“Combining hierarchical radiosity and discontinuity meshing” by Lischinski, Tampieri and Greenberg
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Combining hierarchical radiosity and discontinuity meshing
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
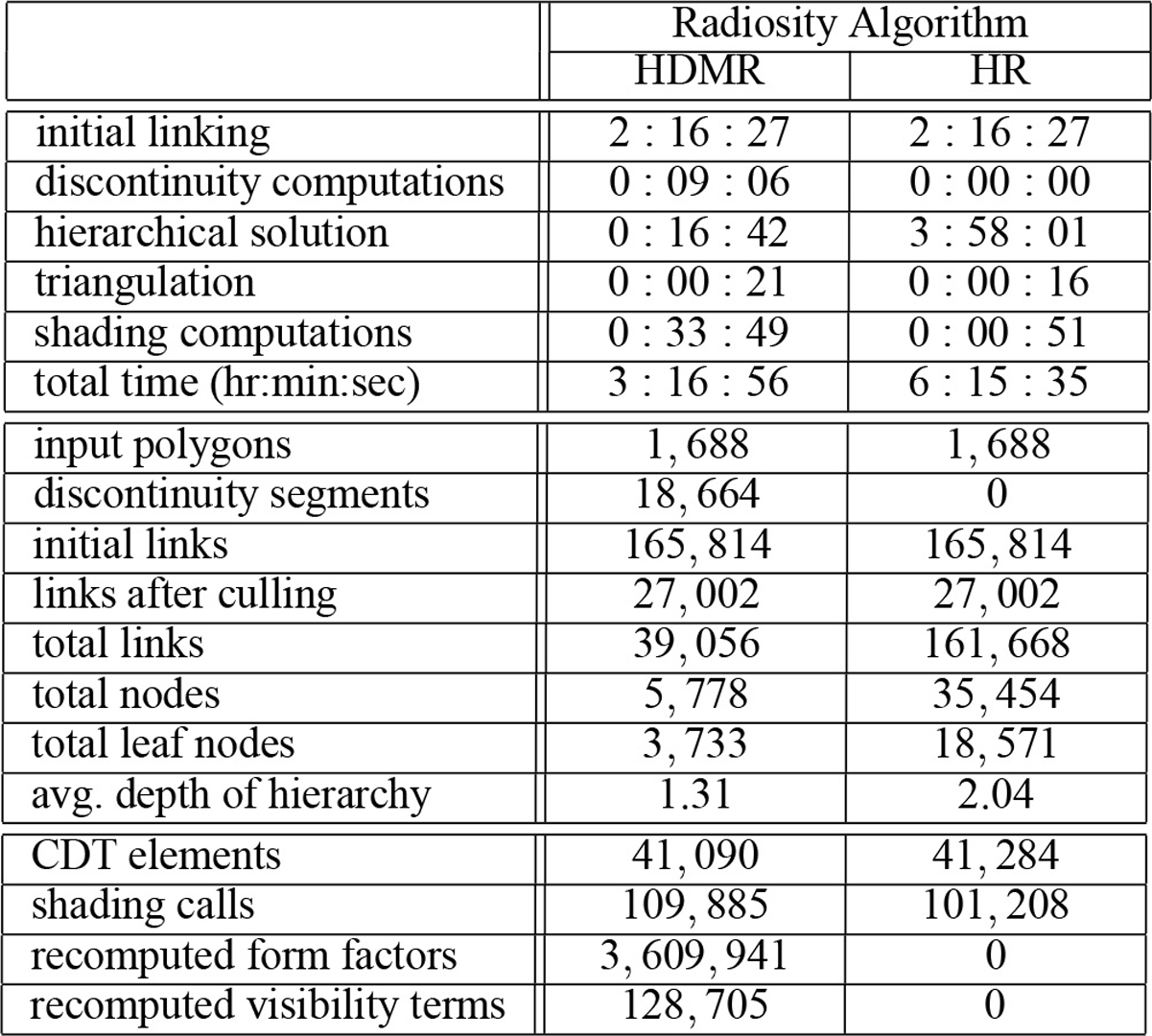
We introduce a new approach for the computation of viewindependent solutions to the diffuse global illumination problem in
polyhedral environments. The approach combines ideas from hierarchical radiosity and discontinuity meshing to yield solutions that
are accurate both numerically and visually. First, we describe a
modified hierarchical radiosity algorithm that uses a discontinuitydriven subdivision strategy to achieve better numerical accuracy and
faster convergence. Second, we present a new algorithm based on
discontinuity meshing that uses the hierarchical solution to reconstruct an object-space approximation to the radiance function that is
visually accurate. Our results show significant improvements over
both hierarchical radiosity and discontinuity meshing algorithms.
References:
1. Baum, Daniel R., Stephen Mann, Kevin E Smith, and James M. Winget. “Making Radiosity Usable: Automatic Preprocessing and Meshing Techniques for the Generation of Accurate Radiosity Solutions,” Computer Graphics, 25(4), July 1991, pages 51-60.]]
