“Compression and direct manipulation of complex blendshape models”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Compression and direct manipulation of complex blendshape models
Session/Category Title:
- Animation
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
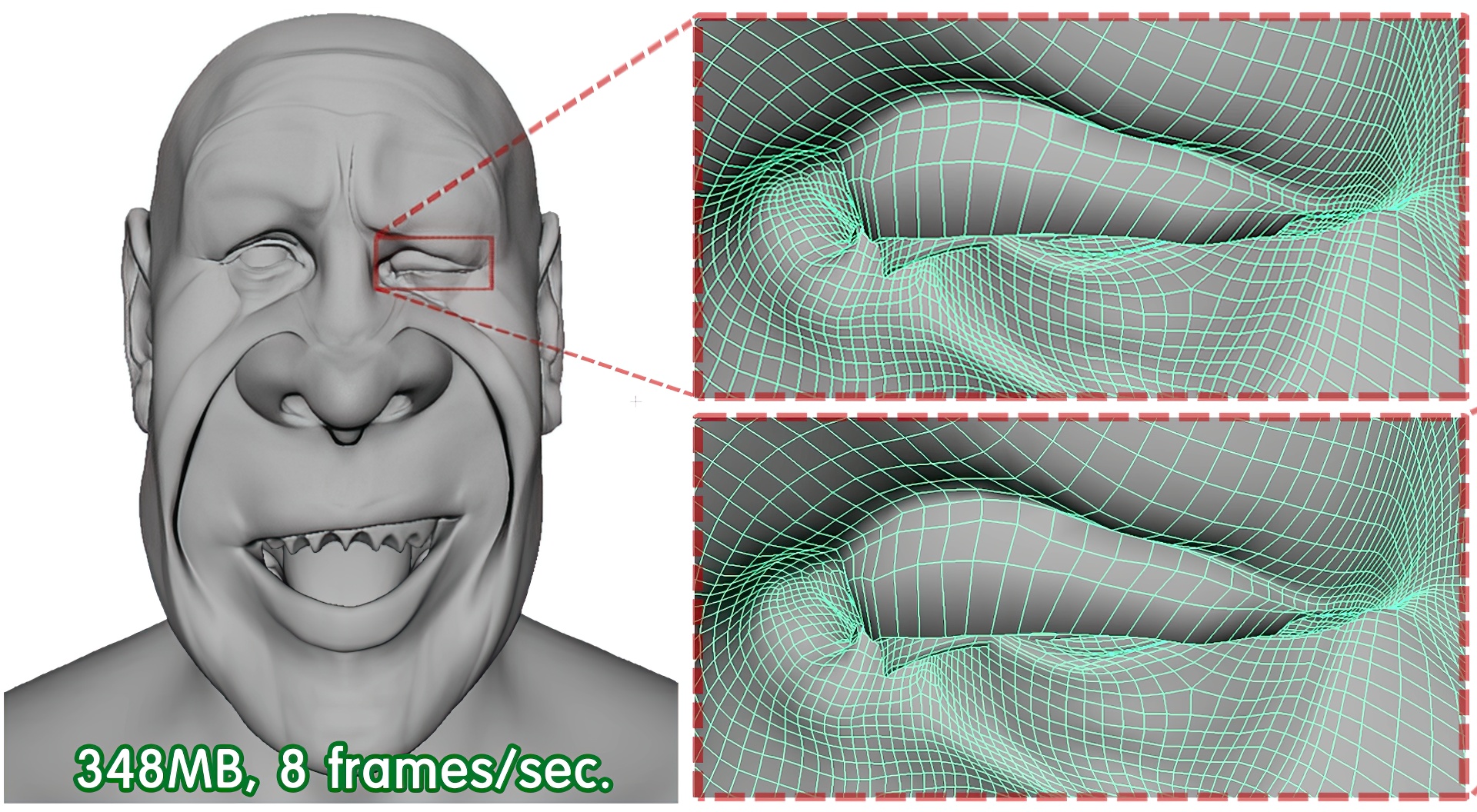
We present a method to compress complex blendshape models and thereby enable interactive, hardware-accelerated animation of these models. Facial blendshape models in production are typically large in terms of both the resolution of the model and the number of target shapes. They are represented by a single huge blendshape matrix, whose size presents a storage burden and prevents real-time processing. To address this problem, we present a new matrix compression scheme based on a hierarchically semi-separable (HSS) representation with matrix block reordering. The compressed data are also suitable for parallel processing. An efficient GPU implementation provides very fast feedback of the resulting animation. Compared with the original data, our technique leads to a huge improvement in both storage and processing efficiency without incurring any visual artifacts. As an application, we introduce an extended version of the direct manipulation method to control a large number of facial blendshapes efficiently and intuitively.
