“NeuralMarker: A Framework for Learning General Marker Correspondence” by Huang, Pan, Pan, Bian, Xu, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- NeuralMarker: A Framework for Learning General Marker Correspondence
Session/Category Title:
- VR and Interaction
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
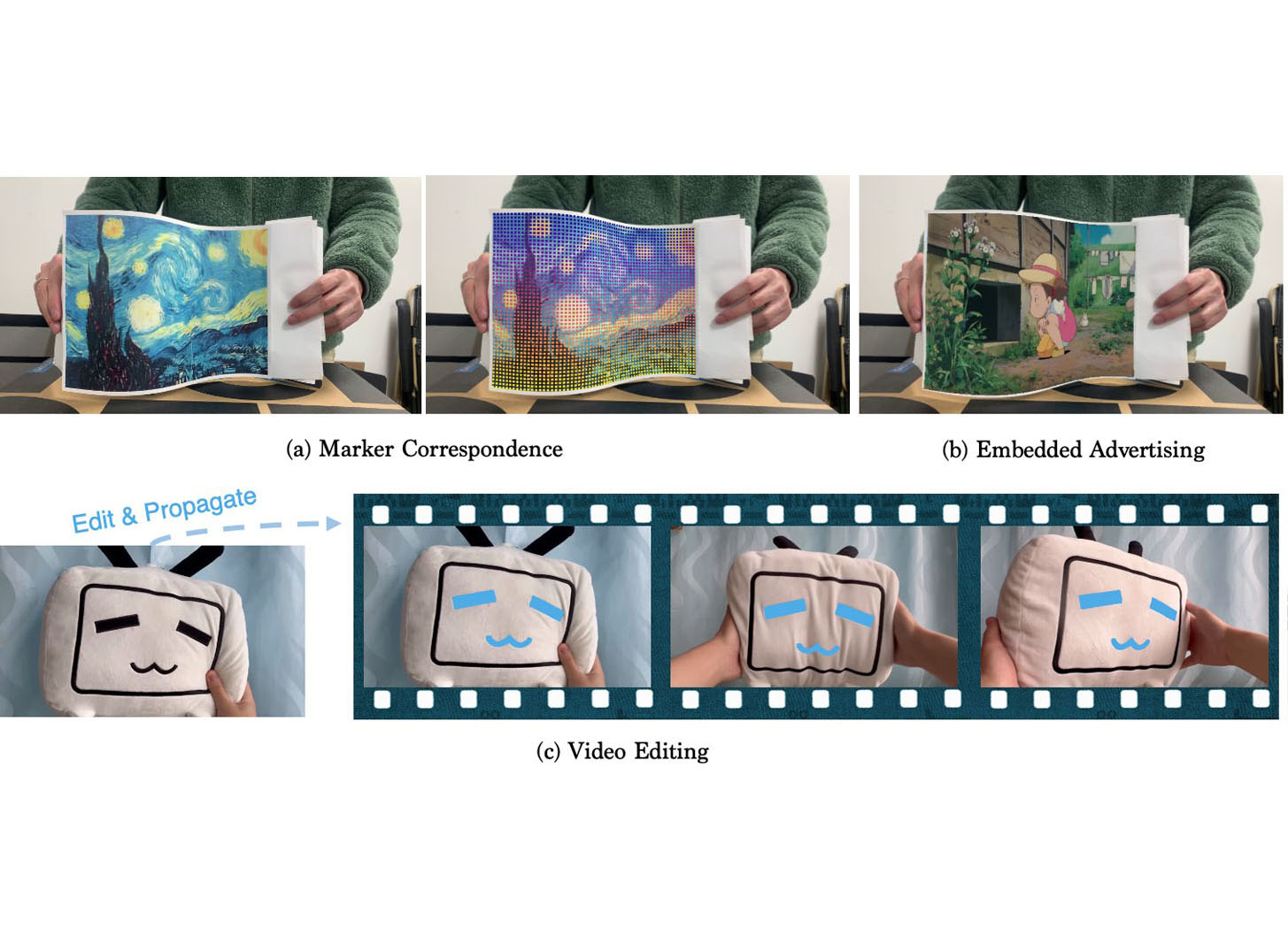
We tackle the problem of estimating correspondences from a general marker, such as a movie poster, to an image that captures such a marker. Conventionally, this problem is addressed by fitting a homography model based on sparse feature matching. However, they are only able to handle plane-like markers and the sparse features do not sufficiently utilize appearance information. In this paper, we propose a novel framework NeuralMarker, training a neural network estimating dense marker correspondences under various challenging conditions, such as marker deformation, harsh lighting, etc. Deep learning has presented an excellent performance in correspondence learning once provided with sufficient training data. However, annotating pixel-wise dense correspondence for training marker correspondence is too expensive. We observe that the challenges of marker correspondence estimation come from two individual aspects: geometry variation and appearance variation. We, therefore, design two components addressing these two challenges in NeuralMarker. First, we create a synthetic dataset FlyingMarkers containing marker-image pairs with ground truth dense correspondences. By training with FlyingMarkers, the neural network is encouraged to capture various marker motions. Second, we propose the novel Symmetric Epipolar Distance (SED) loss, which enables learning dense correspondence from posed images. Learning with the SED loss and the cross-lighting posed images collected by Structure-from-Motion (SfM), NeuralMarker is remarkably robust in harsh lighting environments and avoids synthetic image bias. Besides, we also propose a novel marker correspondence evaluation method circumstancing annotations on real marker-image pairs and create a new benchmark. We show that NeuralMarker significantly outperforms previous methods and enables new interesting applications, including Augmented Reality (AR) and video editing.
