“Curl-Flow: Boundary-Respecting Pointwise Incompressible Velocity Interpolation for Grid-Based Fluids” by Chang, Partono, Azevedo and Batty
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Curl-Flow: Boundary-Respecting Pointwise Incompressible Velocity Interpolation for Grid-Based Fluids
Session/Category Title: Fluid Simulation
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
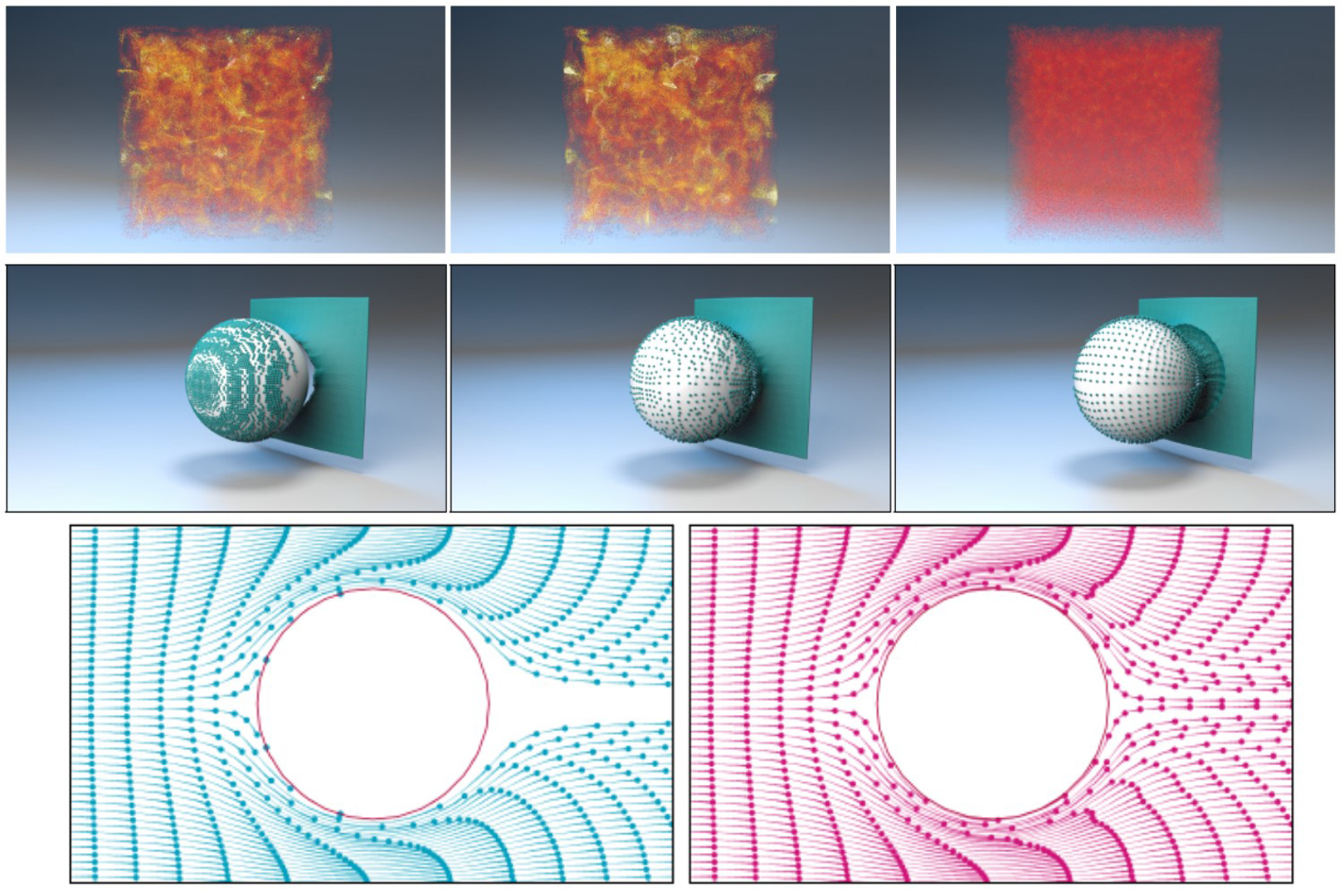
We propose to augment standard grid-based fluid solvers with pointwise divergence-free velocity interpolation, thereby ensuring exact incompressibility down to the sub-cell level. Our method takes as input a discretely divergence-free velocity field generated by a staggered grid pressure projection, and first recovers a corresponding discrete vector potential. Instead of solving a costly vector Poisson problem for the potential, we develop a fast parallel sweeping strategy to find a candidate potential and apply a gauge transformation to enforce the Coulomb gauge condition and thereby make it numerically smooth. Interpolating this discrete potential generates a point-wise vector potential whose analytical curl is a pointwise incompressible velocity field. Our method further supports irregular solid geometry through the use of level set-based cut-cells and a novel Curl-Noise-inspired potential ramping procedure that simultaneously offers strictly non-penetrating velocities and incompressibility. Experimental comparisons demonstrate that the vector potential reconstruction procedure at the heart of our approach is consistently faster than prior such reconstruction schemes, especially those that solve vector Poisson problems. Moreover, in exchange for its modest extra cost, our overall Curl-Flow framework produces significantly improved particle trajectories that closely respect irregular obstacles, do not suffer from spurious sources or sinks, and yield superior particle distributions over time.
References:
1. R. Albanese and G. Rubinacci. 1990. Magnetostatic field computations in terms of two-component vector potentials. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 29, 3 (mar 1990), 515–532.
2. Ryoichi Ando, Nils Thuerey, and Chris Wojtan. 2015. A stream function solver for liquid simulations. ACM Transactions on Graphics 34, 4 (jul 2015), 53:1–53:9.
