“Chordal decomposition for spectral coarsening” by Chen, Liu, Jacobson and Levin
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Chordal decomposition for spectral coarsening
Session/Category Title: Shape Analysis
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
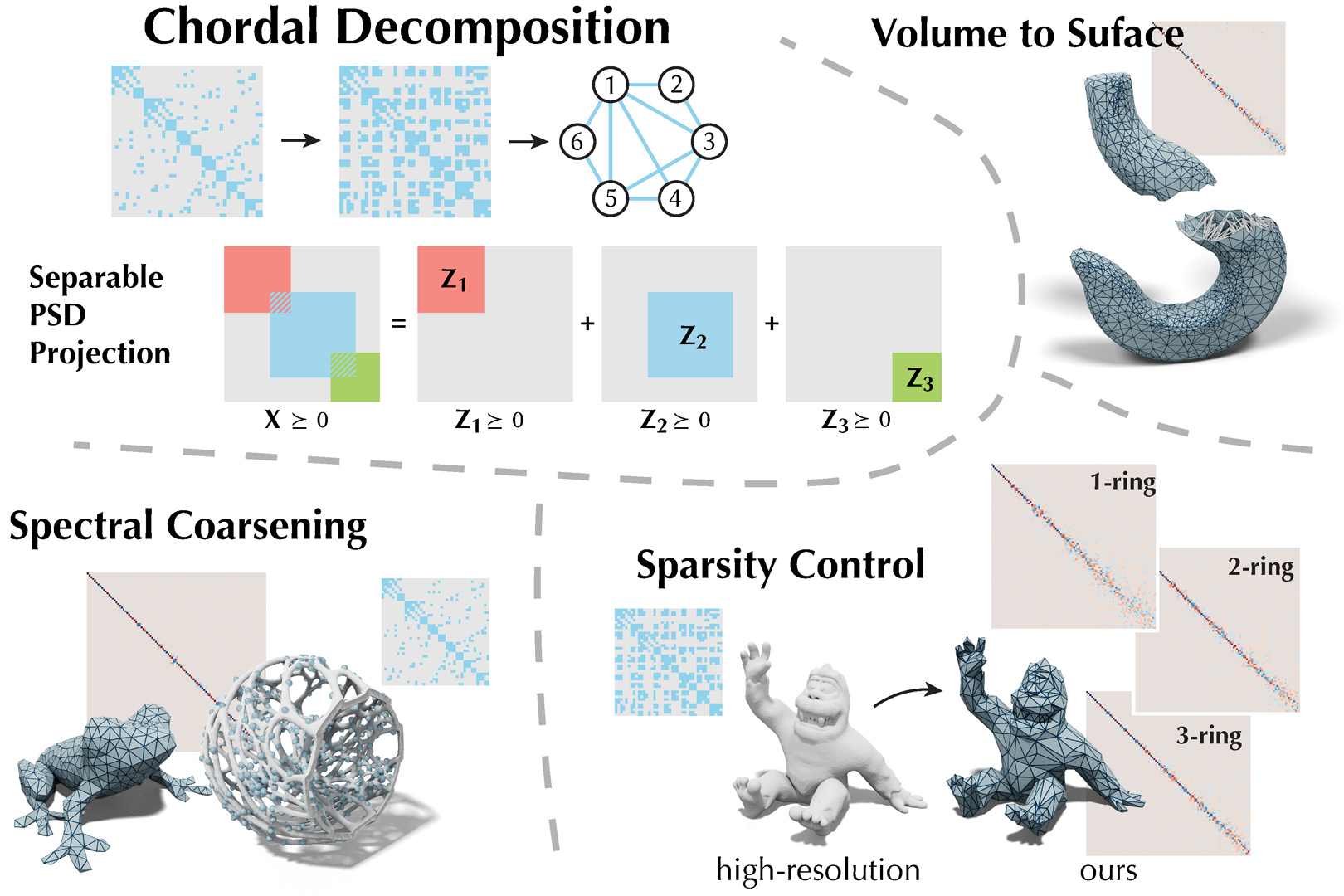
We introduce a novel solver to significantly reduce the size of a geometric operator while preserving its spectral properties at the lowest frequencies. We use chordal decomposition to formulate a convex optimization problem which allows the user to control the operator sparsity pattern. This allows for a trade-off between the spectral accuracy of the operator and the cost of its application. We efficiently minimize the energy with a change of variables and achieve state-of-the-art results on spectral coarsening. Our solver further enables novel applications including volume-to-surface approximation and detaching the operator from the mesh, i.e., one can produce a mesh tailor-made for visualization and optimize an operator separately for computation.