References:
1. Sameer Agarwal, Yasutaka Furukawa, Noah Snavely, Ian Simon, Brian Curless, Steven M Seitz, and Richard Szeliski. 2011. Building rome in a day. Commun. ACM 54, 10 (2011), 105–112.
2. Simon Baker, Ankur Datta, and Takeo Kanade. 2006. Parameterizing homographies. Robotics Institute, Pittsburgh, PA, Tech. Rep. CMU-RI-TR-06-11 (2006).
3. Ross Bencina, Martin Kaltenbrunner, and Sergi Jorda. 2005. Improved topological fiducial tracking in the reactivision system. In 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05)-Workshops. IEEE, 99–99.
4. Daniel J Butler, Jonas Wulff, Garrett B Stanley, and Michael J Black. 2012. A naturalistic open source movie for optical flow evaluation. In European conference on computer vision. Springer, 611–625.
5. Kyunghyun Cho, Bart Van Merriënboer, Dzmitry Bahdanau, and Yoshua Bengio. 2014. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1259 (2014).
6. Xiangxiang Chu, Zhi Tian, Yuqing Wang, Bo Zhang, Haibing Ren, Xiaolin Wei, Huaxia Xia, and Chunhua Shen. 2021. Twins: Revisiting the design of spatial attention in vision transformers. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (2021).
7. Joseph DeGol, Timothy Bretl, and Derek Hoiem. 2017. Chromatag: A colored marker and fast detection algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 1472–1481.
8. Daniel DeTone, Tomasz Malisiewicz, and Andrew Rabinovich. 2018. Superpoint: Self-supervised interest point detection and description. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. 224–236.
9. Alexey Dosovitskiy, Philipp Fischer, Eddy Ilg, Philip Hausser, Caner Hazirbas, Vladimir Golkov, Patrick Van Der Smagt, Daniel Cremers, and Thomas Brox. 2015. Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2758–2766.
10. Mihai Dusmanu, Ignacio Rocco, Tomas Pajdla, Marc Pollefeys, Josef Sivic, Akihiko Torii, and Torsten Sattler. 2019. D2-Net: A Trainable CNN for Joint Detection and Description of Local Features. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
11. Martin A Fischler and Robert C Bolles. 1981. Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 24, 6 (1981), 381–395.
12. Andreas Geiger, Philip Lenz, Christoph Stiller, and Raquel Urtasun. 2013. Vision meets robotics: The kitti dataset. The International Journal of Robotics Research 32, 11 (2013), 1231–1237.
13. Oleg Grinchuk, Vadim Lebedev, and Victor Lempitsky. 2016. Learnable visual markers. Advances In Neural Information Processing Systems 29 (2016).
14. Danying Hu, Daniel DeTone, and Tomasz Malisiewicz. 2019. Deep charuco: Dark charuco marker pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 8436–8444.
15. Zhaoyang Huang, Xiaoyu Shi, Chao Zhang, Qiang Wang, Ka Chun Cheung, Hongwei Qin, Jifeng Dai, and Hongsheng Li. 2022. FlowFormer: A Transformer Architecture for Optical Flow. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.16194 (2022).
16. Zhengqi Li and Noah Snavely. 2018. Megadepth: Learning single-view depth prediction from internet photos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2041–2050.
17. David G Lowe. 2004. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International journal of computer vision 60, 2 (2004), 91–110.
18. Jundan Luo, Zhaoyang Huang, Yijin Li, Xiaowei Zhou, Guofeng Zhang, and Hujun Bao. 2020. NIID-Net: Adapting Surface Normal Knowledge for Intrinsic Image Decomposition in Indoor Scenes. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 26, 12 (2020), 3434–3445.
19. Nikolaus Mayer, Eddy Ilg, Philip Hausser, Philipp Fischer, Daniel Cremers, Alexey Dosovitskiy, and Thomas Brox. 2016. A large dataset to train convolutional networks for disparity, optical flow, and scene flow estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 4040–4048.
20. Iaroslav Melekhov, Aleksei Tiulpin, Torsten Sattler, Marc Pollefeys, Esa Rahtu, and Juho Kannala. 2019. Dgc-net: Dense geometric correspondence network. In 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). IEEE, 1034–1042.