References:
1. Autodesk, 2011. Autodesk Maya API White Paper.Google Scholar
2. Bainville, E., 2010. OpenCL Training Course: GPU matrix-vector product. http://www.bealto.com/.Google Scholar
3. Bergeron, P., and Lachapelle, P. 1985. Controlling facial expressions and body movements in the computer generated animated short ‘Tony de Peltrie’. In SIGGRAPH 85 Tutorial Notes, Advanced Computer Animation Course.Google Scholar
4. Blanz, V., and Vetter, T. 1999. A morphable model for the synthesis of 3d faces. In Proc. of SIGGRAPH 99, ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, 187–194. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Börm, S., Grasedyck, L., and Hackbusch, W. 2003. Introduction to hierarchical matrices with applications. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements 27, 5, 405–422.Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Börm, S. 2010. Efficient numerical methods for non-local operators: H2-matrix compression, algorithms and analysis. EMS Tracts in Math. European Mathematical Society.Google Scholar
7. Carr, J. C., Beatson, R. K., Cherrie, J. B., Mitchell, T. J., Fright, W. R., McCallum, B. C., and Evans, T. R. 2001. Reconstruction and representation of 3d objects with radial basis functions. In Proc. of SIGGRAPH 2001, ACM, Computer Graphics Proceedings, Annual Conference Series, 67–76. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Çivril, A., and Magdon-Ismail, M. 2009. On selecting a maximum volume sub-matrix of a matrix and related problems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 410 (November), 4801–4811. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Chandrasekaran, S., Gu, M., and Pals, T. 2004. Fast and stable algorithms for hierarchically semi-separable representations. Tech. rep., University of California, Berkeley.Google Scholar
10. Chuang, E. S. 2004. Analysis, synthesis, and retargeting of facial expressions. PhD thesis, Stanford, CA, USA. AAI3128633. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Deng, Z., Chiang, P.-Y., Fox, P., and Neumann, U. 2006. Animating blendshape faces by cross-mapping motion capture data. In Proc. of the 2006 Symp. on Interactive 3D graphics and games, ACM, New York, NY, USA, I3D ’06, 43–48. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Ernst, J., 2011. Fast and efficient facial rigging. Talk at Game Developers Conference (GDC) 2011.Google Scholar
13. Feng, W.-W., Kim, B.-U., and Yu, Y. 2008. Real-time data driven deformation using kernel canonical correlation analysis. ACM Trans. Graph. 27 (August), 91:1–91:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Irving, G. 2011. Banded householder representation of linear subspaces. http://arxiv.org/abs/1108.5822.Google Scholar
15. Johnson, S. G., 2010. The NLopt nonlinear-optimization package. http://ab-initio.mit.edu/nlopt.Google Scholar
16. Joshi, P., Tien, W. C., Desbrun, M., and Pighin, F. 2003. Learning controls for blend shape based realistic facial animation. In Proc. of the 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comp. Anim., Eurographics Association, SCA ’03, 187–192. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Joshi, P., Meyer, M., DeRose, T., Green, B., and Sanocki, T. 2007. Harmonic coordinates for character articulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 26 (July). Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Ju, T., Schaefer, S., and Warren, J. 2005. Mean value coordinates for closed triangular meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 24 (July), 561–566. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Karni, Z., and Gotsman, C. 2000. Spectral compression of mesh geometry. In Proc. of SIGGRAPH 2000, ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, 279–286. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Kernighan, B. W., and Lin, S. 1970. An Efficient Heuristic Procedure for Partitioning Graphs. The Bell System Tech. J. 49, 1, 291–307.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. Lau, M., Chai, J., Xu, Y.-Q., and Shum, H.-Y. 2009. Face poser: Interactive modeling of 3d facial expressions using facial priors. ACM Trans. Graph. 29 (December), 3:1–3:17. