“Implicit Conversion of Manifold B-Rep Solids by Neural Halfspace Representation” by Guo, Liu, Pan and Guo
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Implicit Conversion of Manifold B-Rep Solids by Neural Halfspace Representation
Session/Category Title: Computer-Aided Design
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
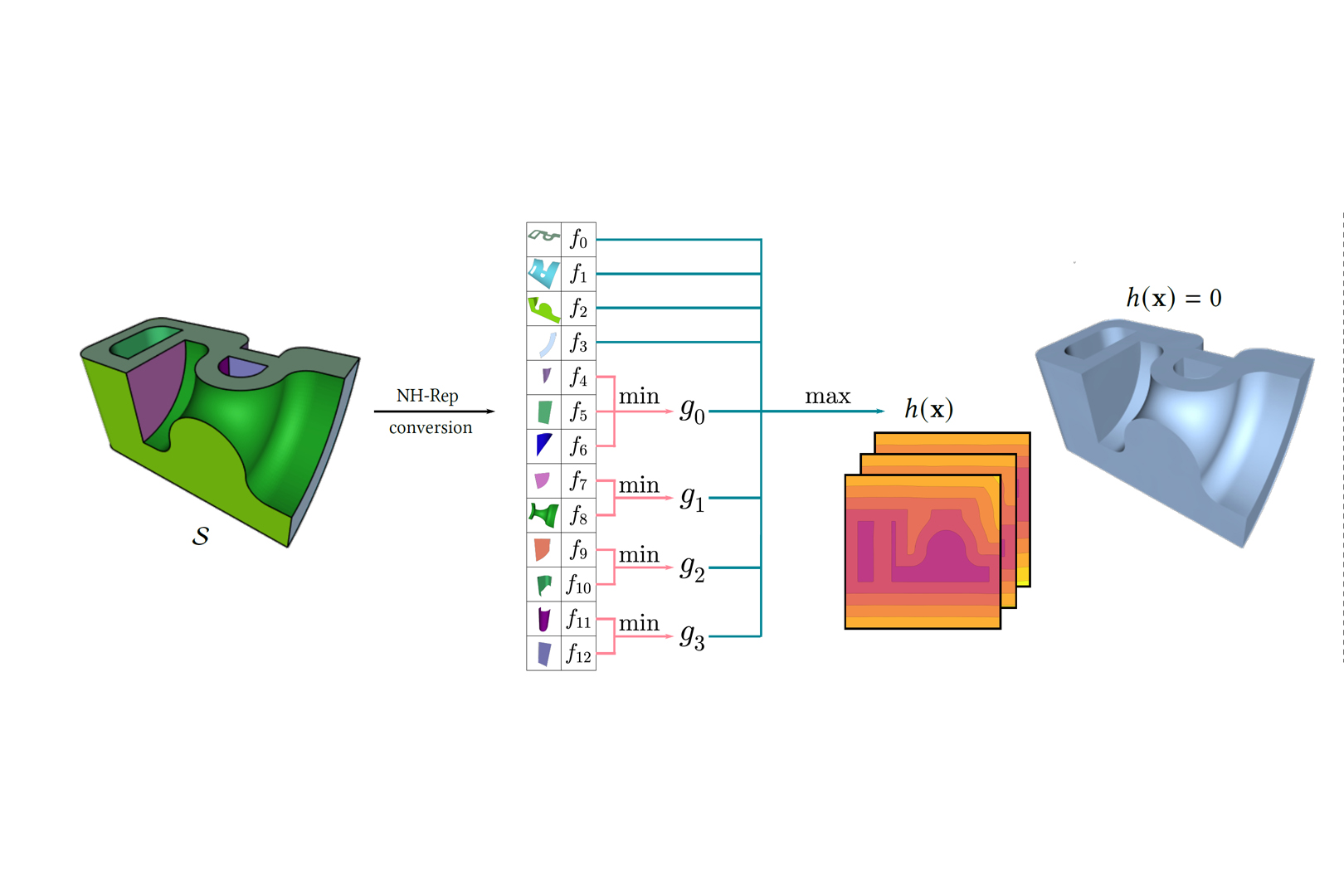
We present a novel implicit representation — neural halfspace representation (NH-Rep), to convert manifold B-Rep solids to implicit representations. NH-Rep is a Boolean tree built on a set of implicit functions represented by the neural network, and the composite Boolean function is capable of representing solid geometry while preserving sharp features. We propose an efficient algorithm to extract the Boolean tree from a manifold B-Rep solid and devise a neural network-based optimization approach to compute the implicit functions. We demonstrate the high quality offered by our conversion algorithm on ten thousand manifold B-Rep CAD models that contain various curved patches including NURBS, and the superiority of our learning approach over other representative implicit conversion algorithms in terms of surface reconstruction, sharp feature preservation, signed distance field approximation, and robustness to various surface geometry, as well as a set of applications supported by NH-Rep.