3. Ryoichi Ando, Nils Thurey, and Reiji Tsuruno. 2012. Preserving fluid sheets with adaptively sampled anisotropic particles. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18, 8 (2012), 1202–1214.
4. Alexis Angelidis and Fabrice Neyret. 2005. Simulation of smoke based on vortex filament primitives. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. ACM, 87–96.
5. Vinicius C Azevedo, Christopher Batty, and Manuel M Oliveira. 2016. Preserving geometry and topology for fluid flows with thin obstacles and narrow gaps. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 4 (2016), 97.
6. Dinshaw S Balsara. 2001. Divergence-free adaptive mesh refinement for magnetohy-drodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 174, 2 (2001), 614–648.
7. Dinshaw S Balsara. 2004. Second-order-accurate schemes for magnetohydrodynamics with divergence-free reconstruction. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 151, 1 (2004), 149.
8. Dinshaw S Balsara. 2009. Divergence-free reconstruction of magnetic fields and WENO schemes for magnetohydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 14 (2009), 5040–5056.
9. Yuanxun Bao, Aleksandar Donev, Boyce E Griffith, David M McQueen, and Charles S Peskin. 2017. An Immersed Boundary method with divergence-free velocity interpolation and force spreading. Journal of computational physics 347 (2017), 183–206.
10. Ayan Biswas, Richard Strelitz, Jonathan Woodring, Chun-Ming Chen, and Han-Wei Shen. 2016. A scalable streamline generation algorithm via flux-based isocontour extraction. In Proceedings of the 16th Eurographics Symposium on Parallel Graphics and Visualization. 69–78.
11. R. Bridson. 2015. Fluid Simulation for Computer Graphics, Second Edition. Taylor & Francis.
12. Robert Bridson, Jim Houriham, and Marcus Nordenstam. 2007. Curl-Noise for Procedural Fluid Flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (July 2007), 46–es.
13. Tyson Brochu, Todd Keeler, and Robert Bridson. 2012. Linear-time smoke animation with vortex sheet meshes. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. Eurographics Association, 87–95.
14. Astrid Bunge, Mario Botsch, and Marc Alexa. 2021. The Diamond Laplace for Polygonal and Polyhedral Meshes. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 40. Wiley Online Library, 217–230.
