“Superimposing Dynamic Range” by Bimber, Iwai and Iwai
Conference:
Experience Type(s):
Title:
- Superimposing Dynamic Range
Entry Number: 37
Organizer(s)/Presenter(s):
Description:
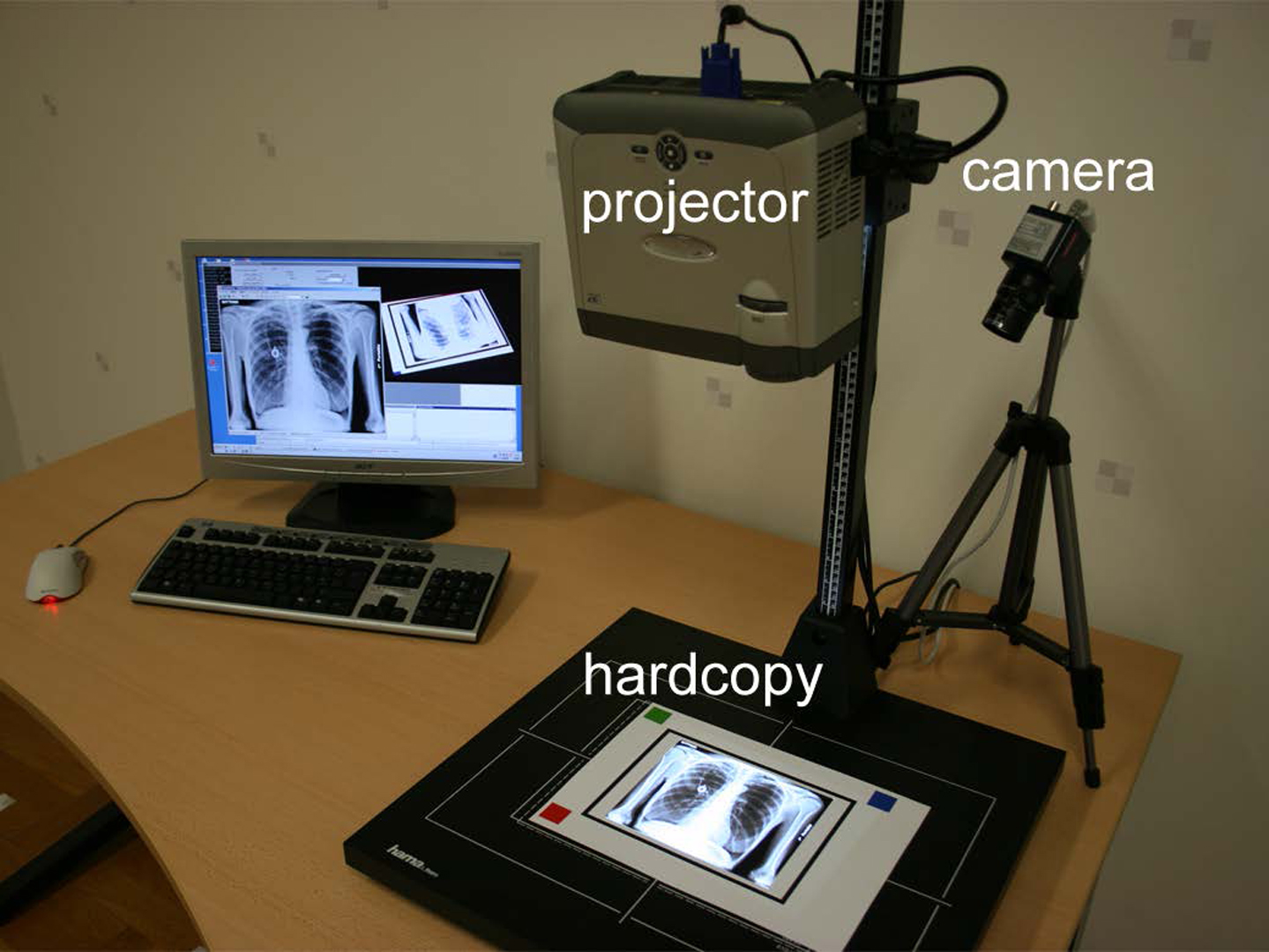
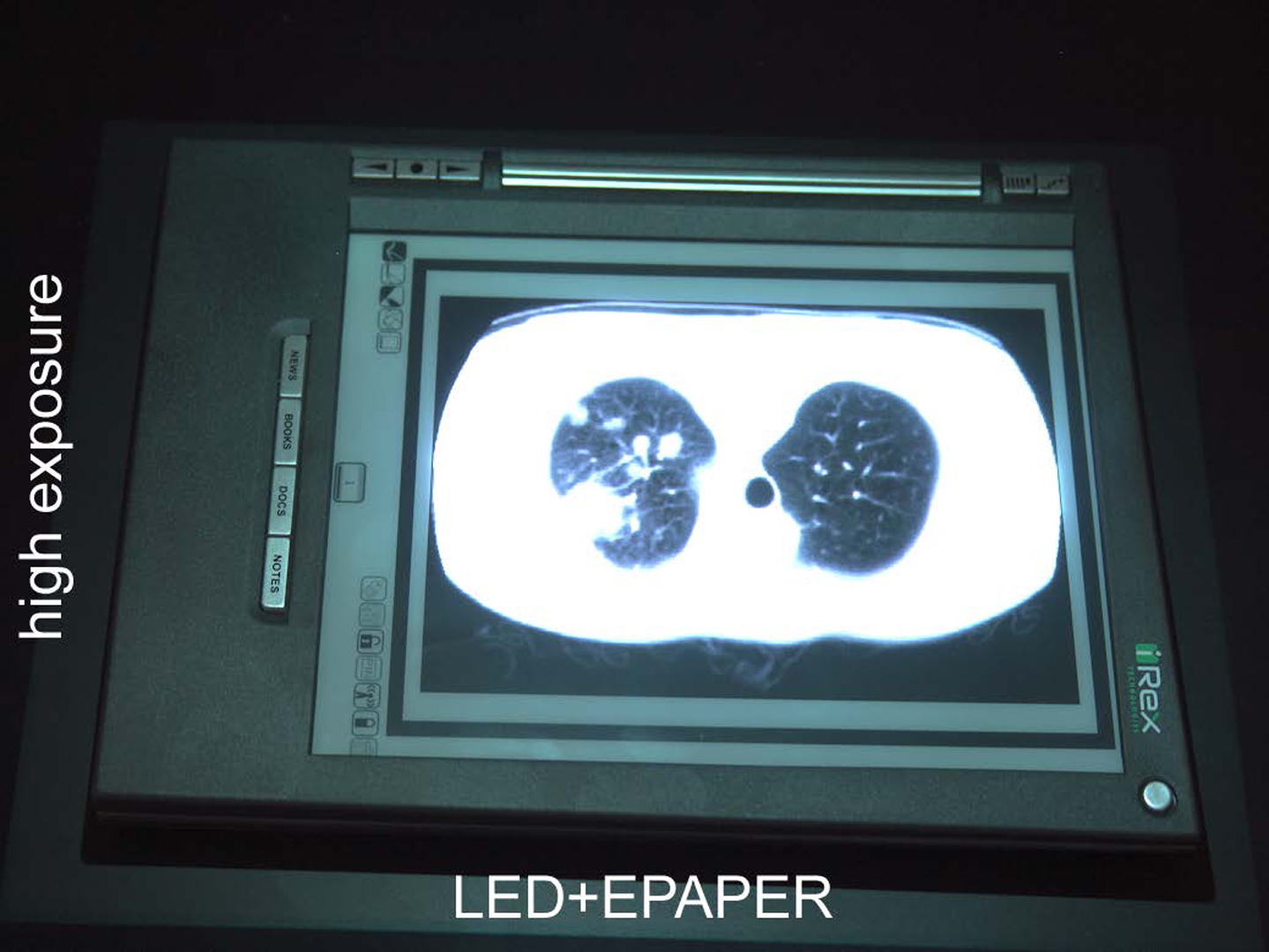
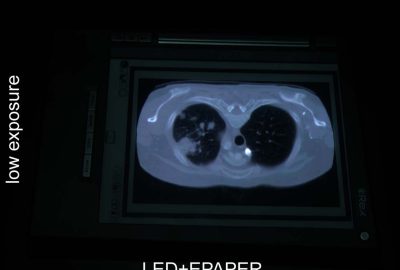
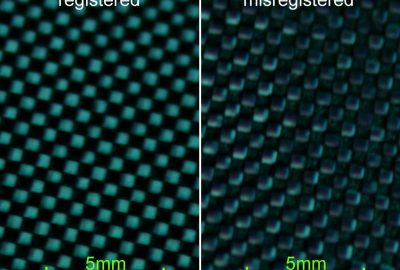
It was only recently that high dynamic range (HDR) displays were introduced which could present content over several orders of magnitude between minimum and maximum luminance (e.g., [Seetzen et al. 2004]). All of the approaches share three common properties: These are firstly that they apply a transmissive image modulation (either through transparencies or LCD/LCoS panels) and consequently suffer from a relatively low light-throughput (e.g., regular color / monochrome LCD panels transmit less than 3-6% / 15-30% of light) and therefore require exceptionally bright backlights. Secondly, one of the two modulation images is of low-resolution and blurred in order to avoid artifacts such as moir´e patterns due to the misalignment of two modulators, as well as to realize acceptable frame-rates. Thus, high contrast values can only be achieved in a resolution of the