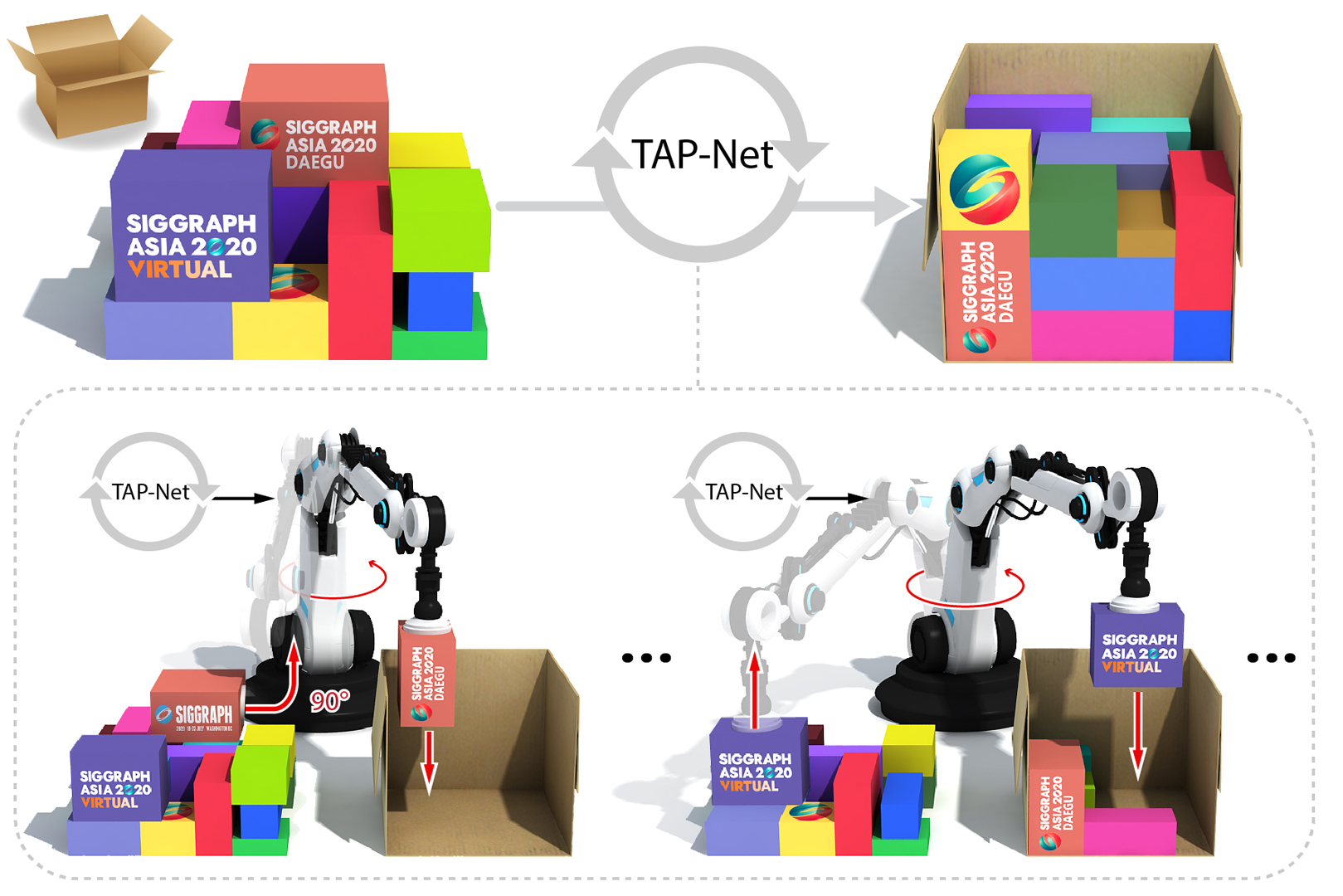
“TAP-Net: transport-and-pack using reinforcement learning” by Hu, Xu, Chen, Gong, Zhang, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- TAP-Net: transport-and-pack using reinforcement learning
Session/Category Title: Learning to Move and Synthesize
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We introduce the transport-and-pack (TAP) problem, a frequently encountered instance of real-world packing, and develop a neural optimization solution based on reinforcement learning. Given an initial spatial configuration of boxes, we seek an efficient method to iteratively transport and pack the boxes compactly into a target container. Due to obstruction and accessibility constraints, our problem has to add a new search dimension, i.e., finding an optimal transport sequence, to the already immense search space for packing alone. Using a learning-based approach, a trained network can learn and encode solution patterns to guide the solution of new problem instances instead of executing an expensive online search. In our work, we represent the transport constraints using a precedence graph and train a neural network, coined TAP-Net, using reinforcement learning to reward efficient and stable packing. The network is built on an encoder-decoder architecture, where the encoder employs convolution layers to encode the box geometry and precedence graph and the decoder is a recurrent neural network (RNN) which inputs the current encoder output, as well as the current box packing state of the target container, and outputs the next box to pack, as well as its orientation. We train our network on randomly generated initial box configurations, without supervision, via policy gradients to learn optimal TAP policies to maximize packing efficiency and stability. We demonstrate the performance of TAP-Net on a variety of examples, evaluating the network through ablation studies and comparisons to baselines and alternative network designs. We also show that our network generalizes well to larger problem instances, when trained on small-sized inputs.