15. Hugo Casquero, Yongjie Jessica Zhang, Carles Bona-Casas, Lisandro Dalcin, and Hector Gomez. 2018. Non-body-fitted fluid-structure interaction: Divergence-conforming B-splines, fully-implicit dynamics, and variational formulation. J. Comput. Phys. 374 (2018), 625–653.
16. Bernardo Cockburn, Fengyan Li, and Chi-Wang Shu. 2004. Locally divergence-free discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Maxwell equations. J. Comput. Phys. 194, 2 (2004), 588–610.
17. Qiaodong Cui, Timothy Langlois, Pradeep Sen, and Theodore Kim. 2021. Spiral-spectral fluid simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 40, 6 (2021), 1–16.
18. Fang Da, David Hahn, Christopher Batty, Chris Wojtan, and Eitan Grinspun. 2016. Surface-only liquids. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 4 (2016), 1–12.
19. Fernando De Goes, Mathieu Desbrun, Mark Meyer, and Tony DeRose. 2016. Subdivision exterior calculus for geometry processing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 4 (2016), 1–11.
20. Tyler De Witt, Christian Lessig, and Eugene Fiume. 2012. Fluid simulation using Laplacian eigenfunctions. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 1 (2012), 10.
21. Ivan DeWolf. 2006. Divergence-free noise. Technical Report. Martian Labs., 2005.
22. Marvin Eisenberger, Zorah Lähner, and Daniel Cremers. 2018. Divergence-Free Shape Interpolation and Correspondence. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.10417 (2018).
23. Sharif Elcott, Yiying Tong, Eva Kanso, Peter Schröder, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2007. Stable, circulation-preserving, simplicial fluids. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 26, 1 (2007), 4.
24. Douglas Enright, Stephen Marschner, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2002. Animation and rendering of complex water surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 21, 3 (2002), 736–744.
25. John A Evans and Thomas JR Hughes. 2013. Isogeometric divergence-conforming B-splines for the unsteady Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 241 (2013), 141–167.
26. Ronald Fedkiw, Jos Stam, and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2001. Visual simulation of smoke. In Proceedings of the 28th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 15–22.
27. F. N. Fritsch and R. E. Carlson. 1980. Monotone Piecewise Cubic Interpolation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 17, 2 (1980), 238–246.
28. Gaël Guennebaud, Benoît Jacob, et al. 2010. Eigen v3. http://eigen.tuxfamily.org.
29. Johnny Guzmán and Michael Neilan. 2014. Conforming and divergence-free Stokes elements in three dimensions. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 34, 4 (2014), 1489–1508.
30. Ben Houston, Chris Bond, and Mark Wiebe. 2003. A unified approach for modeling complex occlusions in fluid simulations. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2003 Sketches. 1–1.
31. Antonio Huerta, Yolanda Vidal, and Pierre Villon. 2004. Pseudo-divergence-free element free Galerkin method for incompressible fluid flow. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 193, 12 (2004), 1119 — 1136.
32. PJenny, SB Pope, M Muradoglu, and DA Caughey. 2001. A hybrid algorithm for the joint PDF equation of turbulent reactive flows. J. Comput. Phys. 166, 2 (2001), 218–252.
33. Chenfanfu Jiang, Craig Schroeder, Andrew Selle, Joseph Teran, and Alexey Stomakhin. 2015. The affine particle-in-cell method. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 51.
34. Chenfanfu Jiang, Craig Schroeder, Joseph Teran, Alexey Stomakhin, and Andrew Selle. 2016. The material point method for simulating continuum materials. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2016 Courses. 1–52.
35. Theodore Kim, Nils Thürey, Doug James, and Markus Gross. 2008. Wavelet Turbulence for Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug. 2008), 1–6.
36. Tassilo Kugelstadt, Andreas Longva, Nils Thurey, and Jan Bender. 2019. Implicit Density Projection for Volume Conserving Liquids. IEEE Computer Architecture Letters 01 (2019), 1–1.
37. Egor Larionov, Christopher Batty, and Robert Bridson. 2017. Variational stokes: a unified pressure-viscosity solver for accurate viscous liquids. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 101.