low-frequency image. Thirdly, since one of the two images is monochrome (mainly to reach a high peak luminance), only luminance is modulated, while chrominance modulation for extending the color space is in some cases considered future work. We present a simple and low-cost method of viewing static HDR content based on reflective image modulation.
Other Information:
References
MANTIUK, R., DALY, S. J., MYSZKOWSKI, K., AND SEIDEL, H.-P. 2005. Predicting visible differences in high dynamic range images – model and its calibration. In Proc. IS&T/SPIE’s Annual Symposium on Electronic Imaging, vol. 5666, 204–214.
SEETZEN, H., HEIDRICH, W., STUERZLINGER, W., WARD, G., WHITEHEAD, L., TRENTACOSTE, M., GHOSH, A., AND VOROZCOVS, A. 2004. High dynamic range display systems. In Proc. ACM Siggraph, 760–768.
Additional Images:
- 2008 ETech Bimber: Superimposing Dynamic Range
- 2008 ETech Bimber: Superimposing Dynamic Range
- 2008 ETech Bimber: Superimposing Dynamic Range
- 2008 ETech Bimber: Superimposing Dynamic Range
- 2008 ETech Bimber: Superimposing Dynamic Range
- 2008 ETech Bimber: Superimposing Dynamic Range
- 2008 ETech Bimber: Superimposing Dynamic Range
- 2008 ETech Bimber: Superimposing Dynamic Range