“Pose and Skeleton-aware Neural IK for Pose and Motion Editing” by Agrawal, Guay, Buhmann, Borer and Sumner
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Pose and Skeleton-aware Neural IK for Pose and Motion Editing
Session/Category Title: All About Animation
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
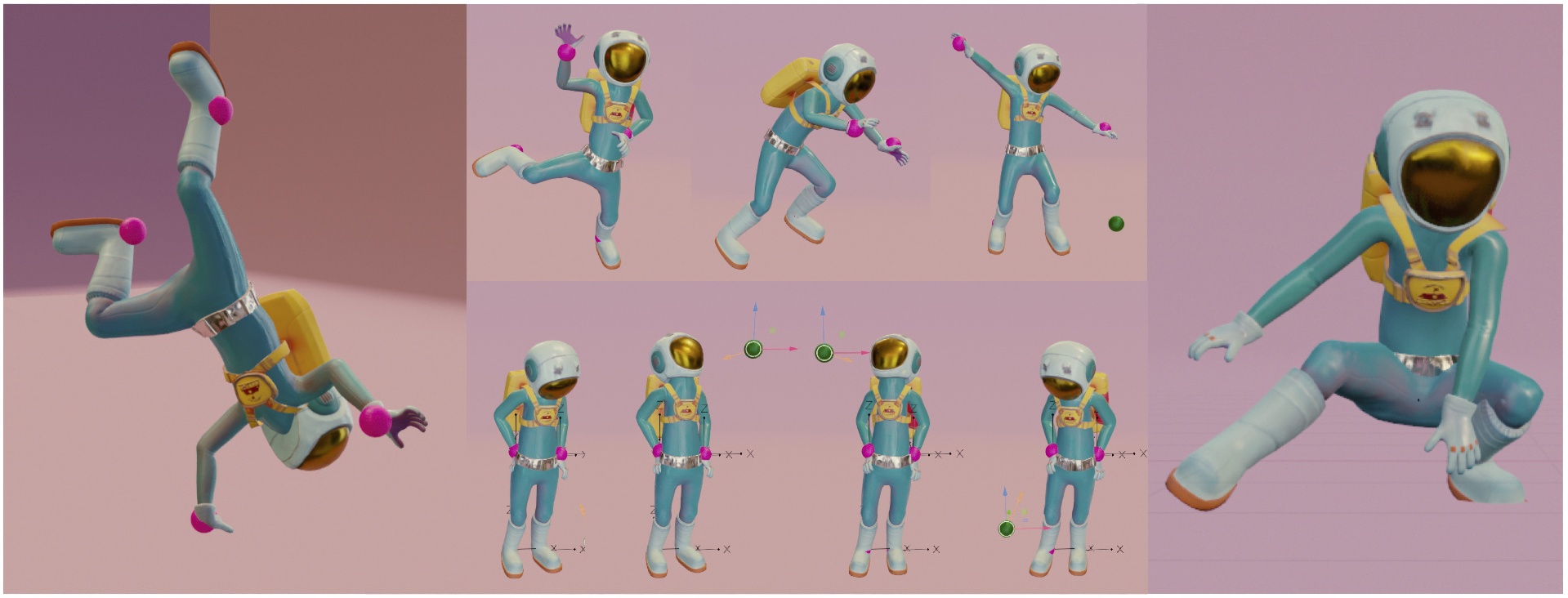
Posing a 3D character for film or game is an iterative and laborious process where many control handles (e.g. joints) need to be manipulated to achieve a compelling result. Neural Inverse Kinematics (IK) is a new type of IK that enables sparse control over a 3D character pose, and leverages full body correlations to complete the un-manipulated joints of the body. While neural IK is promising, current methods are not designed to preserve previous edits in posing workflows. Current models generate a full pose from the handles only—regardless of what was there previously—making it difficult to preserve any variations and hindering tasks such as pose and motion editing. In this paper, we introduce SKEL-IK, a novel architecture and training scheme that is conditioned on a base pose, and designed to flow information directly onto the skeletal graph structure, such that hard constraints can be enforced by blocking information flows at certain joints. As a result, we are able to satisfy both hard and soft constraints, as well as preserve un-manipulated parts of the body when desired. Finally, by controlling the base pose in different ways, we demonstrate the ability of our model to perform tasks such as generating variations and quickly editing poses and motions; with less erosion of the base poses compared to the current state-of-the-art.
References:
[1]
Kfir Aberman, Peizhuo Li, Dani Lischinski, Olga Sorkine-Hornung, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Baoquan Chen. 2020. Skeleton-aware networks for deep motion retargeting. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 39, 4 (2020), 62–1.
[2]
Aldo Balestrino, Giuseppe De Maria, and Lorenzo Sciavicco. 1984. Robust control of robotic manipulators. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 17, 2 (1984), 2435–2440.
[3]
Joan Bruna, Wojciech Zaremba, Arthur Szlam, and Yann Lecun. 2014. Spectral networks and locally connected networks on graphs. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR2014), CBLS, April 2014.