38. Philip L Lederer, Alexander Linke, Christian Merdon, and Joachim Schoberl. 2017. Divergence-free reconstruction operators for pressure-robust Stokes discretizations with continuous pressure finite elements. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 55, 3 (2017), 1291–1314.
39. Christoph Lehrenfeld and Joachim Schöberl. 2016. High order exactly divergence-free hybrid discontinuous Galerkin methods for unsteady incompressible flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 307 (2016), 339–361.
40. Alexander Linke. 2012. A divergence-free velocity reconstruction for incompressible fows. Comptes Rendus Mathematique 350, 17–18 (2012), 837–840.
41. Konstantin Lipnikov, Mikhail Shashkov, and Daniil Svyatskiy. 2006. The mimetic finite difference discretization of diffusion problem on unstructured polyhedral meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 211, 2 (2006), 473–491.
42. Svenja Lowitzsch. 2005. Matrix-valued radial basis functions: stability estimates and applications. Advances in Computational Mathematics 23, 3 (2005), 299–315.
43. Abhishek Madan and David IW Levin. 2022. Fast Evaluation of Smooth Distance Constraints on Co-Dimensional Geometry. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) (to appear) (2022).
44. Jakob M Maljaars, Robert Jan Labeur, and Matthias Möller. 2018. A hybridized discontinuous Galerkin framework for high-order particle-mesh operator splitting of the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 358 (2018), 150–172.
45. J.B. Manges and Z.J. Cendes. 1995. A generalized tree-cotree gauge for magnetic field computation. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 31, 3 (may 1995), 1342–1347.
46. Colin P McNally. 2011. Divergence-free interpolation of vector fields from point values—exact div-B= 0 in numerical simulations. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters 413, 1 (2011), L76–L80.
47. DW Meyer and P Jenny. 2004. Conservative velocity interpolation for PDF methods. In PAMM: Proceedings in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, Vol. 4. Wiley Online Library, 466–467.
48. Yen Ting Ng, Chohong Min, and Frédéric Gibou. 2009. An Efficient Fluid-solid Coupling Algorithm for Single-phase Flows. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 23 (Dec. 2009), 8807–8829.
49. Zherong Pan, Jin Huang, Yiying Tong, Changxi Zheng, and Hujun Bao. 2013. Interactive localized liquid motion editing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 6 (2013), 1–10.
50. Sang Il Park and Myoung Jun Kim. 2005. Vortex fluid for gaseous phenomena. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. ACM, 261–270.
51. Charles S Peskin. 2002. The immersed boundary method. Acta numerica 11 (2002), 479–517.
52. Tobias Pfaff, Nils Thuerey, and Markus Gross. 2012. Lagrangian vortex sheets for animating fluids. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4 (2012), 112.
53. Konstantin Poelke and Konrad Polthier. 2016. Boundary-aware Hodge decompositions for piecewise constant vector fields. Computer-Aided Design 78 (2016), 126–136.
54. Adina E Pusok, Boris JP Kaus, and Anton A Popov. 2017. On the quality of velocity interpolation schemes for marker-in-cell method and staggered grids. Pure and Applied Geophysics 174, 3 (2017), 1071–1089.
55. Wouter Raateland, Torsten Hadrich, Jorge Alejandro Amador Herrera, Daniel T Banuti, Wojciech Pałubicki, Sören Pirk, Klaus Hildebrandt, and Dominik L Michels. 2022. DCGrid: An Adaptive Grid Structure for Memory-Constrained Fluid Simulation on the GPU. (2022).
56. Nick Rasmussen, Douglas Enright, Duc Nguyen, Sebastian Marino, Nigel Sumner, Willi Geiger, Samir Hoon, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2004. Directable photorealistic liquids. In Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. 193–202.
57. Bharath Ravu, Murray Rudman, Guy Metcalfe, Daniel Lester, and Devang Khakhar. 2016. Creating analytically divergence-free velocity fields from grid-based data. J. Comput. Phys. 323 (07 2016).