References:
1. George Allen. 2021. nTopology’s Implicit Modeling Technology. https://ntopology.com/resources/whitepaper-implicit-modeling-technology/. Last accessed 2021-12-1.
2. Matan Atzmon and Yaron Lipman. 2020. SAL: Sign agnostic learning of shapes from raw data. In CVPR.
3. Matthew Berger, Andrea Tagliasacchi, Lee M. Seversky, Pierre Alliez, Gaël Guennebaud, Joshua A. Levine, Andrei Sharf, and Claudio T. Silva. 2017. A survey of surface reconstruction from point clouds. Comput. Graph. Forum 36, 1 (2017), 301–329.
4. Suzanne F Buchele and Richard H Crawford. 2003. Three-dimensional halfspace constructive solid geometry tree construction from implicit boundary representations. In Proceedings of the eighth ACM symposium on Solid modeling and applications. 135–144.
5. J. C. Carr, R. K. Beatson, J. B. Cherrie, T. J. Mitchell, W. R. Fright, B. C. McCallum, and T. R. Evans. 2001. Reconstruction and representation of 3D objects with radial basis functions. In SIGGRAPH. 67–76.
6. Rohan Chabra, Jan Eric Lenssen, Eddy Ilg, Tanner Schmidt, Julian Straub, Steven Lovegrove, and Richard Newcombe. 2020. Deep local shapes: Learning local SDF priors for detailed 3D reconstruction. In ECCV.
7. Angel X. Chang, Thomas Funkhouser, Leonidas Guibas, Pat Hanrahan, Qixing Huang, Zimo Li, Silvio Savarese, Manolis Savva, Shuran Song, Hao Su, Jianxiong Xiao, Li Yi, and Fisher Yu. 2015. ShapeNet: An information-rich 3D model repository. arXiv:1512.03012 [cs.GR].
8. Falai Chen, Tor Dokken, and Géraldine Morin. 2022a. Geometric Modeling: Interoperability and New Challenges (Dagstuhl Seminar 21471). Dagstuhl Reports 11, 10 (2022), 111–150.
9. Zhiqin Chen, Andrea Tagliasacchi, Thomas Funkhouser, and Hao Zhang. 2022b. Neural dual contouring. ACM Trans. Graph. (2022).
10. Zhiqin Chen, Andrea Tagliasacchi, and Hao Zhang. 2020. BSP-Net: Generating compact meshes via binary space partitioning. In CVPR.
11. Zhiqin Chen and Hao Zhang. 2019. Learning implicit fields for generative shape modeling. In CVPR.
12. Zhiqin Chen and Hao Zhang. 2021. Neural marching cubes. ACM Trans. Graph 40, 6 (2021), 1–15.
13. Julian Chibane, Thiemo Alldieck, and Gerard Pons-Moll. 2020. Implicit functions in feature space for 3D shape reconstruction and completion. In CVPR.
14. Paolo Cignoni, Marco Callieri, Massimiliano Corsini, Matteo Dellepiane, Fabio Ganovelli, and Guido Ranzuglia. 2008. MeshLab: an Open-Source Mesh Processing Tool. In Eurographics Italian Chapter Conference, Vittorio Scarano, Rosario De Chiara, and Ugo Erra (Eds.). The Eurographics Association.
15. Boyang Deng, Kyle Genova, Soroosh Yazdani, Sofien Bouaziz, Geoffrey Hinton, and Andrea Tagliasacchi. 2020. CvxNets: Learnable convex decomposition. In CVPR.
16. Tao Du, Jeevana Priya Inala, Yewen Pu, Andrew Spielberg, Adriana Schulz, Daniela Rus, Armando Solar-Lezama, and Wojciech Matusik. 2018. InverseCSG: Automatic conversion of 3D models to CSG trees. ACM Trans. Graph (2018).
17. Xingyi Du, Qingnan Zhou, Nathan Carr, and Tao Ju. 2021. Boundary-sampled halfspaces: A new representation for constructive solid modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4, Article 53 (2021), 15 pages.
18. Markus Friedrich, Pierre-Alain Fayolle, Thomas Gabor, and Claudia Linnhoff-Popien. 2019. Optimizing evolutionary CSG tree extraction. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference. 1183–1191.
