“RMIP: Displacement ray tracing via inversion and oblong bounding” by Thonat, Georgiev, Beaune and Boubekeur
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- RMIP: Displacement ray tracing via inversion and oblong bounding
Session/Category Title: See Details
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
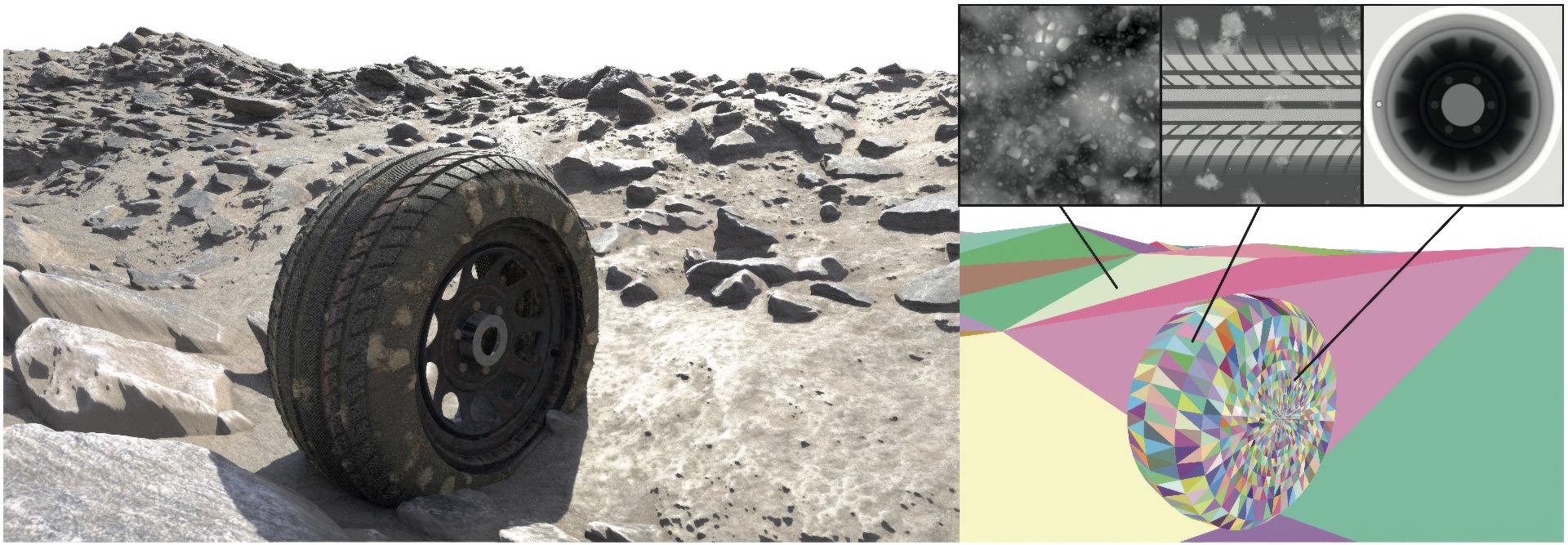
High-performance ray tracing of triangle meshes equipped with displacement maps is a challenging task. Existing methods either rely on pre-tessellation, taking full advantage of the hardware but with a poor memory quality tradeoff, or use custom displacement-centric acceleration structures, preserving all the geometric details, but being orders of magnitude slower. We introduce a method that efficiently probes the displacement map space to find intersections without relying on pre-tessellation. Our method combines inverse displacement mapping with on-the-fly surface bounds computation using a novel data structure that models tight bounds over anisotropic axis-aligned regions in the displacement map space. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in a production GPU path tracer, providing from 2x to an order of magnitude speed-up in render time compared to state of the art in the most challenging real-time path tracing scenarios while maintaining a low memory footprint.
References:
[1]
Amihood Amir, Johannes Fischer, and Moshe Lewenstein. 2007. Two-dimensional range minimum queries. In Combinatorial Pattern Matching: 18th Annual Symposium, CPM 2007, London, Canada, July 9-11, 2007. Proceedings 18. Springer, 286–294.
[2]
Lionel Baboud, Elmar Eisemann, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2011. Precomputed safety shapes for efficient and accurate height-field rendering. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 18, 11 (2011), 1811–1823.
