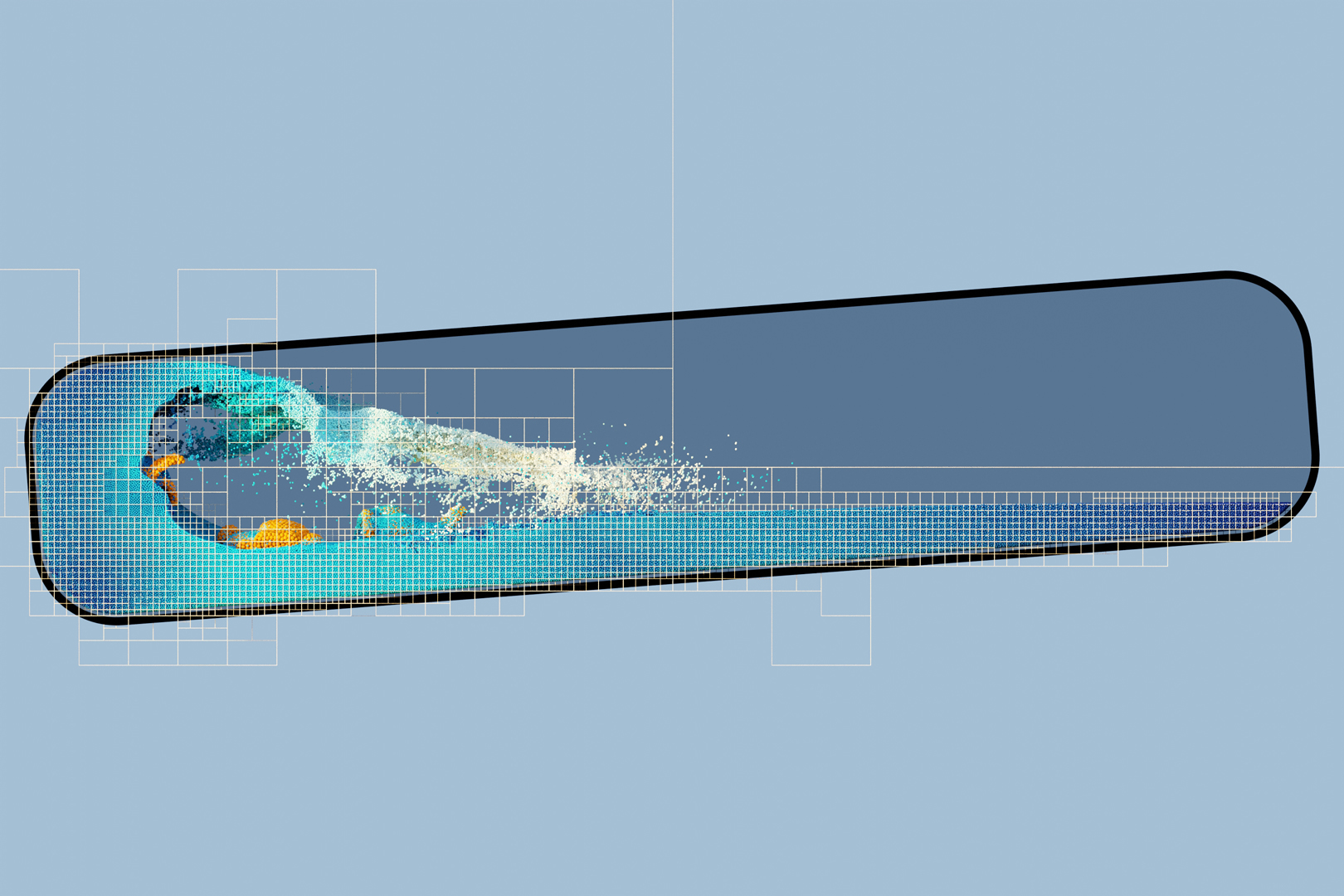
“Fast Octree Neighborhood Search for SPH Simulations” by Fernández-Fernández, Westhofen, Löschner, Jeske, Longva, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Fast Octree Neighborhood Search for SPH Simulations
Session/Category Title: Fluid Simulation
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We present a new octree-based neighborhood search method for SPH simulation. A speedup of up to 1.9x is observed in comparison to state-of-the-art methods which rely on uniform grids. While our method focuses on maximizing performance in fixed-radius SPH simulations, we show that it can also be used in scenarios where the particle support radius is not constant thanks to the adaptive nature of the octree acceleration structure.Neighborhood search methods typically consist of an acceleration structure that prunes the space of possible particle neighbor pairs, followed by direct distance comparisons between the remaining particle pairs. Previous works have focused on minimizing the number of comparisons. However, in an effort to minimize the actual computation time, we find that distance comparisons exhibit very high throughput on modern CPUs. By permitting more comparisons than strictly necessary, the time spent on preparing and searching the acceleration structure can be reduced, yielding a net positive speedup. The choice of an octree acceleration structure, instead of the uniform grid typically used in fixed-radius methods, ensures balanced computational tasks. This benefits both parallelism and provides consistently high computational intensity for the distance comparisons. We present a detailed account of high-level considerations that, together with low-level decisions, enable high throughput for performance-critical parts of the algorithm.Finally, we demonstrate the high performance of our algorithm on a number of large-scale fixed-radius SPH benchmarks and show in experiments with a support radius ratio up to 3 that our method is also effective in multi-resolution SPH simulations.