58. Sander Rhebergen and Garth N Wells. 2018. A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for the Navier-Stokes equations with pointwise divergence-free velocity field. Journal of Scientific Computing 76, 3 (2018), 1484–1501.
59. Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, and Theodore Kim. 2021. Stream-Guided Smoke Simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 40, 4, Article 161 (2021).
60. Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, and Tomoyuki Nishita. 2018a. Editing fluid animation using flow interpolation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 5 (2018), 1–12.
61. Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, Yonghao Yue, Kei Iwasaki, and Tomoyuki Nishita. 2015. Incompressibility-preserving deformation for fluid flows using vector potentials. The Visual Computer 31, 6 (2015), 959–965.
62. Takahiro Sato, Christopher Wojtan, Nils Thuerey, Takeo Igarashi, and Ryoichi Ando. 2018b. Extended narrow band FLIP for liquid simulations. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. Wiley Online Library, 169–177.
63. Hagit Schechter and Robert Bridson. 2008. Evolving sub-grid turbulence for smoke animation. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. Eurographics Association, 1–7.
64. Craig Schroeder, Ritoban Roy Chowdhury, and Tamar Shinar. 2022. Local divergence-free polynomial interpolation on MAC grids. J. Comput. Phys. 468 (2022), 111500.
65. Andrew Selle, Ronald Fedkiw, Byungmoon Kim, Yingjie Liu, and Jarek Rossignac. 2008. An unconditionally stable MacCormack method. Journal of Scientific Computing 35, 2–3 (2008), 350–371.
66. Han Shao, Libo Huang, and Dominik L. Michels. 2022. A Fast Unsmoothed Aggregation Algebraic Multigrid Framework for the Large-Scale Simulation of Incompressible Flow. ACM Transaction on Graphics 41, 4, Article 49 (07 2022).
67. Zachary J. Silberman, Thomas R. Adams, Joshua A. Faber, Zachariah B. Etienne, and Ian Ruchlin. 2019. Numerical generation of vector potentials from specified magnetic fields. J. Comput. Phys. 379 (2019), 421 — 437.
68. Jos Stam. 1999. Stable Fluids. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’99). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley
69. Publishing Co., New York, NY, USA, 121–128.
70. Jos Stam and Eugene Fiume. 1993. Turbulent wind fields for gaseous phenomena. In Proceedings of the 20th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 369–376.
71. Michael Steffen, Robert M Kirby, and Martin Berzins. 2008. Analysis and reduction of quadrature errors in the material point method (MPM). International journal for numerical methods in engineering 76, 6 (2008), 922–948.
72. Tetsuya Takahashi and Ming C Lin. 2019. A geometrically consistent viscous fluid solver with two-way fluid-solid coupling. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 38. Wiley Online Library, 49–58.
73. Yiying Tong, Santiago Lombeyda, Anil N Hirani, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2003. Discrete multiscale vector field decomposition. ACM Transaction on Graphics (TOG) 22, 3 (2003), 445–452.
74. Charles Van Loan. 1992. Computational frameworks for the fast Fourier transform. SIAM.
75. Wolfram Von Funck, Holger Theisel, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2006. Vector field based shape deformations. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 25. ACM, 1118–1125.
76. Hongliang Wang, Roberto Agrusta, and Jeroen van Hunen. 2015. Advantages of a conservative velocity interpolation (CVI) scheme for particle-in-cell methods with application in geodynamic modeling. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 16, 6 (2015), 2015–2023.
77. Ke Wang, Yiying Tong, Mathieu Desbrun, and Peter Schröder. 2006. Edge subdivision schemes and the construction of smooth vector fields. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 25, 3 (2006), 1041–1048.
78. Rundong Zhao, Mathieu Desbrun, Guo-Wei Wei, and Yiying Tong. 2019. 3D Hodge decompositions of edge-and face-based vector fields. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6 (2019), 1–13.
79. Yongning Zhu and Robert Bridson. 2005. Animating sand as a fluid. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 24, 3 (2005), 965–972.
ACM Digital Library Publication:
- Curl-Flow: Boundary-Respecting Pointwise Incompressible Velocity Interpolation for Grid-Based Fluids