References:
1. Jim Agler, William Helton, Scott McCullough, and Leiba Rodman. 1988. Positive semidefinite matrices with a given sparsity pattern. Linear algebra and its applications 107 (1988), 101–149.Google Scholar
2. Martin S. Andersen, Joachim Dahl, and Lieven Vandenberghe. 2010. Implementation of nonsymmetric interior-point methods for linear optimization over sparse matrix cones. Math. Program. Comput. 2, 3–4 (2010), 167–201.Google ScholarCross Ref
3. Jean RS Blair and Barry Peyton. 1993. An introduction to chordal graphs and clique trees. In Graph theory and sparse matrix computation. 1–29.Google Scholar
4. Stephen P. Boyd, Neal Parikh, Eric Chu, Borja Peleato, and Jonathan Eckstein. 2011. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning 3, 1 (2011), 1–122.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Gecia Bravo-Hermsdorff and Lee Gunderson. 2019. A Unifying Framework for Spectrum-Preserving Graph Sparsification and Coarsening. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32. 7736–7747.Google Scholar
6. Max Budninskiy, Houman Owhadi, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2019. Operator-adapted wavelets for finite-element differential forms. J. Comput. Phys. 388 (2019), 144–177.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Samuel Burer. 2003. Semidefinite Programming in the Space of Partial Positive Semidefinite Matrices. SIAM Journal on Optimization 14, 1 (2003), 139–172.Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Desai Chen, David I. W. Levin, Wojciech Matusik, and Danny M. Kaufman. 2017. Dynamics-aware numerical coarsening for fabrication design. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 84:1–84:15.Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Desai Chen, David I. W. Levin, Shinjiro Sueda, and Wojciech Matusik. 2015. Data-driven finite elements for geometry and material design. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 74:1–74:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Jiong Chen, Hujun Bao, Tianyu Wang, Mathieu Desbrun, and Jin Huang. 2018. Numerical Coarsening Using Discontinuous Shape Functions. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 37, 4, Article 120 (July 2018), 12 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Jiong Chen, Max Budninskiy, Houman Owhadi, Hujun Bao, Jin Huang, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2019a. Material-Adapted Refinable Basis Functions for Elasticity Simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 6, Article Article 161 (Nov. 2019), 15 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Yu Ju Edwin Chen, David I. W. Levin, Danny Kaufmann, Uri M. Ascher, and Dinesh K. Pai. 2019b. EigenFit for consistent elastodynamic simulation across mesh resolution. In Proceedings of the 18th annual ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, SCA 2019. 5:1–5:13.Google Scholar
13. Paolo Cignoni, Claudio Montani, and Roberto Scopigno. 1998. A comparison of mesh simplification algorithms. Comput. Graph. 22, 1 (1998), 37–54.Google ScholarCross Ref
14. Jonathan D. Cohen, Dinesh Manocha, and Marc Olano. 2003. Successive Mappings: An Approach to Polygonal Mesh Simplification with Guaranteed Error Bounds. Int. J. Comput. Geometry Appl. 13, 1 (2003), 61.Google ScholarCross Ref
15. David Cohen-Steiner, Pierre Alliez, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2004. Variational shape approximation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 23, 3 (2004), 905–914.Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Katsuki Fujisawa, Sunyoung Kim, Masakazu Kojima, Yoshio Okamoto, and Makoto Yamashita. 2009. B-453 User’s Manual for SparseCoLO: Conversion Methods for SPARSE COnic-form Linear Optimization Problems. (2009).Google Scholar
17. Mituhiro Fukuda, Masakazu Kojima, Kazuo Murota, and Kazuhide Nakata. 2001. Exploiting Sparsity in Semidefinite Programming via Matrix Completion I: General Framework. SIAM Journal on Optimization 11, 3 (2001), 647–674.Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Michael Garland and Paul S. Heckbert. 1997. Surface simplification using quadric error metrics. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH 1997. 209–216.Google Scholar
19. Michael Garland and Paul S. Heckbert. 1998. Simplifying surfaces with color and texture using quadric error metrics. In Visualization ’98, Proceedings. 263–269.Google Scholar
