“Bounded distortion tetrahedral metric interpolation” by Aharon, Chen, Zorin and Weber
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Bounded distortion tetrahedral metric interpolation
Session/Category Title:
- Composing & Decomposing Geometry
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
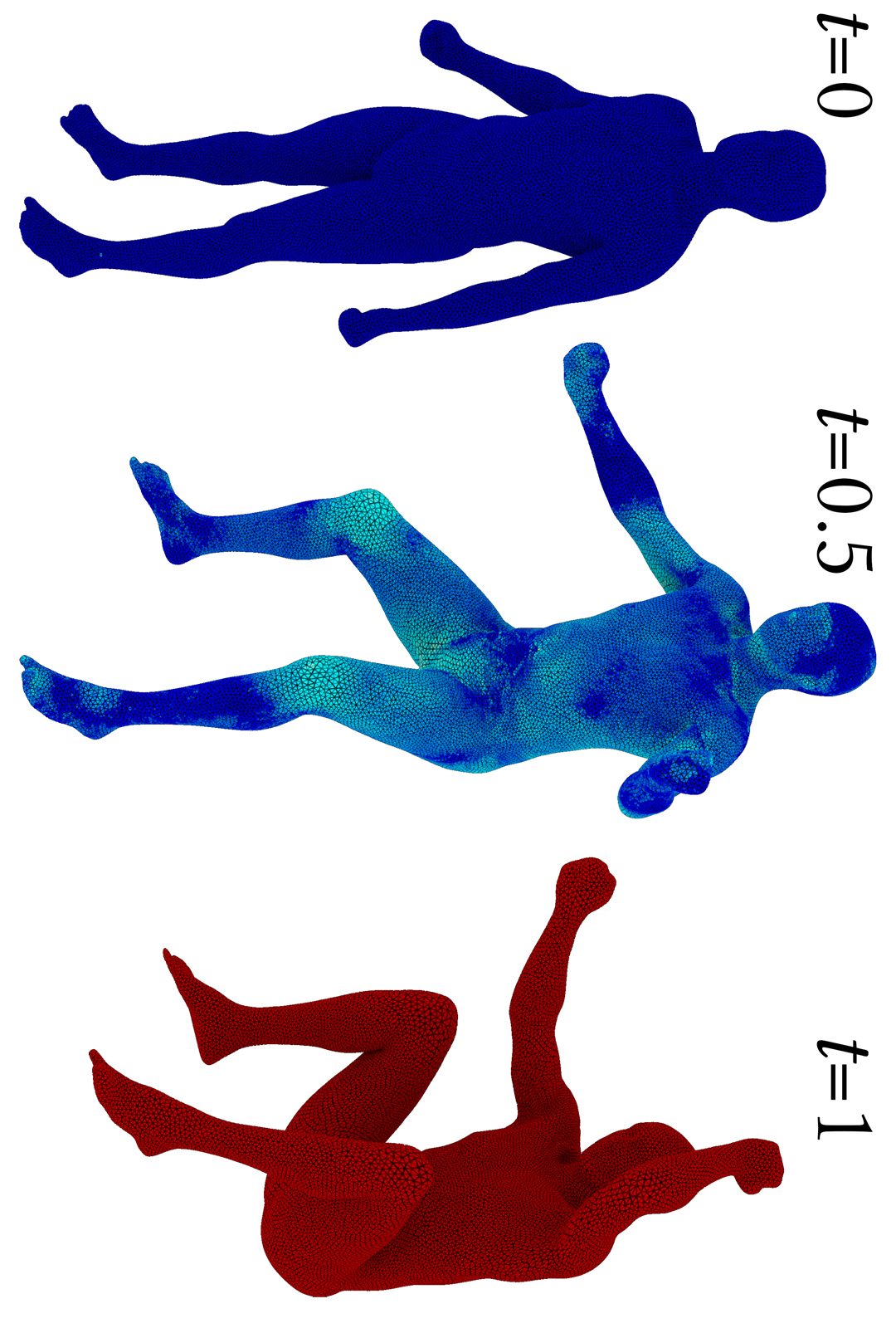
We present a method for volumetric shape interpolation with unique shape preserving features. The input to our algorithm are two or more 3-manifolds, immersed into R3 and discretized as tetrahedral meshes with shared connectivity. The output is a continuum of shapes that naturally blends the input shapes, while striving to preserve the geometric character of the input. The basis of our approach relies on the fact that the space of metrics with bounded isometric and angular distortion is convex [Chien et al. 2016b]. We show that for high dimensional manifolds, the bounded distortion metrics form a positive semidefinite cone product space. Our method can be seen as a generalization of the bounded distortion interpolation technique of [Chen et al. 2013] from planar shapes immersed in R2 to solids in R3. The convexity of the space implies that a linear blend of the (squared) edge lengths of the input tetrahedral meshes is a simple yet powerful-and-natural choice. Linearly blending flat metrics results in a new metric which is, in general, not flat, and cannot be immersed into three-dimensional space. Nonetheless, the amount of curvature that is introduced in the process tends to be very low in practical settings. We further design an extremely robust nonconvex optimization procedure that efficiently flattens the metric. The flattening procedure strives to preserve the low distortion exhibited in the blended metric while guaranteeing the validity of the metric, resulting in a locally injective map with bounded distortion. Our method leads to volumetric interpolation with superb quality, demonstrating significant improvement over the state-of-the-art and qualitative properties which were obtained so far only in interpolating manifolds of lower dimensions.
