“ActRay: Online Active Ray Sampling for Radiance Fields” by Wu, Liu, Tan, Jia, Zhang, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- ActRay: Online Active Ray Sampling for Radiance Fields
Session/Category Title:
- Technical Papers Fast-Forward
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
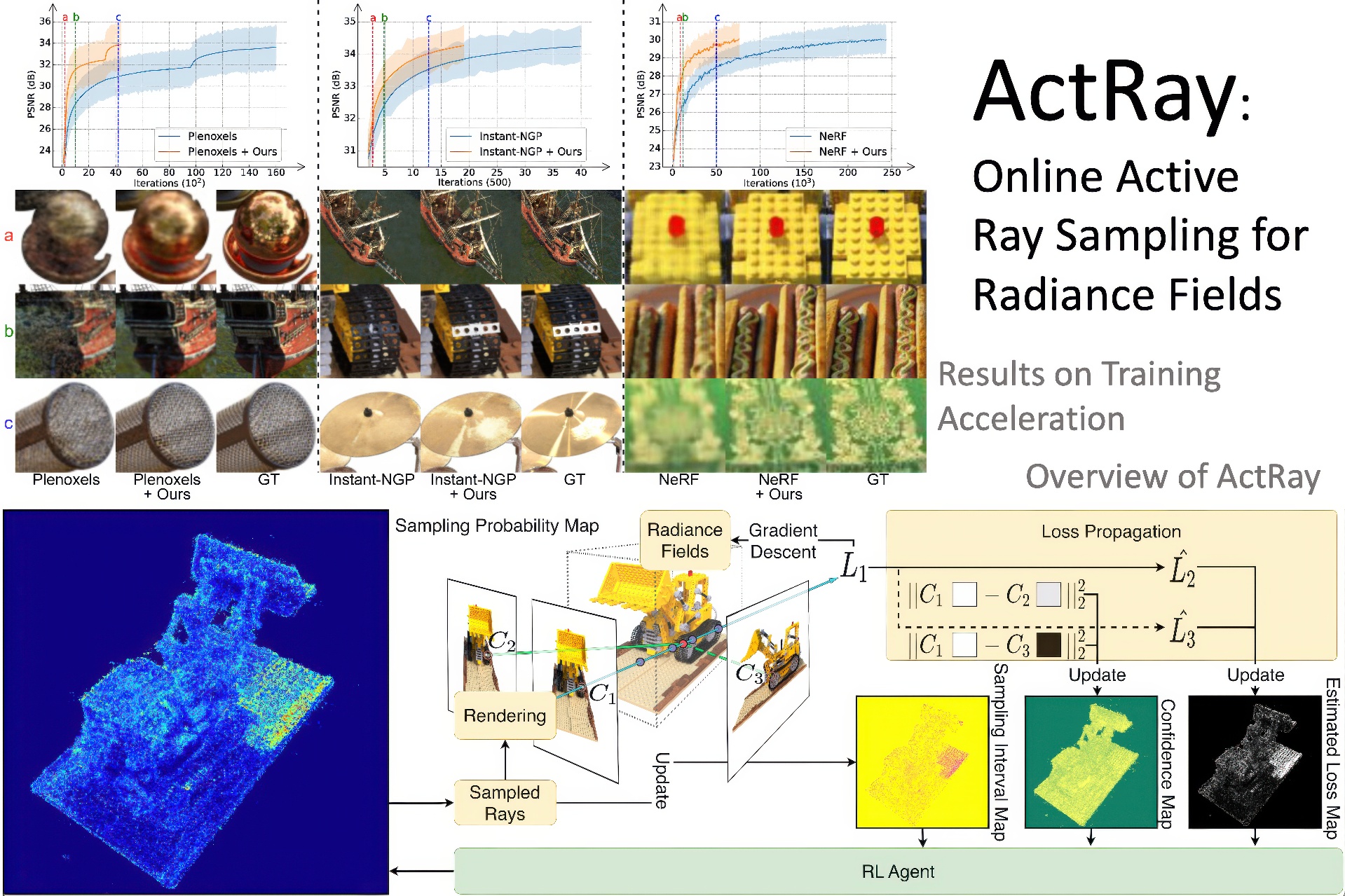
Thanks to the high-quality reconstruction and photorealistic rendering, the Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has garnered extensive attention and has been continuously improved. Despite its high visual quality, the prohibitive training time limits its practical application. Although significant acceleration has been achieved, it is still far from real-time training, due to the need for tens of thousands of iterations. In this paper, a feasible solution is to reduce the number of required iterations by always training the rays with the highest loss values, instead of the traditional method of training each ray with a uniform probability. To this end, we propose an online active ray sampling strategy, ActRay. Specifically, to avoid the substantial overhead of calculating the actual loss values for all rays in each iteration, a rendering-gradient-based loss propagation algorithm is presented to efficiently estimate the loss values. To further narrow the gap between the estimated loss and the actual loss, an online learning algorithm based on the Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) is proposed to control the sampling probability of the rays, thereby compensating for the bias in loss estimation. We evaluate ActRay on both real-world and synthetic scenes, and the promising results show that it accelerates radiance field training to 6.5x. Besides, we test ActRay under all kinds of representations of radiance fields (implicit, explicit, and hybrid), demonstrating that it is general and effective to different representations. We believe this work will contribute to the practical application of radiance fields, because it has taken a step closer to real-time radiance field training.