[4]
Samuel R Buss and Jin-Su Kim. 2005. Selectively damped least squares for inverse kinematics. Journal of Graphics tools 10, 3 (2005), 37–49.
[5]
Angela Castillo, Maria Escobar, Guillaume Jeanneret, Albert Pumarola, Pablo Arbeláez, Ali Thabet, and Artsiom Sanakoyeu. 2023. BoDiffusion: Diffusing Sparse Observations for Full-Body Human Motion Synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.11118 (2023).
[6]
Akos Csiszar, Jan Eilers, and Alexander Verl. 2017. On solving the inverse kinematics problem using neural networks. In 2017 24th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP). IEEE, 1–6.
[7]
Aaron D’Souza, Sethu Vijayakumar, and Stefan Schaal. 2001. Learning inverse kinematics. In Proceedings 2001 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Expanding the Societal Role of Robotics in the the Next Millennium (Cat. No. 01CH37180), Vol. 1. IEEE, 298–303.
[8]
Vijay Prakash Dwivedi and Xavier Bresson. 2021. A Generalization of Transformer Networks to Graphs. AAAI Workshop on Deep Learning on Graphs: Methods and Applications (2021).
[9]
Justin Gilmer, Samuel S Schoenholz, Patrick F Riley, Oriol Vinyals, and George E Dahl. 2017. Neural message passing for quantum chemistry. In International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 1263–1272.
[10]
Michael Girard and Anthony A Maciejewski. 1985. Computational modeling for the computer animation of legged figures. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics 19, 3 (1985), 263–270.
[11]
Artur Grigorev, Bernhard Thomaszewski, Michael J Black, and Otmar Hilliges. 2023. HOOD: Hierarchical Graphs for Generalized Modelling of Clothing Dynamics. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
[12]
Yinghao Huang, Manuel Kaufmann, Emre Aksan, Michael J. Black, Otmar Hilliges, and Gerard Pons-Moll. 2018. Deep Inertial Poser Learning to Reconstruct Human Pose from SparseInertial Measurements in Real Time. ACM Transactions on Graphics, (Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia) 37, 6 (Nov. 2018), 185:1–185:15.
[13]
Yifeng Jiang, Yuting Ye, Deepak Gopinath, Jungdam Won, Alexander W Winkler, and C Karen Liu. 2022. Transformer Inertial Poser: Real-time Human Motion Reconstruction from Sparse IMUs with Simultaneous Terrain Generation. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2022 Conference Papers. 1–9.
[14]
Jiaman Li, Ruben Villegas, Duygu Ceylan, Jimei Yang, Zhengfei Kuang, Hao Li, and Yajie Zhao. 2021. Task-generic hierarchical human motion prior using vaes. In 2021 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). IEEE, 771–781.
[15]
Matthew Loper, Naureen Mahmood, Javier Romero, Gerard Pons-Moll, and Michael J. Black. 2015. SMPL: A Skinned Multi-Person Linear Model. ACM Trans. Graphics (Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia) 34, 6 (Oct. 2015), 248:1–248:16.
[16]
Boris N. Oreshkin, Florent Bocquelet, Felix G. Harvey, Bay Raitt, and Dominic Laflamme. 2022. ProtoRes: Proto-Residual Network for Pose Authoring via Learned Inverse Kinematics. In International Conference on Learning Representations.
[17]
Tobias Pfaff, Meire Fortunato, Alvaro Sanchez-Gonzalez, and Peter Battaglia. 2021. Learning Mesh-Based Simulation with Graph Networks. In International Conference on Learning Representations. https://openreview.net/forum?id=roNqYL0_XP
[18]
Hailin Ren and Pinhas Ben-Tzvi. 2020. Learning inverse kinematics and dynamics of a robotic manipulator using generative adversarial networks. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 124 (2020), 103386.
[19]
Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez, Łukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017).
[20]
Petar Veličković, Guillem Cucurull, Arantxa Casanova, Adriana Romero, Pietro Liò, and Yoshua Bengio. 2018. Graph Attention Networks. In International Conference on Learning Representations. https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJXMpikCZ
[21]
Vikram Voleti, Boris Oreshkin, Florent Bocquelet, Félix Harvey, Louis-Simon Ménard, and Christopher Pal. 2022. SMPL-IK: Learned Morphology-Aware Inverse Kinematics for AI Driven Artistic Workflows. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2022 Technical Communications. 1–7.
[22]
Yu Wang, Liang Hu, Yang Wu, and Wanfu Gao. 2022. Graph Multihead Attention Pooling with Self-Supervised Learning. Entropy 24, 12 (2022), 1745.
[23]
Katsu Yamane and Yoshihiko Nakamura. 2003. Natural motion animation through constraining and deconstraining at will. IEEE Transactions on visualization and computer graphics 9, 3 (2003), 352–360.
[24]
Xinyu Yi, Yuxiao Zhou, Marc Habermann, Soshi Shimada, Vladislav Golyanik, Christian Theobalt, and Feng Xu. 2022. Physical inertial poser (pip): Physics-aware real-time human motion tracking from sparse inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 13167–13178.