References:
1. Aigerman Noam and Lipman Yaron. 2013. Injective and bounded distortion mappings in 3D. ACM Transactions on Graphics 32, 4 (2013), 106.Google Scholar
2. Alexa Marc. 2002. Recent advances in mesh morphing. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 21. Wiley Online Library, 173–198.Google Scholar
3. Alexa Marc, Cohen-Or Daniel, and Levin David. 2000. As-rigid-as-possible Shape Interpolation. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’00). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, 157–164.Google Scholar
4. Alsing Paul M, McDonald Jonathan R, and Miller Warner A. 2011. The simplicial Ricci tensor. Classical and Quantum Gravity 28, 15 (2011), 155007.Google ScholarCross Ref
5. ApS MOSEK. 2018. The MOSEK optimization software. http://www.mosek.com/Google Scholar
6. Boggs Paul T and Tolle Jon W. 1995. Sequential Quadratic Programming. Acta numerica 4 (1995), 1–51.Google Scholar
7. Boyd Stephen, El Ghaoui Laurent, Feron Eric, and Balakrishnan Venkataramanan. 1994. Linear matrix inequalities in system and control theory. Vol. 15. Siam.Google Scholar
8. Boyd Stephen and Vandenberghe Lieven. 2004. Convex optimization. Cambridge university press.Google Scholar
9. Chao Isaac, Pinkall Ulrich, Sanan Patrick, and Schröder Peter. 2010. A simple geometric model for elastic deformations. ACM Transactions on Graphics 29, 4 (2010), Article 38, 6 pages.Google Scholar
10. Chen Renjie and Weber Ofir. 2015. Bounded distortion harmonic mappings in the plane. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 4 (2015), Article 73, 12 pages.Google Scholar
11. Chen Renjie and Weber Ofir. 2017. GPU-Accelerated Locally Injective Shape Deformation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 6 (2017), Article 214, 13 pages.Google Scholar
12. Chen Renjie, Weber Ofir, Keren Daniel, and Ben-Chen Mirela. 2013. Planar shape interpolation with bounded distortion. ACM Transactions on Graphics 32, 4 (2013), Article 108, 11 pages.Google Scholar
13. Chern Albert, Pinkall Ulrich, and Schröder Peter. 2015. Close-to-conformal Deformations of Volumes. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 4, Article 56 (2015), 13 pages.Google Scholar
14. Chien Edward, Chen Renjie, and Weber Ofir. 2016a. Bounded Distortion Harmonic Shape Interpolation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 35, 4 (2016), Article 105, 15 pages.Google Scholar
15. Chien Edward, Levi Zohar, and Weber Ofir. 2016b. Bounded Distortion Parametrization in the Space of Metrics. ACM Transactions on Graphics 35, 6 (2016), Article 215, 16 pages.Google Scholar
16. Conboye Rory and Miller Warner A. 2017. Piecewise flat curvature and Ricci flow in three dimensions. Asian Journal of Mathematics 21, 6 (2017), 1063–1098.Google ScholarCross Ref
17. Crane Keenan, Pinkall Ulrich, and Schröder Peter. 2011. Spin transformations of discrete surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics 30, 4 (2011), 104.Google Scholar
18. Dattorro Jon. 2010. Convex optimization & Euclidean distance geometry. Lulu. com.Google Scholar
19. Dinh Quoc Tran and Diehl Moritz. 2010. Local convergence of sequential convex programming for nonconvex optimization. In Recent Advances in Optimization and its Applications in Engineering. Springer, 93–102.Google Scholar
20. Fu Xiao-Ming, Bai Chong-Yang, and Liu Yang. 2016. Efficient Volumetric PolyCube-Map Construction. Comput. Graph. Forum 35, 7 (Oct. 2016), 97–106.Google Scholar
21. Grant Michael, Boyd Stephen, and Ye Yinyu. 2008. CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming.Google Scholar