References:
1. Irwan Bello, Hieu Pham, Quoc V. Le, Mohammad Norouzi, and Samy Bengio. 2017. Neural Combinatorial Optimization with Reinforcement Learning. (2017). https://openreview.net/forum?id=Bk9mxlSFxGoogle Scholar
2. Nathan A. Carr and John C. Hart. 2002. Meshed Atlases for Real-time Procedural Solid Texturing. ACM Trans. on Graphics 21, 2 (2002), 106–131.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Bernard Chazelle, Herbert Edelsbrunner, and Leonidas J Guibas. 1989. The complexity of cutting complexes. Discrete & Computational Geometry 4, 2 (1989), 139–181.Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Xuelin Chen, Hao Zhang, Jinjie Lin, Ruizhen Hu, Lin Lu, Qi xing Huang, Bedrich Benes, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Baoquan Chen. 2015. Dapper: Decompose-and-Pack for 3D Printing. ACM Trans. on Graphics 34, 6 (2015), Article 213.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Karl Cobbe, Oleg Klimov, Christopher Hesse, Taehoon Kim, and John Schulman. 2018. Quantifying Generalization in Reinforcement Learning. CoRR abs/1812.02341 (2018). arXiv:1812.02341 http://arxiv.org/abs/1812.02341Google Scholar
6. Lars Doyle, Forest Anderson, Ehren Choy, and David Mould. 2019. Automated pebble mosaic stylization of images. Computational Visual Media 5, 1 (2019), 33–44.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Lu Duan, Haoyuan Hu, Yu Qian, Yu Gong, Xiaodong Zhang, Jiangwen Wei, and Yinghui Xu. 2019. A Multi-task Selected Learning Approach for Solving 3D Flexible Bin Packing Problem. (2019), 1386–1394.Google Scholar
8. Bruce L Golden, Subramanian Raghavan, and Edward A Wasil. 2008. The vehicle routing problem: latest advances and new challenges. Vol. 43. Springer Science & Business Media.Google Scholar
9. Haoyuan Hu, Xiaodong Zhang, Xiaowei Yan, Longfei Wang, and Yinghui Xu. 2017. Solving a new 3d bin packing problem with deep reinforcement learning method. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.05930 (2017).Google Scholar
10. Craig S Kaplan and David H Salesin. 2000. Escherization. In Proceedings of the 27th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 499–510.Google Scholar
11. Korhan Karabulut and Mustafa Murat İnceoğlu. 2004. A hybrid genetic algorithm for packing in 3D with deepest bottom left with fill method. (2004), 441–450.Google Scholar
12. Yaser Keneshloo, Tian Shi, Naren Ramakrishnan, and Chandan K. Reddy. 2019. Deep Reinforcement Learning For Sequence to Sequence Models. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS AND LEARNING SYSTEMS (2019).Google Scholar
13. Bongjin Koo, Jean Hergel, Sylvain Lefebvre, and Niloy J Mitra. 2016. Towards zero-waste furniture design. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 23, 12 (2016), 2627–2640.Google Scholar
14. Bruno Lévy, Sylvain Petitjean, Nicolas Ray, and Jérome Maillot. 2002. Least squares conformal maps for automatic texture atlas generation. In ACM transactions on graphics (TOG), Vol. 21. ACM, 362–371.Google Scholar
15. Max Limper, Nicholas Vining, and Alla Sheffer. 2018. BoxCutter: Atlas Refinement for Efficient Packing via Void Elimination. ACM Trans. on Graphics 37, 4 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Hao-Yu Liu, Xiao-Ming Fu, Chunyang Ye, Shuangming Chai, and Ligang Liu. 2019. Atlas refinement with bounded packing efficiency. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 4 (2019), 1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Xiao Liu, Jia-min Liu, An-xi Cao, et al. 2015. HAPE3D—a new constructive algorithm for the 3D irregular packing problem. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering 16, 5 (2015), 380–390.Google ScholarCross Ref