References:
1. Bart Adams, Mark Pauly, Richard Keiser, and Leonidas J. Guibas. 2007. Adaptively Sampled Particle Fluids. ACM Transactions on Graphics 26, 3 (2007), 48.
2. Stefan Band, Christoph Gissler, and Matthias Teschner. 2020. Compressed Neighbour Lists for SPH. Computer Graphics Forum 39, 1 (2020), 531–542.
3. Jan Bender et al. 2022. SPlisHSPlasH Library. https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/SPlisHSPlasH.
4. Jan Bender and Dan Koschier. 2017. Divergence-Free SPH for Incompressible and Viscous Fluids. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 23, 3 (2017), 1193–1206.
5. Jan Bender, Dan Koschier, Tassilo Kugelstadt, and Marcel Weiler. 2018. Turbulent micropolar SPH fluids with foam. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 25, 6 (2018), 2284–2295.
6. Jan Bender, Tassilo Kugelstadt, Marcel Weiler, and Dan Koschier. 2020. Implicit Frictional Boundary Handling for SPH. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 26, 10 (2020), 2982–2993.
7. Mathieu Desbrun and Marie-Paule Cani. 1999. Space-time adaptive simulation of highly deformable substances. Ph. D. Dissertation. INRIA.
8. J. M. Domínguez, A. J. C. Crespo, M. Gómez-Gesteira, and J. C. Marongiu. 2010. Neighbour lists in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 67, 12 (nov 2010), 2026–2042.
9. Robert A Gingold and Joseph J Monaghan. 1977. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: theory and application to non-spherical stars. Monthly notices of the royal astronomical society 181, 3 (1977), 375–389.
10. Christoph Gissler, Andreas Henne, Stefan Band, Andreas Peer, and Matthias Teschner. 2020. An Implicit Compressible SPH Solver for Snow Simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 39, 4 (Aug. 2020), 1–16.
11. Simon Green. 2010. Particle simulation using CUDA. NVIDIA whitepaper 6 (2010), 121–128.
12. Julian Gross, Marcel Köster, and Antonio Krüger. 2019. Fast and Efficient Nearest Neighbor Search for Particle Simulations. In Computer Graphics and Visual Computing (CGVC). The Eurographics Association.
13. Takahiro Harada, Seiichi Koshizuka, and Yoichiro Kawaguchi. 2007. Sliced data structure for particle-based simulations on GPUs. In Proceedings of the 5th international conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques in Australia and Southeast Asia – GRAPHITE ’07. ACM Press.
14. Lars Hernquist and Neal Katz. 1989. TREESPH-A unification of SPH with the hierarchical tree method. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 70 (1989), 419–446.
15. Christopher Jon Horvath and Barbara Solenthaler. 2013. Mass Preserving Multi-Scale SPH. Technical Report.
16. Markus Ihmsen, Nadir Akinci, Markus Becker, and Matthias Teschner. 2011. A parallel SPH implementation on multi-core CPUs. Comput. Graph. Forum 30 (03 2011), 99–112.