22. Heeren Behrend, Rumpf Martin, Schröder Peter, Wardetzky Max, and Wirth Benedikt. 2014. Exploring the geometry of the space of shells. Computer Graphics Forum 33, 5 (2014), 247–256.Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Heeren Behrend, Rumpf Martin, Wardetzky Max, and Wirth Benedikt. 2012. Time-discrete geodesics in the space of shells. Computer Graphics Forum 31, 5 (2012), 1755–1764.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Hefetz Fedida Eden, Chien Edward, and Weber Ofir. 2017. Fast Planar Harmonic Deformations with Alternating Tangential Projections. Computer Graphics Forum 36, 5 (2017), 175–188. Proceedings of Symposium on Geometry Processing 2017.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Hefetz Fedida Eden, Chien Edward, and Weber Ofir. 2019. A Subspace Method for Fast Locally Injective Harmonic Mapping. Computer Graphics Forum 38, 2 (2019).Google Scholar
26. Jiang Zhongshi, Schaefer Scott, and Panozzo Daniele. 2017. Simplicial Complex Augmentation Framework for Bijective Maps. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 6 (Nov. 2017), Article 186, 9 pages.Google Scholar
27. Kilian M., Mitra N.J., and Pottmann H. 2007. Geometric modeling in shape space. In ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 26. ACM, 64.Google Scholar
28. Kircher S. and Garland M. 2008. Free-form motion processing. ACM Transactions on Graphics 27, 2 (2008), 12.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Kovalsky Shahar Z., Aigerman Noam, Basri Ronen, and Lipman Yaron. 2014. Controlling Singular Values with Semidefinite Programming. ACM Transactions on Graphics 33, 4 (2014).Google Scholar
30. Kovalsky Shahar Z., Aigerman Noam, Basri Ronen, and Lipman Yaron. 2015. Large-scale bounded distortion mappings. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 6 (2015), Article 191.Google Scholar
31. Kovalsky Shahar Z., Galun Meirav, and Lipman Yaron. 2016. Accelerated QuadraticGoogle Scholar
32. Proxy for Geometric Optimization. ACM Transactions on Graphics 35, 4 (2016), Article 134.Google Scholar
33. Lee Jung Rye. 1997. The law of cosines in a tetrahedron. J. Korea Soc. Math. Ed. Ser. B: Pure Appl. Math 4, 1 (1997), 1–6.Google Scholar
34. Levi Zohar and Weber Ofir. 2016. On the convexity and feasibility of the bounded distortion harmonic mapping problem. ACM Transactions on Graphics 35, 4 (2016), Article 106, 15 pages.Google Scholar
35. Lipman Yaron. 2012. Bounded distortion mapping spaces for triangular meshes. ACM Transactions on Graphics 31, 4 (2012), 108.Google Scholar
36. Liu Ligang, Ye Chunyang, Ni Ruiqi, and Fu Xiao-Ming. 2018. Progressive Parameterizations. ACM Transactions on Graphics 37, 4, Article 41 (2018), 12 pages.Google Scholar
37. Nocedal Jorge and Wright Stephen. 2006. Numerical Optimization. Springer New York.Google Scholar
38. Paillé Gilles-Philippe, Ray Nicolas, Poulin Pierre, Sheffer Alla, and Lévy Bruno. 2015. Dihedral Angle-based Maps of Tetrahedral Meshes. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 4 (2015), 54.Google Scholar
39. Poranne Roi and Lipman Yaron. 2014. Provably good planar mappings. ACM Transactions on Graphics 33, 4 (2014), 76.Google Scholar
40. Rabinovich Michael, Poranne Roi, Panozzo Daniele, and Sorkine-Hornung Olga. 2017. Scalable Locally Injective Mappings. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 2, Article 16 (2017).Google Scholar
41. Regge Tullio. 1961. General relativity without coordinates. Il Nuovo Cimento (1955–1965) 19, 3 (1961), 558–571.Google Scholar
