. Point sampling with general noise spectrum. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (2012).Google ScholarDigital Library
96. Zhi-Hua Zhou. 2017. A brief introduction to weakly supervised learning. National Science Review 5, 1 (2017).Google Scholar