19. Sarah F. Frisken, Ronald N. Perry, Alyn P. Rockwood, and Thouis R. Jones. 2000. Adaptively sampled distance fields: A general representation of shape for computer graphics. In SIGGRAPH. 249–254.
20. Amos Gropp, Lior Yariv, Niv Haim, Matan Atzmon, and Yaron Lipman. 2020. Implicit geometric regularization for learning shapes. In ICML.
21. Jian Huang, Yan Li, Roger Crawfis, Shao-Chiung Lu, and Shuh-Yuan Liou. 2001. A complete distance field representation. In IEEE VIS. IEEE, 247–561.
22. Pradeep Kumar Jayaraman, Aditya Sanghi, Joseph G Lambourne, Karl DD Willis, Thomas Davies, Hooman Shayani, and Nigel Morris. 2021. UV-Net: Learning from boundary representations. In CVPR. 11703–11712.
23. Chiyu Max Jiang, Avneesh Sud, Ameesh Makadia, Jingwei Huang, Matthias Nießner, and Thomas Funkhouser. 2020. Local implicit grid representations for 3D scenes. In CVPR.
24. Mark W Jones, J Andreas Baerentzen, and Milos Sramek. 2006. 3D distance fields: A survey of techniques and applications. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graphics 12, 4 (2006), 581–599.
25. Tao Ju, Frank Losasso, Scott Schaefer, and Joe Warren. 2002. Dual contouring of Hermite data. ACM Trans. Graph. 21, 3 (2002), 339–346.
26. Kacper Kania, Maciej Zięba, and Tomasz Kajdanowicz. 2020. UCSG-Net – Unsupervised discovering of constructive solid geometry tree. In NeurIPS.
27. Michael Kazhdan, Matthew Bolitho, and Hugues Hoppe. 2006. Poisson surface reconstruction. In Symp. Geom. Proc. 61–70.
28. Michael Kazhdan and Hugues Hoppe. 2013. Screened Poisson surface reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 3 (2013), 29:1–29:13.
29. Leif P. Kobbelt, Mario Botsch, Ulrich Schwanecke, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2001. Feature sensitive surface extraction from volume data. In SIGGRAPH. 57–66.
30. Sebastian Koch, Albert Matveev, Zhongshi Jiang, Francis Williams, Alexey Artemov, Evgeny Burnaev, Marc Alexa, Denis Zorin, and Daniele Panozzo. 2019. ABC: A big CAD model dataset for geometric deep learning. In CVPR.
31. Dan Koschier, Crispin Deul, and Jan Bender. 2016. Hierarchical hp-adaptive signed distance fields. In Symposium on Computer Animation. 189–198.
32. Joseph G. Lambourne, Karl D.D. Willis, Pradeep Kumar Jayaraman, Aditya Sanghi, Peter Meltzer, and Hooman Shayani. 2021. BRepNet: A topological message passing system for solid models. In CVPR. 12773–12782.
33. Jiabao Lei and Kui Jia. 2020. Analytic marching: An analytic meshing solution from deep implicit surface networks. In ICML. PMLR, 5789–5798.
34. Shi-Lin Liu, Hao-Xiang Guo, Hao Pan, Peng-Shuai Wang, Xin Tong, and Yang Liu. 2021. Deep implicit moving least-squares functions for 3D reconstruction. In CVPR. 1788–1797.
35. William E. Lorensen and Harvey E. Cline. 1987. Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. In SIGGRAPH. Association for Computing Machinery, 163–169.
36. Thomas Müller, Alex Evans, Christoph Schied, and Alexander Keller. 2022. Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding. ACM Trans. Graph. 41, 4, Article 102 (2022), 102:1–102:15 pages.
37. Pavol Novotný and Milos Srámek. 2005. Representation of objects with sharp details in truncated distance fields. In Volume Graphics 2005.
38. Yutaka Ohtake, Alexander Belyaev, Marc Alexa, Greg Turk, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2003. Multi-level partition of unity implicits. ACM Trans. Graph. 22, 3 (2003), 463–470.
39. Cengiz Oztireli, Gaël Guennebaud, and Markus Gross. 2009. Feature preserving point set surfaces based on non-linear kernel regression. Comput. Graph. Forum 28, 2 (2009), 493–501.
40. Jeong Joon Park, Peter Florence, Julian Straub, Richard Newcombe, and Steven Love-grove. 2019. DeepSDF: learning continuous signed distance functions for shape representation. In CVPR.
41. Alexander Pasko, Valery Adzhiev, Alexei Sourin, and Vladimir Savchenko. 1995. Function representation in geometric modeling: concepts, implementation and applications. The visual computer 11, 8 (1995), 429–446.