[3]
Gerth Stølting Brodal, Pooya Davoodi, and S Srinivasa Rao. 2012. On space efficient two dimensional range minimum data structures. Algorithmica 63 (2012), 815–830.
[4]
Nathan A Carr, Jared Hoberock, Keenan Crane, and John C Hart. 2006. Fast GPU ray tracing of dynamic meshes using geometry images. In Graphics Interface, Vol. 2006. Citeseer, 203–209.
[5]
Per H. Christensen, David M. Laur, Julia Fong, Wayne L. Wooten, and Dana Batali. 2003. Ray Differentials and Multiresolution Geometry Caching for Distribution Ray Tracing in Complex Scenes. Computer Graphics Forum 22, 3 (2003), 543–552. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8659.t01-1-00702 arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/1467-8659.t01-1-00702
[6]
Peter Djeu, Warren Hunt, Rui Wang, Ikrima Elhassan, Gordon Stoll, and William R. Mark. 2011. Razor: An Architecture for Dynamic Multiresolution Ray Tracing. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 5, Article 115 (Oct. 2011), 26 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/2019627.2019634
[7]
William Donnelly. 2005. Per-pixel displacement mapping with distance functions. GPU gems 2, 22 (2005), 3.
[8]
Jonathan Dummer. 2006. Cone step mapping: An iterative ray-heightfield intersection algorithm. URL: http://www. lonesock. net/files/ConeStepMapping. pdf 2, 3 (2006), 4.
[9]
Johannes Fischer and Volker Heun. 2011. Space-efficient preprocessing schemes for range minimum queries on static arrays. SIAM J. Comput. 40, 2 (2011), 465–492.
[10]
Ned Greene, Michael Kass, and Gavin Miller. 1993. Hierarchical Z-buffer visibility. In Proceedings of the 20th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 231–238.
[11]
Johannes Hanika, Alexander Keller, and Hendrik P. A. Lensch. 2010. Two-Level Ray Tracing with Reordering for Highly Complex Scenes. In Proceedings of Graphics Interface 2010 (Ottawa, Ontario, Canada) (GI ’10). Canadian Information Processing Society, CAN, 145–152.
[12]
Takahiro Harada. 2015. Rendering Vector Displacement Mapped Surfaces in a GPU Ray Tracer. GPU Pro 6: Advanced Rendering Techniques (2015), 459.
[13]
John C Hart. 1996. Sphere tracing: A geometric method for the antialiased ray tracing of implicit surfaces. The Visual Computer 12, 10 (1996), 527–545.
[14]
W. Heidrich and H. Seidel. 1998. Ray-tracing Procedural Displacement Shaders. In Graphics Interface.
[15]
Warren Hunt, William R. Mark, and Don Fussell. 2007. Fast and Lazy Build of Acceleration Structures from Scene Hierarchies. In 2007 IEEE Symposium on Interactive Ray Tracing. 47–54. https://doi.org/10.1109/RT.2007.4342590
[16]
Stefan Jeschke, Stephan Mantler, and Michael Wimmer. 2007. Interactive Smooth and Curved Shell Mapping. In Proceedings of the 18th Eurographics Conference on Rendering Techniques (Grenoble, France) (EGSR’07). Eurographics Association, Goslar, DEU, 351–360.
[17]
Tomomichi Kaneko, Toshiyuki Takahei, Masahiko Inami, Naoki Kawakami, Yasuyuki Yanagida, Taro Maeda, and Susumu Tachi. 2001. Detailed shape representation with parallax mapping. In Proceedings of ICAT, Vol. 2001. 205–208.
[18]
Khronos. 2020. Vulkan Ray Tracing specification. https://www.khronos.org/blog/vulkan-ray-tracing-final-specification-release
[19]
Alexandr Kuznetsov, Krishna Mullia, Zexiang Xu, Miloš Hašan, and Ravi Ramamoorthi. 2021. NeuMIP: multi-resolution neural materials. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 40, 4 (2021), 1–13.
[20]
Alexandr Kuznetsov, Xuezheng Wang, Krishna Mullia, Fujun Luan, Zexiang Xu, Milos Hasan, and Ravi Ramamoorthi. 2022. Rendering Neural Materials on Curved Surfaces. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 Conference Proceedings. 1–9.