References:
[1]
Jonas Adler and Ozan Öktem. 2018. Learned primal-dual reconstruction. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 37, 6 (2018), 1322–1332.
[2]
Jonathan T Barron, Ben Mildenhall, Matthew Tancik, Peter Hedman, Ricardo Martin-Brualla, and Pratul P Srinivasan. 2021. Mip-nerf: A multiscale representation for anti-aliasing neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 5855–5864.
[3]
Jonathan T. Barron, Ben Mildenhall, Dor Verbin, Pratul P. Srinivasan, and Peter Hedman. 2022a. Mip-NeRF 360: Unbounded Anti-Aliased Neural Radiance Fields. CVPR (2022).
[4]
Jonathan T Barron, Ben Mildenhall, Dor Verbin, Pratul P Srinivasan, and Peter Hedman. 2022b. Mip-nerf 360: Unbounded anti-aliased neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 5470–5479.
[5]
Stavros Diolatzis, Julien Philip, and George Drettakis. 2022. Active exploration for neural global illumination of variable scenes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 41, 5 (2022), 1–18.
[6]
Zhiwen Fan, Yifan Jiang, Peihao Wang, Xinyu Gong, Dejia Xu, and Zhangyang Wang. 2022. Unified implicit neural stylization. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part XV. Springer, 636–654.
[7]
Jiemin Fang, Taoran Yi, Xinggang Wang, Lingxi Xie, Xiaopeng Zhang, Wenyu Liu, Matthias Nießner, and Qi Tian. 2022. Fast dynamic radiance fields with time-aware neural voxels. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2022 Conference Papers. 1–9.
[8]
Sara Fridovich-Keil, Giacomo Meanti, Frederik Warburg, Benjamin Recht, and Angjoo Kanazawa. 2023. K-planes: Explicit radiance fields in space, time, and appearance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.10241 (2023).
[9]
Sara Fridovich-Keil, Alex Yu, Matthew Tancik, Qinhong Chen, Benjamin Recht, and Angjoo Kanazawa. 2022. Plenoxels: Radiance fields without neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 5501–5510.
[10]
Zhang Jiakai, Liu Xinhang, Ye Xinyi, Zhao Fuqiang, Zhang Yanshun, Wu Minye, Zhang Yingliang, Xu Lan, and Yu Jingyi. 2021. Editable Free-Viewpoint Video using a Layered Neural Representation. In ACM SIGGRAPH.
[11]
Andreas Kurz, Thomas Neff, Zhaoyang Lv, Michael Zollhöfer, and Markus Steinberger. 2022. AdaNeRF: Adaptive Sampling for Real-Time Rendering of Neural Radiance Fields. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part XVII. Springer, 254–270.
[12]
Kevin Lin and Brent Yi. 2022. Active View Planning for Radiance Fields. In Robotics Science and Systems.
[13]
Lingjie Liu, Jiatao Gu, Kyaw Zaw Lin, Tat-Seng Chua, and Christian Theobalt. 2020. Neural sparse voxel fields. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33 (2020), 15651–15663.
[14]
Nelson Max. 1995. Optical models for direct volume rendering. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 1, 2 (1995), 99–108.
[15]
Ben Mildenhall, Peter Hedman, Ricardo Martin-Brualla, Pratul P. Srinivasan, and Jonathan T. Barron. 2022. NeRF in the Dark: High Dynamic Range View Synthesis From Noisy Raw Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 16190–16199.
[16]
Ben Mildenhall, Pratul P Srinivasan, Rodrigo Ortiz-Cayon, Nima Khademi Kalantari, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Ren Ng, and Abhishek Kar. 2019. Local light field fusion: Practical view synthesis with prescriptive sampling guidelines. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 4 (2019), 1–14.
[17]
Ben Mildenhall, Pratul P Srinivasan, Matthew Tancik, Jonathan T Barron, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Ren Ng. 2021. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 65, 1 (2021), 99–106.