2. Bern, Marshall and David Eppstein. “Mesh Generation and Optimal Triangulation,” in Hwang, F.K. and D.-Z. Du, editors, Computing in Euclidian Geometry, World Scientific, 1992.]]
3. Campbell, III, A. T. Modeling Global Diffuse Illumination for Image Synthesis, PhD dissertation, U. of Texas at Austin, Texas, December 1991.]]
4. Chen, Shenchang Eric, Holly E. Rushmeier, Gavin Miller, and Douglass Turner. “A Progressive Multi-Pass Method for Global Illumination,” Computer Graphics, 25(4), July 1991, pages 165-174.]]
5. Chew, L. Paul. “Constrained Delaunay Triangulations,”Algorithmica, 4, 1989, pages 97-108.]]
6. Chin, Norman and Steven Feiner. “Fast Object-Precision Shadow Generation for Area Light Sources Using BSP Trees,” in Proceedings of 1992 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics, March 1992.]]
7. Cohen, Michael F. and Donald E Greenberg. “The Hemi-Cube: A Radiosity Solution for Complex Environments,” Computer Graphics, 19(3), July 1985, pages 31-40.]]
8. Cohen, Michael F., Donald E Greenberg, and David S. Immel. “An Efficient Radiosity Approach for Realistic Image Synthesis,” IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 6(2), March 1986, pages 26-35.]]
9. Gigus, Ziv and Jitendra Malik. “Computing the Aspect Graph for Line Drawings of Polyhedral Objects,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 12(2), February 1990, pages 113-122.]]
10. Goral, Cindy M., Kenneth E. Torrance, Donald E Greenberg, and Bennett Battaile. “Modeling the Interaction of Light Between Diffuse Surfaces,” Computer Graphics, 18(3), July 1984, pages 213-222.]]
11. Guibas, Leonidas and Jorge Stolfi. “Primitives for the Manipulation of General Subdivisions and the Computation of Voronoi Diagrams,” ACM Transactions on Graphics, 4(2), April 1985, pages 74-123.]]
12. Haines, Eric A. “Ronchamp: A Case Study for Radiosity,” SIG- GRAPH’ 91 Frontiers in Rendering Course Notes, July 1991.]]
13. Haines, Eric A. and John R. Wallace. “Shaft Culling for Efficient Ray- Traced Radiosity,” in Proceedings of the Second Eurographics Workshop on Rendering, May 1991.]]
14. Hanrahan, Pat, David Salzman, and Larry Aupperle. “A Rapid Hierarchical Radiosity Algorithm,” Computer Graphics, 25(4), July 1991, pages 197-206.]]
15. Heckbert, Paul S. “Discontinuity Meshing for Radiosity,” in Proceedings of the Third Eurographics Workshop on Rendering, May 1992, pages 203-216.]]
16. Heckbert, Paul S. Simulating Global Illumination Using Adaptive Meshing, PhD dissertation, UC Berkeley, California, June 1991.]]
17. Kok, Arjan J. F. and Frederik Jansen. “Source Selection for the Direct Lighting Computation in Global Illumination,” in Proceedings of the Second Eurographics Workshop on Rendering, May 1991.]]
18. Lischinski, Dani, Filippo Tampieri, and Donald E Greenberg. “Discontinuity Meshing for Accurate Radiosity,”IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 12(6), November 1992, pages 25-39.]]
19. Nishita, Tomoyuki and Eihachiro Nakamae. “Continuous Tone Representation of Three-Dimensional Objects Taking Account of Shadows and Interreflections,” Computer Graphics, 19(3), July 1985, pages 23- 30.]]
20. Reichert, Mark C. A Two-Pass Radiosity Method Driven by Lights and Viewer Position, Master’s thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, January 1992.]]
21. Salesin, David, Dani Lischinski, and Tony DeRose. “Reconstructing Illumination Functions with Selected Discontinuities,” in Proceedings of the Third Eurographics Workshop on Rendering, May 1992, pages 99-112.]]
22. Smits, Brian E., James R. Arvo, and David H. Salesin. “An Importance-Driven Radiosity Algorithm,” Computer Graphics, 26(4), July 1992, pages 273-282.]]
23. Sparrow, Ephraim M. “On the Calculation of Radiant Interchange between Surfaces,” in Ibele, Warren E., editor, Modern Developements in Heat Transfer, Academic Press, New York, 1963.]]
24. Tampieri, Filippo. Discontinuity Meshing for Radiosity Image Synthesis, PhD dissertation, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, May 1993.]]
25. Teller, Seth J. “Computing the Antipenumbra of an Area Light Source,” Computer Graphics, 26(4), July 1992, pages 139-148.]]
26. Teller, Seth and Pat Hanrahan. “Global Visibility Algorithms for Illumination Computations,” Computer Graphics, 27(4), August 1993.]]
27. Zienkiewicz, O. C. and R. L. Taylor. The Finite Element Method, pages 128-132, Vol. 1, McGraw-Hill, London, 4th edition, 1989.]]