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Lewis, J., and Anjyo, K.-i. 2010. Direct manipulation blend-shapes. IEEE Comp. Graph. and Appl. 30, 4 (July-Aug.), 42–50. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Lewis, J. P., Mooser, J., Deng, Z., and Neumann, U. 2005. Reducing blendshape interference by selected motion attenuation. In Proc. of the 2005 Symp. on Interactive 3D graphics and games, ACM, New York, NY, USA, I3D ’05, 25–29. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Li, H., Weise, T., and Pauly, M. 2010. Example-based facial rigging. ACM Trans. Graph. 29 (July), 32:1–32:6. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Lipman, Y., Kopf, J., Cohen-Or, D., and Levin, D. 2007. Gpu-assisted positive mean value coordinates for mesh deformations. In Proc. of the fifth Eurographics Symp. on Geom. Proc. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Loiola, E. M., Maria, N., Abreu, M., Boaventuranetto, P. O., Hahn, P., and Querido, T. 2007. An analytical survey for the quadratic assignment problem. European Journal Operational Research 176, 657–690.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Nguyen, H. 2007. GPU Gems 3. Addison-Wesley Professional. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. NVIDIA. 2010. CUDA Compute Unified Device Architecture – Programming Guide.Google Scholar
29. Osipa, J. 2010. Stop Staring: Facial Modeling and Animation Done Right, 3rd Ed. Sybex. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Peng, J., Kim, C.-S., and Kuo, C.-C. J. 2005. Technologies for 3d mesh compression: A survey. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation 16, 6, 688–733. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Pighin, F., Hecker, J., Lischinski, D., Szeliski, R., and Salesin, D. H. 1998. Synthesizing realistic facial expressions from photographs. In Proc. of SIGGRAPH 98, ACM, New York, NY, USA, 75–84. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Powell, M. J. D. 2009. The BOBYQA algorithm for bound constrained optimization without derivatives. Tech. rep., Cambridge, England.Google Scholar
33. Raitt, B., 2004. The making of gollum. Presentation at U. Southern California Institute for Creative Technologies’ Frontiers of Facial Animation Workshop, August.Google Scholar
34. Seol, Y., Seo, J., Kim, P. H., Lewis, J. P., and Noh, J. 2011. Artist friendly facial animation retargeting. ACM Trans. Graph. (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ASIA 2011) 30, 6. Google Scholar
35. Sifakis, E., Neverov, I., and Fedkiw, R. 2005. Automatic determination of facial muscle activations from sparse motion capture marker data. ACM Trans. Graph. 24 (July), 417–425. Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Sorkine, O., Cohen-Or, D., Irony, D., and Toledo, S. 2005. Geometry-aware bases for shape approximation. IEEE Trans. on Viz. and Comp. Graph. 11, 2 (March-April), 171–180. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Stefanoski, N., and Ostermann, J. 2008. Spatially and temporally scalable compression of animated 3d meshes with MPEG-4/FAMC. In ICIP ’08 – IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 0.Google Scholar
38. Sumner, R. W., Zwicker, M., Gotsman, C., and Popović, J. 2005. Mesh-based inverse kinematics. ACM Trans. Graph. 24 (July), 488–495. Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Vlasic, D., Brand, M., Pfister, H., and Popović, J. 2005. Face transfer with multilinear models. ACM Trans. Graph. 24 (July), 426–433. Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Wu, Q., Xia, T., Chen, C., Lin, H.-Y. S., Wang, H., and Yu, Y. 2008. Hierarchical tensor approximation of multidimensional visual data. IEEE Trans. on Vis. and Comp. Graph. 14 (January), 186–199. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Xia, J., Chandrasekaran, S., Gu, M., and Li, X. S. 2010. Fast algorithms for hierarchically semiseparable matrices. Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications 17, 6, 953–976.Google ScholarCross Ref
42. Zhang, L., Snavely, N., Curless, B., and Seitz, S. M. 2004. Spacetime faces: high resolution capture for modeling and animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 23 (August), 548–558. Google ScholarDigital Library