[18]
Volodymyr Mnih, Koray Kavukcuoglu, David Silver, Alex Graves, Ioannis Antonoglou, Daan Wierstra, and Martin Riedmiller. 2013. Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.5602 (2013).
[19]
Thomas Müller, Alex Evans, Christoph Schied, and Alexander Keller. 2022. Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 41, 4 (2022), 1–15.
[20]
Thomas Neff, Pascal Stadlbauer, Mathias Parger, Andreas Kurz, Joerg H Mueller, Chakravarty R Alla Chaitanya, Anton Kaplanyan, and Markus Steinberger. 2021. DONeRF: Towards Real-Time Rendering of Compact Neural Radiance Fields using Depth Oracle Networks. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 40. Wiley Online Library, 45–59.
[21]
Michael Niemeyer and Andreas Geiger. 2021. Giraffe: Representing scenes as compositional generative neural feature fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 11453–11464.
[22]
Takashi Otonari, Satoshi Ikehata, and Kiyoharu Aizawa. 2022. Non-uniform Sampling Strategies for NeRF on 360 images. (2022).
[23]
Sida Peng, Yuanqing Zhang, Yinghao Xu, Qianqian Wang, Qing Shuai, Hujun Bao, and Xiaowei Zhou. 2021. Neural Body: Implicit Neural Representations with Structured Latent Codes for Novel View Synthesis of Dynamic Humans. In CVPR.
[24]
Albert Pumarola, Enric Corona, Gerard Pons-Moll, and Francesc Moreno-Noguer. 2021. D-nerf: Neural radiance fields for dynamic scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 10318–10327.
[25]
Johannes L Schonberger and Jan-Michael Frahm. 2016. Structure-from-motion revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 4104–4113.
[26]
John Schulman, Filip Wolski, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alec Radford, and Oleg Klimov. 2017. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06347 (2017).
[27]
Aleksandrs Slivkins 2019. Introduction to multi-armed bandits. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning 12, 1-2 (2019), 1–286.
[28]
Liangchen Song, Anpei Chen, Zhong Li, Zhang Chen, Lele Chen, Junsong Yuan, Yi Xu, and Andreas Geiger. 2023. Nerfplayer: A streamable dynamic scene representation with decomposed neural radiance fields. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 29, 5 (2023), 2732–2742.
[29]
Pratul P Srinivasan, Boyang Deng, Xiuming Zhang, Matthew Tancik, Ben Mildenhall, and Jonathan T Barron. 2021. Nerv: Neural reflectance and visibility fields for relighting and view synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 7495–7504.
[30]
Dor Verbin, Peter Hedman, Ben Mildenhall, Todd Zickler, Jonathan T Barron, and Pratul P Srinivasan. 2022. Ref-nerf: Structured view-dependent appearance for neural radiance fields. In 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, 5481–5490.
[31]
Zhou Wang, Alan C Bovik, Hamid R Sheikh, and Eero P Simoncelli. 2004. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE transactions on image processing 13, 4 (2004), 600–612.
[32]
Zian Wang, Tianchang Shen, Jun Gao, Shengyu Huang, Jacob Munkberg, Jon Hasselgren, Zan Gojcic, Wenzheng Chen, and Sanja Fidler. 2023. Neural Fields meet Explicit Geometric Representation for Inverse Rendering of Urban Scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03266 (2023).
[33]
Qiangeng Xu, Zexiang Xu, Julien Philip, Sai Bi, Zhixin Shu, Kalyan Sunkavalli, and Ulrich Neumann. 2022. Point-nerf: Point-based neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 5438–5448.
[34]
Wang Yifan, Shihao Wu, Cengiz Oztireli, and Olga Sorkine-Hornung. 2021. Iso-points: Optimizing neural implicit surfaces with hybrid representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 374–383.
[35]
Jae Shin Yoon. 2022. Metaverse in the Wild: Modeling, Adapting, and Rendering of 3D Human Avatars from a Single Camera. Ph. D. Dissertation. University of Minnesota.
[36]
Huangying Zhan, Jiyang Zheng, Yi Xu, Ian Reid, and Hamid Rezatofighi. 2022b. ActiveRMAP: Radiance Field for Active Mapping And Planning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.12656 (2022).
[37]
Xueying Zhan, Qingzhong Wang, Kuan-hao Huang, Haoyi Xiong, Dejing Dou, and Antoni B Chan. 2022a. A comparative survey of deep active learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.13450 (2022).
[38]
Kai Zhang, Gernot Riegler, Noah Snavely, and Vladlen Koltun. 2020. Nerf++: Analyzing and improving neural radiance fields. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.07492 (2020).
[39]
Richard Zhang, Phillip Isola, Alexei A Efros, Eli Shechtman, and Oliver Wang. 2018. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 586–595.