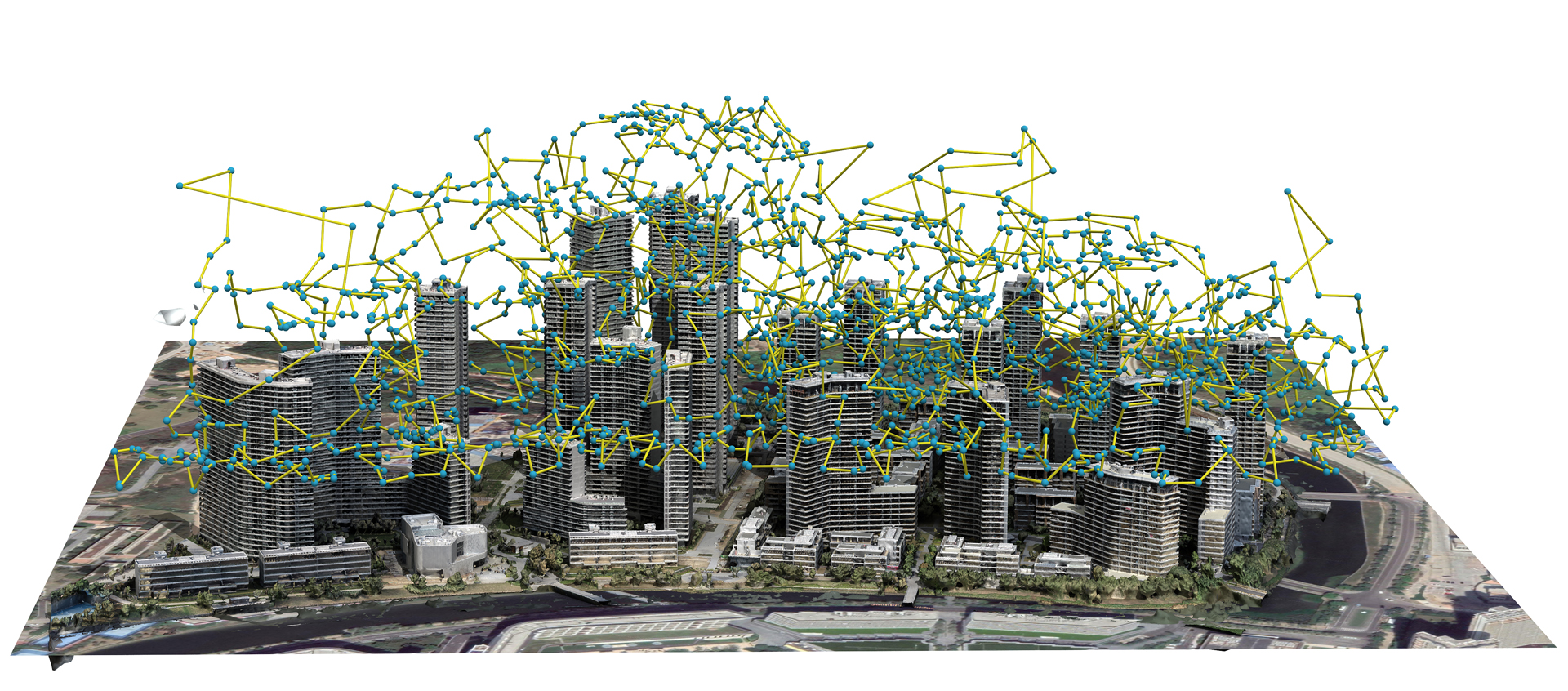
“Offsite aerial path planning for efficient urban scene reconstruction” by Zhou, Xie, Huang, Liu, Zhou, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Offsite aerial path planning for efficient urban scene reconstruction
Session/Category Title: Computational Robotics
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
With rapid development in UAV technologies, it is now possible to reconstruct large-scale outdoor scenes using only images captured by low-cost drones. The problem, however, becomes how to plan the aerial path for a drone to capture images so that two conflicting goals are optimized: maximizing the reconstruction quality and minimizing mid-air image acquisition effort. Existing approaches either resort to pre-defined dense and thus inefficient view sampling strategy, or plan the path adaptively but require two onsite flight passes and intensive computation in-between. Hence, using these methods to capture and reconstruct large-scale scenes can be tedious. In this paper, we present an adaptive aerial path planning algorithm that can be done before the site visit. Using only a 2D map and a satellite image of the to-be-reconstructed area, we first compute a coarse 2.5D model for the scene based on the relationship between buildings and their shadows. A novel Max-Min optimization is then proposed to select a minimal set of viewpoints that maximizes the reconstructability under the the same number of viewpoints. Experimental results on benchmark show that our planning approach can effectively reduce the number of viewpoints needed than the previous state-of-the-art method, while maintaining comparable reconstruction quality. Since no field computation or a second visit is needed, and the view number is also minimized, our approach significantly reduces the time required in the field as well as the off-line computation cost for multi-view stereo reconstruction, making it possible to reconstruct a large-scale urban scene in a short time with moderate effort.