42. Rumpf Martin and Wirth Benedikt. 2009. A Nonlinear Elastic Shape Averaging Approach. SIAM J. Img. Sci. 2, 3 (July 2009), 800–833.Google Scholar
43. Sanan Patrick. 2014. Geometric Elasticity for Graphics, Simulation, and Computation. Ph.D. Dissertation. California Institute of Technology.Google Scholar
44. Schenk Olaf. 2018. PARDISO 6.0. https://www.pardiso-project.org/Google Scholar
45. Sederberg T.W. and Greenwood E. 1992. A physically based approach to 2-D shape blending. In ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, Vol. 26. ACM, 25–34.Google Scholar
46. Shtengel Anna, Poranne Roi, Sorkine-Hornung Olga, Kovalsky Shahar Z., and Lipman Yaron. 2017. Geometric Optimization via Composite Majorization. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 4, Article 38 (2017), Article 38, 11 pages pages.Google Scholar
47. Smith Breannan, de Goes Fernando, and Kim Theodore. 2019. Analytic Eigensystems for Isotropic Distortion Energies. ACM Transactions on Graphics (2019), Article 3.Google Scholar
48. Smith Jason and Schaefer Scott. 2015. Bijective Parameterization with Free Boundaries. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 4 (2015), Article 70, 9 pages.Google Scholar
49. Springborn Boris, Schröder Peter, and Pinkall Ulrich. 2008. Conformal equivalence of triangle meshes. ACM Transactions on Graphics 27, 3 (2008), 77.Google Scholar
50. Tutte W.T. 1963. How to draw a graph. Proc. London Math. Soc 13, 3 (1963), 743–768.Google ScholarCross Ref
51. Von-Tycowicz Christoph, Schulz Christian, Seidel Hans-Peter, and Hildebrandt Klaus. 2015. Real-Time Nonlinear Shape Interpolation. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 3, Article 34 (May 2015), 10 pages.Google Scholar
52. Weber Ofir and Gotsman Craig. 2010. Controllable conformal maps for shape deformation and interpolation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 29, 4 (2010), Article 78, 11 pages.Google Scholar
53. Weber Ofir, Myles Ashish, and Zorin Denis. 2012. Computing Extremal Quasiconformal Maps. Computer Graphics Forum 31, 5 (2012), 1679–1689.Google ScholarDigital Library
54. Winkler Tim, Drieseberg Jens, Alexa Marc, and Hormann Kai. 2010. Multi-scale geometry interpolation. Computer Graphics Forum 29, 2 (2010), 309–318.Google ScholarCross Ref
55. Wirth Benedikt, Bar Leah, Rumpf Martin, and Sapiro Guillermo. 2009. Geodesics in shape space via variational time discretization. In International Workshop on Energy Minimization Methods in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Springer, 288–302.Google Scholar
56. Xu Dong, Zhang Hongxin, Wang Qing, and Bao Hujun. 2006. Poisson shape interpolation. Graphical models 68 (2006), 268–281.Google Scholar
57. Yang Yang, Fu Xiao-Ming, Chai Shuangming, Xiao Shiwei, and Liu Ligang. 2018. Volume-Enhanced Compatible Remeshing of 3D Models. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics (2018).Google Scholar
58. Yin Xiaotian, Jin Miao, Luo Feng, and Gu Xianfeng David. 2008. Discrete curvature flows for surfaces and 3-manifolds. In Emerging Trends in Visual Computing. Springer, 38–74.Google Scholar
59. Zhu Yufeng, Bridson Robert, and Kaufman Danny M. 2018. Blended Cured Quasinewton for Distortion Optimization. ACM Transactions on Graphics 37, 4, Article 40 (2018), 14 pages.Google Scholar
60. Zhu Yufeng, Popović Jovan, Bridson Robert, and Kaufman Danny M. 2017. Planar interpolation with extreme deformation, topology change and dynamics. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 6 (2017), 213.Google Scholar