18. Yuexin Ma, Zhonggui Chen, Wenchao Hu, and Wenping Wang. 2018. Packing irregular objects in 3D space via hybrid optimization. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. Wiley Online Library, 49–59.Google Scholar
19. Volodymyr Mnih, Adria Puigdomenech Badia, Mehdi Mirza, Alex Graves, Timothy Lillicrap, Tim Harley, David Silver, and Koray Kavukcuoglu. 2016. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. In International conference on machine learning. 1928–1937.Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Yuichi Nagata and Shinji Imahori. 2020. An Efficient Exhaustive Search Algorithm for the Escherization Problem. Algorithmica (2020), 1–33.Google Scholar
21. MohammadReza Nazari, Afshin Oroojlooy, Lawrence Snyder, and Martin Takac. 2018. Reinforcement Learning for Solving the Vehicle Routing Problem. (2018), 9839–9849. http://papers.nips.cc/paper/8190-reinforcement-learning-for-solving-the-vehicle-routing-problem.pdfGoogle Scholar
22. Tobias Nöll and Didier Stricker. 2011. Efficient Packing of Arbitrarily Shaped Charts for Automatic Texture Atlas Generation. In Proc. of Eurographics Conference on Rendering (EGSR). 1309–1317.Google Scholar
23. Charles Packer, Katelyn Gao, Jernej Kos, Philipp Krähenbühl, Vladlen Koltun, and Dawn Song. 2018. Assessing Generalization in Deep Reinforcement Learning. CoRR abs/1810.12282 (2018). arXiv:1810.12282 http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.12282Google Scholar
24. A Galrão Ramos, José F Oliveira, José F Gonçalves, and Manuel P Lopes. 2016. A container loading algorithm with static mechanical equilibrium stability constraints. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological 91 (2016), 565–581.Google ScholarCross Ref
25. Bernhard Reinert, Tobias Ritschel, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2013. Interactive By-example Design of Artistic Packing Layouts. ACM Trans. on Graphics 31, 6 (2013).Google Scholar
26. Daniel Saakes, Thomas Cambazard, Jun Mitani, and Takeo Igarashi. 2013. PacCAM: Material capture and interactive 2D packing for efficient material usage on CNC cutting machines. In ACM UIST.Google Scholar
27. Pedro V Sander, Zoë J Wood, Steven Gortler, John Snyder, and Hugues Hoppe. 2003. Multi-chart geometry images. (2003).Google Scholar
28. I Sutskever, O Vinyals, and QV Le. 2014. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Advances in NIPS (2014).Google Scholar
29. Juraj Vanek, JA Garcia Galicia, Bedrich Benes, R Měch, N Carr, Ondrej Stava, and GS Miller. 2014. PackMerger: A 3D print volume optimizer. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 33. Wiley Online Library, 322–332.Google Scholar
30. Oriol Vinyals, Meire Fortunato, and Navdeep Jaitly. 2015. Pointer Networks. (2015), 2692–2700. http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5866-pointer-networks.pdfGoogle Scholar
31. Fan Wang and Kris Hauser. 2019. Stable bin packing of non-convex 3D objects with a robot manipulator. (2019), 8698–8704.Google Scholar
32. Chen Wei, Lingxi Xie, Xutong Ren, Yingda Xia, Chi Su, Jiaying Liu, Qi Tian, and Alan L Yuille. 2019. Iterative reorganization with weak spatial constraints: Solving arbitrary jigsaw puzzles for unsupervised representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 1910–1919.Google ScholarCross Ref