20. Michael Grant and Stephen Boyd. 2008. Graph implementations for nonsmooth convex programs. In Recent Advances in Learning and Control. 95–110.Google Scholar
21. Michael Grant and Stephen Boyd. 2014. CVX: Matlab Software for Disciplined Convex Programming, version 2.1.Google Scholar
22. Robert Grone, Charles R Johnson, Eduardo M Sá, and Henry Wolkowicz. 1984. Positive definite completions of partial Hermitian matrices. Linear algebra and its applications 58 (1984), 109–124.Google Scholar
23. Pinar Heggernes. 2006. Minimal triangulations of graphs: A survey. Discret. Math. 306, 3 (2006), 297–317.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Hugues Hoppe. 1996. Progressive Meshes. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH 1996. 99–108.Google Scholar
25. Hugues Hoppe. 1997. View-dependent refinement of progressive meshes. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH 1997. 189–198.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Hugues Hoppe, Tony DeRose, Tom Duchamp, John Alan McDonald, and Werner Stuetzle. 1993. Mesh optimization. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH 1993. 19–26.Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Alec Jacobson et al. 2018. gptoolbox: Geometry Processing Toolbox. http://github.com/alecjacobson/gptoolbox.Google Scholar
28. Doug L. James and Dinesh K. Pai. 1999. ArtDefo: Accurate Real Time Deformable Objects. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’99). 65–72.Google Scholar
29. Yu Jin, Andreas Loukas, and Joseph JáJá. 2020. Graph Coarsening with Preserved Spectral Properties. In The 23rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, AISTATS 2020, Vol. 108. 4452–4462.Google Scholar
30. Naonori Kakimura. 2010. A direct proof for the matrix decomposition of chordalstructured positive semidefinite matrices. Linear Algebra Appl. 433, 4 (2010), 819–823.Google ScholarCross Ref
31. Liliya Kharevych, Patrick Mullen, Houman Owhadi, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2009. Numerical coarsening of inhomogeneous elastic materials. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 28, 3 (2009), 51.Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Sunyoung Kim, Masakazu Kojima, Martin Mevissen, and Makoto Yamashita. 2011. Exploiting sparsity in linear and nonlinear matrix inequalities via positive semidefinite matrix completion. Math. Program. 129, 1 (2011), 33–68.Google ScholarCross Ref
33. Thibault Lescoat, Hsueh-Ti Derek Liu, Jean-Marc Thiery, Alec Jacobson, Tamy Boubekeur, and Maks Ovsjanikov. 2020. Spectral Mesh Simplification. Computer Graphics Forum 39, 2 (2020), 49–58.Google ScholarCross Ref
34. Dingzeyu Li, Yun (Raymond) Fei, and Changxi Zheng. 2015. Interactive Acoustic Transfer Approximation for Modal Sound. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 1 (2015), 2:1–2:16.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Hsueh-Ti Derek Liu, Alec Jacobson, and Maks Ovsjanikov. 2019. Spectral Coarsening of Geometric Operators. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 4, Article Article 105 (July 2019), 13 pages.Google Scholar
36. Andreas Loukas. 2019. Graph Reduction with Spectral and Cut Guarantees. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 20 (2019), 116:1–116:42.Google Scholar
37. Andreas Loukas and Pierre Vandergheynst. 2018. Spectrally Approximating Large Graphs with Smaller Graphs. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2018, Vol. 80. 3243–3252.Google Scholar
38. Yunlong Lu, Qing Liu, Yi Wang, Peter Gardner, Wang He, Yi Chen, Jifu Huang, and Taijun Liu. 2020. Seamless Integration of Active Antenna With Improved Power Efficiency. IEEE Access 8 (2020), 48399–48407.Google ScholarCross Ref
39. Ramtin Madani, Abdulrahman Kalbat, and Javad Lavaei. 2015. ADMM for sparse semidefinite programming with applications to optimal power flow problem. In 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, CDC 2015. 5932–5939.Google ScholarCross Ref
40. Haggai Maron, Nadav Dym, Itay Kezurer, Shahar Kovalsky, and Yaron Lipman. 2016. Point Registration via Efficient Convex Relaxation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 4, Article Article 73 (July 2016), 12 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Kazuhide Nakata, Katsuki Fujisawa, and Mituhiro Fukuda. 2003. Exploiting sparsity in semidefinite programming via matrix completion II: implementation and numerical results. Math. Program. 95, 2 (2003), 303–327.Google ScholarCross Ref