[21]
L. Lee, Shih-Wei Tseng, and W. Tai. 2009. Improved Relief Texture Mapping Using Minmax Texture. 2009 Fifth International Conference on Image and Graphics (2009), 547–552.
[22]
James R Logie and John W. Patterson. 1995. Inverse displacement mapping in the general case. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 14. Wiley Online Library, 261–273.
[23]
Andrea Maggiordomo, Henry Moreton, and Marco Tarini. 2023. Micro-Mesh Construction. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 42, 4 (2023), 1–18.
[24]
Kyoungsu Oh, Hyunwoo Ki, and Cheol-Hi Lee. 2006. Pyramidal displacement mapping: a gpu based artifacts-free ray tracing through an image pyramid. In Proceedings of the ACM symposium on Virtual reality software and technology. 75–82.
[25]
John W Patterson, Stuart G Hoggar, and James R Logie. 1991. Inverse displacement mapping. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 10. Wiley Online Library, 129–139.
[26]
Fabio Policarpo and Manuel M Oliveira. 2007. Relaxed cone stepping for relief mapping. GPU gems 3 (2007), 409–428.
[27]
Fábio Policarpo, Manuel M Oliveira, and João LD Comba. 2005. Real-time relief mapping on arbitrary polygonal surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2005 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games. 155–162.
[28]
Serban D. Porumbescu, Brian Budge, Louis Feng, and Kenneth I. Joy. 2005. Shell Maps. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (July 2005), 626–633. https://doi.org/10.1145/1073204.1073239
[29]
V. V. Sanzharov, V. A. Frolov, and V. A. Galaktionov. 2020. Survey of Nvidia RTX Technology. Program. Comput. Softw. 46, 4 (jul 2020), 297–304. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0361768820030068
[30]
Jeremy Shopf, Joshua Barczak, Christopher Oat, and Natalya Tatarchuk. 2008. March of the Froblins: simulation and rendering massive crowds of intelligent and detailed creatures on GPU. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Games. 52–101.
[31]
Brian Smits, Peter Shirley, and Michael M Stark. 2000. Direct ray tracing of displacement mapped triangles. In Eurographics Workshop on Rendering Techniques. Springer, 307–318.
[32]
László Szirmay-Kalos, Tamás Umenhoffer, Gustavo Patow, László Szécsi, and Mateu Sbert. 2009. Specular effects on the gpu: State of the art. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 28. Wiley Online Library, 1586–1617.
[33]
Natalya Tatarchuk. 2006. Dynamic parallax occlusion mapping with approximate soft shadows. In Proceedings of the 2006 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games. 63–69.
[34]
Art Tevs, Ivo Ihrke, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2008. Maximum mipmaps for fast, accurate, and scalable dynamic height field rendering. In Proceedings of the 2008 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games. 183–190.
[35]
Theo Thonat, Francois Beaune, Xin Sun, Nathan Carr, and Tamy Boubekeur. 2021. Tessellation-Free Displacement Mapping for Ray Tracing. 40, 6, Article 282 (dec 2021), 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3478513.3480535
[36]
Ingo Wald, Sven Woop, Carsten Benthin, Gregory S Johnson, and Manfred Ernst. 2014. Embree: a kernel framework for efficient CPU ray tracing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 33, 4 (2014), 1–8.
[37]
Beibei Wang, Miloš Hašan, Nicolas Holzschuch, and Ling-Qi Yan. 2020. Example-based microstructure rendering with constant storage. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 39, 5 (2020), 1–12.
[38]
Lifeng Wang, Xi Wang, Xin Tong, Stephen Lin, Shimin Hu, Baining Guo, and Heung-Yeung Shum. 2003. View-dependent displacement mapping. ACM Transactions on graphics (TOG) 22, 3 (2003), 334–339.
[39]
Xi Wang, Xin Tong, Stephen Lin, Shimin Hu, Baining Guo, and Heung-Yeung Shum. 2004. Generalized displacement maps. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Eurographics conference on Rendering Techniques. 227–233.
[40]
Keith Yerex and Martin Jägersand. 2004. Displacement mapping with ray-casting in hardware. In SIGGRAPH sketches. 149.
[41]
Hao Yuan and Mikhail J Atallah. 2010. Data structures for range minimum queries in multidimensional arrays. In Proceedings of the twenty-first annual ACM-SIAM symposium on Discrete Algorithms. SIAM, 150–160.