42. Adam Paszke, Sam Gross, Soumith Chintala, Gregory Chanan, Edward Yang, Zachary DeVito, Zeming Lin, Alban Desmaison, Luca Antiga, and Adam Lerer. 2017. Automatic differentiation in pytorch. (2017).
43. Songyou Peng, Michael Niemeyer, Lars Mescheder, Marc Pollefeys, and Andreas Geiger. 2020. Convolutional occupancy networks. In ECCV.
44. Huamin Qu, Nan Zhang, Ran Shao, Arie Kaufman, and Klaus Mueller. 2004. Feature preserving distance fields. In 2004 IEEE Symposium on Volume Visualization and Graphics. IEEE, 39–46.
45. Daxuan Ren, Jianmin Zheng, Jianfei Cai, Jiatong Li, Haiyong Jiang, Zhongang Cai, Junzhe Zhang, Liang Pan, Mingyuan Zhang, Haiyu Zhao, et al. 2021. CSG-Stump: A learning friendly CSG-Like representation for interpretable shape parsing. In ICCV. 12478–12487.
46. Antonio Ricci. 1973. A constructive geometry for computer graphics. Comput. J. 16, 2 (1973), 157–160.
47. Vadim Shapiro. 2002. Solid Modeling. Handbook of computer aided geometric design 20 (2002), 473–518.
48. Vadim Shapiro. 2007. Semi-analytic geometry with R-functions. ACTA numerica 16 (2007), 239–303.
49. Vadim Shapiro and Donald L Vossler. 1991a. Efficient CSG representations of two-dimensional solids. J. Mech. Des. 113 (1991), 292–305. Issue 3.
50. Vadim Shapiro and Donald L. Vossler. 1991b. Construction and optimization of CSG representations. Computer-Aided Design 23, 1 (1991), 4–20.
51. Vadim Shapiro and Donald L. Vossler. 1993. Separation for boundary to CSG conversion. ACM Trans. Graph. 12, 1 (1993), 35–55.
52. Gopal Sharma, Rishabh Goyal, Difan Liu, Evangelos Kalogerakis, and Subhransu Maji. 2018. CSGNet: Neural shape parser for constructive solid geometry. In CVPR.
53. Gopal Sharma, Difan Liu, Subhransu Maji, Evangelos Kalogerakis, Siddhartha Chaudhuri, and Radomír Měch. 2020. ParseNet: A parametric surface fitting network for 3D point clouds. In ECCV. 261–276.
54. Vincent Sitzmann, Julien NP Martel, Alexander W Bergman, David B Lindell, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2020. Implicit neural representations with periodic activation functions. In NeurIPS.
55. Towaki Takikawa, Joey Litalien, Kangxue Yin, Karsten Kreis, Charles Loop, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, Alec Jacobson, Morgan McGuire, and Sanja Fidler. 2021. Neural geometric level of detail: Real-time rendering with implicit 3D shapes. (2021).
56. Francis Williams, Matthew Trager, Joan Bruna, and Denis Zorin. 2021. Neural splines: Fitting 3D surfaces with infinitely-wide neural networks. In CVPR. 9949–9958.
57. Karl DD Willis, Pradeep Kumar Jayaraman, Hang Chu, Yunsheng Tian, Yifei Li, Daniele Grandi, Aditya Sanghi, Linh Tran, Joseph G Lambourne, Armando Solar-Lezama, et al. 2022. JoinABLe: Learning bottom-up assembly of parametric CAD joints. In CVPR.
58. Q. Wu, K. Xu, and J. Wang. 2018. Constructing 3D CSG models from 3D raw point clouds. Comput. Graph. Forum 37, 5 (2018), 221–232.
59. Rundi Wu, Chang Xiao, and Changxi Zheng. 2021. DeepCAD: A deep generative network for computer-aided design models. In ICCV. 6772–6782.
60. Xianghao Xu, Wenzhe Peng, Chin-Yi Cheng, Karl DD Willis, and Daniel Ritchie. 2021. Inferring CAD modeling sequences using zone graphs. In CVPR. 6062–6070.
61. Guandao Yang, Serge Belongie, Bharath Hariharan, and Vladlen Koltun. 2021. Geometry processing with neural fields. NeurIPS 34 (2021).
62. Fenggen Yu, Zhiqin Chen, Manyi Li, Aditya Sanghi, Hooman Shayani, Ali Mahdavi-Amiri, and Hao Zhang. 2022. CAPRI-Net: Learning compact CAD shapes with adaptive primitive assembly. In CVPR.
63. Zhan Yuan, Yizhou Yu, and Wenping Wang. 2012. Object-space multiphase implicit functions. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (2012), 1–10.