42. Ahmad Nasikun, Christopher Brandt, and Klaus Hildebrandt. 2018. Fast Approximation of Laplace-Beltrami Eigenproblems. Comput. Graph. Forum 37, 5 (2018), 121–134.Google ScholarCross Ref
43. Maks Ovsjanikov, Mirela Ben-Chen, Justin Solomon, Adrian Butscher, and Leonidas J. Guibas. 2012. Functional maps: a flexible representation of maps between shapes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4 (2012), 30:1–30:11.Google ScholarDigital Library
44. Maks Ovsjanikov, Etienne Corman, Michael M. Bronstein, Emanuele Rodolà, Mirela Ben-Chen, Leonidas J. Guibas, Frédéric Chazal, and Alexander M. Bronstein. 2017. Computing and processing correspondences with functional maps. In Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Conference, SIGGRAPH ’17 Courses. 5:1–5:62.Google Scholar
45. Houman Owhadi. 2017. Multigrid with Rough Coefficients and Multiresolution Operator Decomposition from Hierarchical Information Games. SIAM Rev. 59, 1 (2017), 99–149.Google ScholarDigital Library
46. A. Cengiz Öztireli, Marc Alexa, and Markus H. Gross. 2010. Spectral sampling of manifolds. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 29, 6 (2010), 168.Google ScholarDigital Library
47. E. Rodolí, L. Cosmo, M. M. Bronstein, A. Torsello, and D. Cremers. 2017. Partial Functional Correspondence. Comput. Graph. Forum 36, 1 (Jan. 2017), 222–236.Google Scholar
48. Nicholas Sharp, Yousuf Soliman, and Keenan Crane. 2019. Navigating intrinsic triangulations. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 4 (2019), 55.Google ScholarDigital Library
49. Hang Si. 2015. TetGen, a Delaunay-Based Quality Tetrahedral Mesh Generator. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 41, 2, Article 11 (Feb. 2015), 36 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
50. Gun Srijuntongsiri and Stephen A. Vavasis. 2004. A Fully Sparse Implementation of a Primal-Dual Interior-Point Potential Reduction Method for Semidefinite Programming. CoRR (2004).Google Scholar
51. Yifan Sun. 2015. Decomposition methods for semidefinite optimization. Ph.D. Dissertation. UCLA.Google Scholar
52. Yifan Sun, Martin S. Andersen, and Lieven Vandenberghe. 2014. Decomposition in Conic Optimization with Partially Separable Structure. SIAM Journal on Optimization 24, 2 (2014), 873–897.Google ScholarCross Ref
53. Yifan Sun and Lieven Vandenberghe. 2015. Decomposition Methods for Sparse Matrix Nearness Problems. SIAM J. Matrix Analysis Applications 36, 4 (2015), 1691–1717.Google ScholarCross Ref
54. Lieven Vandenberghe and Martin S. Andersen. 2015. Chordal Graphs and Semidefinite Optimization. Foundations and Trends in Optimization 1, 4 (2015), 241–433.Google ScholarDigital Library
55. M. Yannakakis. 1981. Computing the Minimum Fill-In is NP-Complete. SIAM Journal on Algebraic Discrete Methods 2, 1 (1981), 77–79.Google ScholarDigital Library
56. Zhiqiang Zhao, Yongyu Wang, and Zhuo Feng. 2018. Nearly-Linear Time Spectral Graph Reduction for Scalable Graph Partitioning and Data Visualization. CoRR (2018).Google Scholar
57. Yang Zheng, Giovanni Fantuzzi, and Antonis Papachristodoulou. 2017a. Exploiting sparsity in the coefficient matching conditions in sum-of-squares programming using ADMM. IEEE control systems letters 1, 1 (2017), 80–85.Google ScholarCross Ref
58. Yang Zheng, Giovanni Fantuzzi, and Antonis Papachristodoulou. 2019. Fast ADMM for Sum-of-Squares Programs Using Partial Orthogonality. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 64, 9 (2019), 3869–3876.Google ScholarCross Ref
59. Yang Zheng, Giovanni Fantuzzi, Antonis Papachristodoulou, Paul Goulart, and Andrew Wynn. 2017b. Fast ADMM for semidefinite programs with chordal sparsity. In 2017 American Control Conference. 3335–3340.Google ScholarCross Ref
60. Yang Zheng, Giovanni Fantuzzi, Antonis Papachristodoulou, Paul Goulart, and Andrew Wynn. 2020. Chordal decomposition in operator-splitting methods for sparse semidefinite programs. Math. Program. 180, 1 (2020), 489–532.Google ScholarDigital Library
61. Yang Zheng, Richard P. Mason, and Antonis Papachristodoulou. 2018. Scalable Design of Structured Controllers Using Chordal Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 63, 3 (2018), 752–767.Google ScholarCross Ref