17. Markus Ihmsen, Jens Cornelis, Barbara Solenthaler, Christopher Horvath, and Matthias Teschner. 2014a. Implicit Incompressible SPH. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 20, 3 (mar 2014), 426–435.
18. Markus Ihmsen, Jens Orthmann, Barbara Solenthaler, Andreas Kolb, and Matthias Teschner. 2014b. SPH Fluids in Computer Graphics.
19. Dan Koschier, Jan Bender, Barbara Solenthaler, and Matthias Teschner. 2022. A Survey on SPH Methods in Computer Graphics. Computer Graphics Forum 41, 2 (2022).
20. Tassilo Kugelstadt, Jan Bender, José Antonio Fernández-Fernández, Stefan Rhys Jeske, Fabian Löschner, and Andreas Longva. 2021. Fast Corotated Elastic SPH Solids with Implicit Zero-Energy Mode Control. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 4, 3, Article 33 (Sept. 2021), 21 pages.
21. JJ Monaghan. 1992. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics 30, 1 (1992), 543–574. arXiv:arXiv:1007.1245v2
22. Guy M Morton. 1966. A computer oriented geodetic data base and a new technique in file sequencing. (1966).
23. Andreas Peer, Christoph Gissler, Stefan Band, and Matthias Teschner. 2017. An Implicit SPH Formulation for Incompressible Linearly Elastic Solids. Computer Graphics Forum 37, 6 (dec 2017), 135–148.
24. Brandon Pelfrey and Donald House. 2010. Adaptive Neighbor Pairing for Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. In Advances in Visual Computing. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 192–201.
25. Barbara Solenthaler and Markus Gross. 2011. Two-Scale Particle Simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 30, 4, Article 81 (jul 2011), 8 pages.
26. Tetsuya Takahashi, Yoshinori Dobashi, Issei Fujishiro, Tomoyuki Nishita, and Ming C. Lin. 2015. Implicit Formulation for SPH-based Viscous Fluids. Computer Graphics Forum 34, 2 (may 2015), 493–502.
27. Min Tang, Zhongyuan Liu, Ruofeng Tong, and Dinesh Manocha. 2018. PSCC: Parallel Self-Collision Culling with Spatial Hashing on GPUs. Proceedings of the ACM on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques 1, 1 (jul 2018), 1–18.
28. Loup Verlet. 1967. Computer “Experiments” on Classical Fluids. I. Thermodynamical Properties of Lennard-Jones Molecules. Physical Review 159, 1 (jul 1967), 98–103.
29. G. Viccione, V. Bovolin, and E. Pugliese Carratelli. 2008. Defining and optimizing algorithms for neighbouring particle identification in SPH fluid simulations. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 58, 6 (oct 2008), 625–638.
30. Marcel Weiler, Dan Koschier, Magnus Brand, and Jan Bender. 2018. A Physically Consistent Implicit Viscosity Solver for SPH Fluids. Computer Graphics Forum 37, 2 (2018), 145–155.
31. James S. Willis, Matthieu Schaller, Pedro Gonnet, Richard G. Bower, and Peter W. Draper. 2018. An Efficient SIMD Implementation of Pseudo-Verlet Lists for Neighbour Interactions in Particle-Based Codes. Advances in Parallel Computing 32 (2018).
32. Rene Winchenbach, Hendrik Hochstetter, and Andreas Kolb. 2016. Constrained Neighbor Lists for SPH-based Fluid Simulations.
33. Rene Winchenbach, Hendrik Hochstetter, and Andreas Kolb. 2017. Infinite Continuous Adaptivity for Incompressible SPH. ACM Transactions on Graphics 36, 4 (2017).
34. Rene Winchenbach and Andreas Kolb. 2020. Multi-Level Memory Structures for Simulating and Rendering Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Computer Graphics Forum 39, 6 (2020), 527–541.
35. Rene Winchenbach and Andreas Kolb. 2021. Optimized Refinement for Spatially Adaptive SPH. ACM Transactions on Graphics 40, 1 (feb 2021), 1–15.
36. Xilin Xia and Qiuhua Liang. 2016. A GPU-accelerated smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) model for the shallow water equations. Environmental Modelling & Software 75 (jan 2016), 28–43.