References:
1. Helmut Alt and Emo Welzl. 1988. Visibility Graphs and Obstacle-avoiding Shortest Paths. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research 32, 3 (1988), 145–164.Google ScholarCross Ref
2. M. Corsini, P. Cignoni, and R. Scopigno. 2012. Efficient and Flexible Sampling with Blue Noise Properties of Triangular Meshes. IEEE Trans. Visualization & Computer Graphics 18, 6 (2012), 914–924.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Liuyun Duan and Florent Lafarge. 2016. Towards Large-scale City Reconstruction from Satellites. In Proc. of Euro. Conf. on Computer Vision. Springer, 89–104.Google ScholarCross Ref
4. J. Engel, T. Schöps, and D. Cremers. 2014. LSD-SLAM: Large-Scale Direct Monocular SLAM. In Proc. of Euro. Conf. on Computer Vision. 834–849.Google Scholar
5. Xinyi Fan, Linguang Zhang, Benedict Brown, and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2016. Automated View and Path Planning for Scalable Multi-Object 3D Scanning. ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH Asia 2016) 35, 6 (2016), 239:1–239:13.Google Scholar
6. Simon Fuhrmann, Fabian Langguth, Nils Moehrle, Michael Waechter, and Michael Goesele. 2015. MVE – An Image-based Reconstruction Environment. Computers & Graphics 53 (2015), 44–53.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Yasutaka Furukawa, Carlos Hernández, et al. 2015. Multi-view Stereo: A Tutorial. Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision 9, 1–2 (2015), 1–148.Google ScholarCross Ref
8. Ruiqi Guo, Qieyun Dai, and D. Hoiem. 2011. Single-image Shadow Detection and Removal using Paired Regions. In Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. 2033–2040.Google Scholar
9. Keld Helsgaun. 2015. Solving the Equality Generalized Traveling Salesman Problem using the Lin-Kernighan-Helsgaun Algorithm. Mathematical Programming Computation 7, 3 (2015), 269–287.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. Benjamin Hepp, Debadeepta Dey, Sudipta N Sinha, Ashish Kapoor, Neel Joshi, and Otmar Hilliges. 2018a. Learn-to-score: Efficient 3D scene exploration by predicting view utility. In Proc. of Euro. Conf. on Computer Vision. 437–452.Google ScholarCross Ref
11. B. Hepp, M. Nießner, and O. Hilliges. 2018b. Plan3D: Viewpoint and Trajectory Optimization for Aerial Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction. ACM Trans. on Graphics 38, 1 (2018), 4:1–4:17.Google Scholar
12. A. Hornung, B. Zeng, and L. Kobbelt. 2008. Image Selection for Improved Multi-View Stereo. In Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. 1–8.Google Scholar
13. Xiaowei Hu, Chi-Wing Fu, Lei Zhu, Jing Qin, and Pheng-Ann Heng. 2018. Direction-aware Spatial Context Features for Shadow Detection and Removal. In Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 7454–7462.Google Scholar
14. Rui Huang, Danping Zou, Richard Vaughan, and Ping Tan. 2018. Active Image-based Modeling with a Toy Drone. Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (2018), 1–8.Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Alejandro Jenkins. 2013. The Sun’s Position in the Sky. European Journal of Physics 34, 3 (2013), 633–652.Google ScholarCross Ref
16. Arno Knapitsch, Jaesik Park, Qian-Yi Zhou, and Vladlen Koltun. 2017. Tanks and Temples: Benchmarking Large-scale Scene Reconstruction. ACM Trans. on Graphics 36, 4 (2017), 78:1–78:13.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Tobias Koch, Marco Körner, and Friedrich Fraundorfer. 2019. Automatic and semantically-aware 3D UAV flight planning for image-based 3D reconstruction. Remote Sensing 11, 13 (2019), 1550.Google ScholarCross Ref
18. Gregoris Liasis and Stavros Stavrou. 2016. Satellite Images Analysis for Shadow Detection and Building Height Estimation. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 119 (2016), 437–450.Google ScholarCross Ref
19. Ligang Liu, Xi Xia, Han Sun, Qi Shen, Junzhan Xu, Bin Chen, Hui Huang, and Kai Xu. 2018. Object-Aware Guidance for Autonomous Scene Reconstruction. ACM Trans. on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH) 37, 4 (2018), 104:1–104:12.Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Scott Mason. 1997. Heuristic Reasoning Strategy for Automated Sensor Placement. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing 63, 9 (1997), 1093–1102.Google Scholar
21. Massimo Mauro, Hayko Riemenschneider, Alberto Signoroni, Riccardo Leonardi, and Luc Van Gool. 2014. A Unified Framework for Content-aware View Selection and Planning Through View Importance. In Proc. of British Machine Vision Conference.Google ScholarCross Ref
22. Oscar Mendez Maldonado, Simon Hadfield, Nicolas Pugeault, and Richard Bowden. 2016. Next-best Stereo: Extending Next Best View Optimization for Collaborative Sensors. In Proc. of British Machine Vision Conference.Google ScholarCross Ref