21. Gaku Narita, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa. 2016. Dynamic projection mapping onto deforming non-rigid surface using deformable dot cluster marker. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 23, 3 (2016), 1235–1248.
22. Edwin Olson. 2011. AprilTag: A robust and flexible visual fiducial system. In 2011 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. IEEE, 3400–3407.
23. OpenCV. 2015. Open Source Computer Vision Library.
24. J Brennan Peace, Eric Psota, Yanfeng Liu, and Lance C Pérez. 2021. E2ETag: An End-to-End Trainable Method for Generating and Detecting Fiducial Markers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.14184 (2021).
25. William Peebles, Jun-Yan Zhu, Richard Zhang, Antonio Torralba, Alexei Efros, and Eli Shechtman. 2021. GAN-Supervised Dense Visual Alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.05143 (2021).
26. Jerome Revaud, Cesar De Souza, Martin Humenberger, and Philippe Weinzaepfel. 2019. R2D2: Reliable and Repeatable Detector and Descriptor. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, H. Wallach, H. Larochelle, A. Beygelzimer, F. d’Alché-Buc, E. Fox, and R. Garnett (Eds.), Vol. 32. Curran Associates, Inc. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2019/file/3198dfd0aef271d22f7bcddd6f12f5cb-Paper.pdf
27. Ignacio Rocco, Relja Arandjelovic, and Josef Sivic. 2017. Convolutional neural network architecture for geometric matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 6148–6157.
28. Paul-Edouard Sarlin, Daniel DeTone, Tomasz Malisiewicz, and Andrew Rabinovich. 2020. Superglue: Learning feature matching with graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 4938–4947.
29. M Sarosa, A Chalim, S Suhari, Z Sari, and HB Hakim. 2019. Developing augmented reality based application for character education using unity with Vuforia SDK. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 1375. IOP Publishing, 012035.
30. Johannes Lutz Schönberger and Jan-Michael Frahm. 2016. Structure-from-Motion Revisited. In Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
31. Xi Shen, François Darmon, Alexei A Efros, and Mathieu Aubry. 2020. RANSAC-Flow: generic two-stage image alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.01526 (2020).
32. Alexandro Simonetti Ibanez and Josep Paredes Figueras. 2013. Vuforia v1. 5 SDK: Analysis and evaluation of capabilities. Master’s thesis. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya.
33. Richard Szeliski et al. 2007. Image alignment and stitching: A tutorial. Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision 2, 1 (2007), 1–104.
34. Zachary Teed and Jia Deng. 2020. Raft: Recurrent all-pairs field transforms for optical flow. In European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 402–419.
35. Prune Truong, Martin Danelljan, and Radu Timofte. 2020. Glu-net: Global-local universal network for dense flow and correspondences. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 6258–6268.
36. Prune Truong, Martin Danelljan, Luc Van Gool, and Radu Timofte. 2021. Learning accurate dense correspondences and when to trust them. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 5714–5724.
37. Hideaki Uchiyama and Eric Marchand. 2011. Deformable random dot markers. In 2011 10th IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality. IEEE, 237–238.
38. Levi Valgaerts, Andrés Bruhn, and Joachim Weickert. 2008. A variational model for the joint recovery of the fundamental matrix and the optical flow. In Joint Pattern Recognition Symposium. Springer, 314–324.
39. Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez, Łukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017).
40. John Wang and Edwin Olson. 2016. AprilTag 2: Efficient and robust fiducial detection. In 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE, 4193–4198.
41. Qianqian Wang, Xiaowei Zhou, Bharath Hariharan, and Noah Snavely. 2020. Learning feature descriptors using camera pose supervision. In European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 757–774.
42. Andreas Wedel, Daniel Cremers, Thomas Pock, and Horst Bischof. 2009. Structure- and motion-adaptive regularization for high accuracy optic flow. In 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 1663–1668.
43. Anqi Xu and Gregory Dudek. 2011. Fourier tag: A smoothly degradable fiducial marker system with configurable payload capacity. In 2011 Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision. IEEE, 40–47.
44. Mustafa B Yaldiz, Andreas Meuleman, Hyeonjoong Jang, Hyunho Ha, and Min H Kim. 2021. DeepFormableTag: end-to-end generation and recognition of deformable fiducial markers. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 40, 4 (2021), 1–14.
45. Koichiro Yamaguchi, David McAllester, and Raquel Urtasun. 2013. Robust monocular epipolar flow estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 1862–1869.
46. Guandao Yang, Tomasz Malisiewicz, Serge J Belongie, Erez Farhan, Sungsoo Ha, Yuewei Lin, Xiaojing Huang, Hanfei Yan, and Wei Xu. 2019. Learning Data-Adaptive Interest Points through Epipolar Adaptation.. In CVPR Workshops. 1–7.