23. Miguel Mendoza, J Irving Vasquez-Gomez, Hind Taud, Luis Enrique Sucar, and Carolina Reta. 2019. Supervised Learning of the Next-Best-View for 3D Object Reconstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.05833 (2019).Google Scholar
24. Lichao Mou and Xiao Xiang Zhu. 2018. IM2HEIGHT: Height Estimation from Single Monocular Imagery via Fully Residual Convolutional-Deconvolutional Network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.10249 (2018).Google Scholar
25. Gustavo Olague and Roger Mohr. 2002. Optimal Camera Placement for Accurate Reconstruction. Pattern Recognition 35, 4 (2002), 927–944.Google ScholarCross Ref
26. Mike Roberts, Debadeepta Dey, Anh Truong, Sudipta Sinha, Shital Shah, Ashish Kapoor, Pat Hanrahan, and Neel Joshi. 2017. Submodular Trajectory Optimization for Aerial 3D Scanning. In Proc. of Int. Conf. on Computer Vision.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Mike Roberts and Pat Hanrahan. 2016. Generating Dynamically Feasible Trajectories for Quadrotor Cameras. ACM Trans. on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH) 35, 4 (2016), 61:1–61:11.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. D. Scaramuzza, M. C. Achtelik, L. Doitsidis, F. Friedrich, E. Kosmatopoulos, A. Martinelli, M. W. Achtelik, M. Chli, S. Chatzichristofis, L. Kneip, D. Gurdan, L. Heng, G. H. Lee, S. Lynen, M. Pollefeys, A. Renzaglia, R. Siegwart, J. C. Stumpf, P. Tanskanen, C. Troiani, S. Weiss, and L. Meier. 2014. Vision-Controlled Micro Flying Robots: From System Design to Autonomous Navigation and Mapping in GPS-Denied Environments. IEEE Robotics Automation Magazine 21, 3 (2014), 26–40.Google ScholarCross Ref
29. Johannes Lutz Schönberger and Jan-Michael Frahm. 2016. Structure-from-Motion Revisited. In Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition.Google Scholar
30. Steven M Seitz, Brian Curless, James Diebel, Daniel Scharstein, and Richard Szeliski. 2006. A Comparison and Evaluation of Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction Algorithms. In Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. 519–528.Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Zhexiong Shang, Justin Bradley, and Zhigang Shen. 2020. A co-optimal coverage path planning method for aerial scanning of complex structures. Expert Systems with Applications 158 (2020), 113535.Google ScholarCross Ref
32. S. Shen, N. Michael, and V. Kumar. 2011. Autonomous Multi-floor Indoor Navigation with a Computationally Constrained MAV. In Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation. 20–25.Google Scholar
33. Neil Smith, Nils Moehrle, Michael Goesele, and Wolfgang Heidrich. 2018. Aerial Path Planning for Urban Scene Reconstruction: A Continuous Optimization Method and Benchmark. ACM Trans. on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH Asia) 37, 6 (2018), 183:1–183:15.Google Scholar
34. Shihao Wu, Wei Sun, Pinxin Long, Hui Huang, Daniel Cohen-Or, Minglun Gong, Oliver Deussen, and Baoquan Chen. 2014. Quality-driven Poisson-guided autoscanning. ACM Trans. on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH Asia) 33 (2014), 203:1–203:12. Issue 6.Google Scholar
35. Ke Xie, Hao Yang, Shengqiu Huang, Dani Lischinski, Marc Christie, Kai Xu, Minglun Gong, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Hui Huang. 2018. Creating and Chaining Camera Moves for Quadrotor Videography. ACM Trans. on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH) 37, 4 (2018), 88:1–88:13.Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Kai Xu, Yifei Shi, Lintao Zheng, Junyu Zhang, Min Liu, Hui Huang, Hao Su, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Baoquan Chen. 2016. 3D Attention-driven Depth Acquisition for Object Identification. ACM Trans. on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH Asia) 35, 6 (2016), 238:1–238:14.Google Scholar
37. Hao Yang, Ke Xie, Shengqiu Huang, and Hui Huang. 2018. Uncut Aerial Video via a Single Sketch. Computer Graphics Forum (Proc. of Pacific Conf. on Computer Graphics & Applications) 37, 7 (2018), 191–199.Google ScholarCross Ref
38. Xujie Zhang, Pengcheng Zhao, Qingwu Hu, Mingyao Ai, Datian Hu, and Jiayuan Li. 2020. A UAV-based panoramic oblique photogrammetry (POP) approach using spherical projection. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 159 (2020), 198–219.Google ScholarCross Ref
39. Qian Zheng, Andrei Sharf, Guowei Wan, Yangyan Li, Niloy J. Mitra, Baoquan Chen, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2010. Non-local Scan Consolidation for 3D Urban Scene. ACM Trans. on Graphics (Proc. of SIGGRAPH) 29 (2010), 94:1–94:9. Issue 4.Google ScholarDigital Library