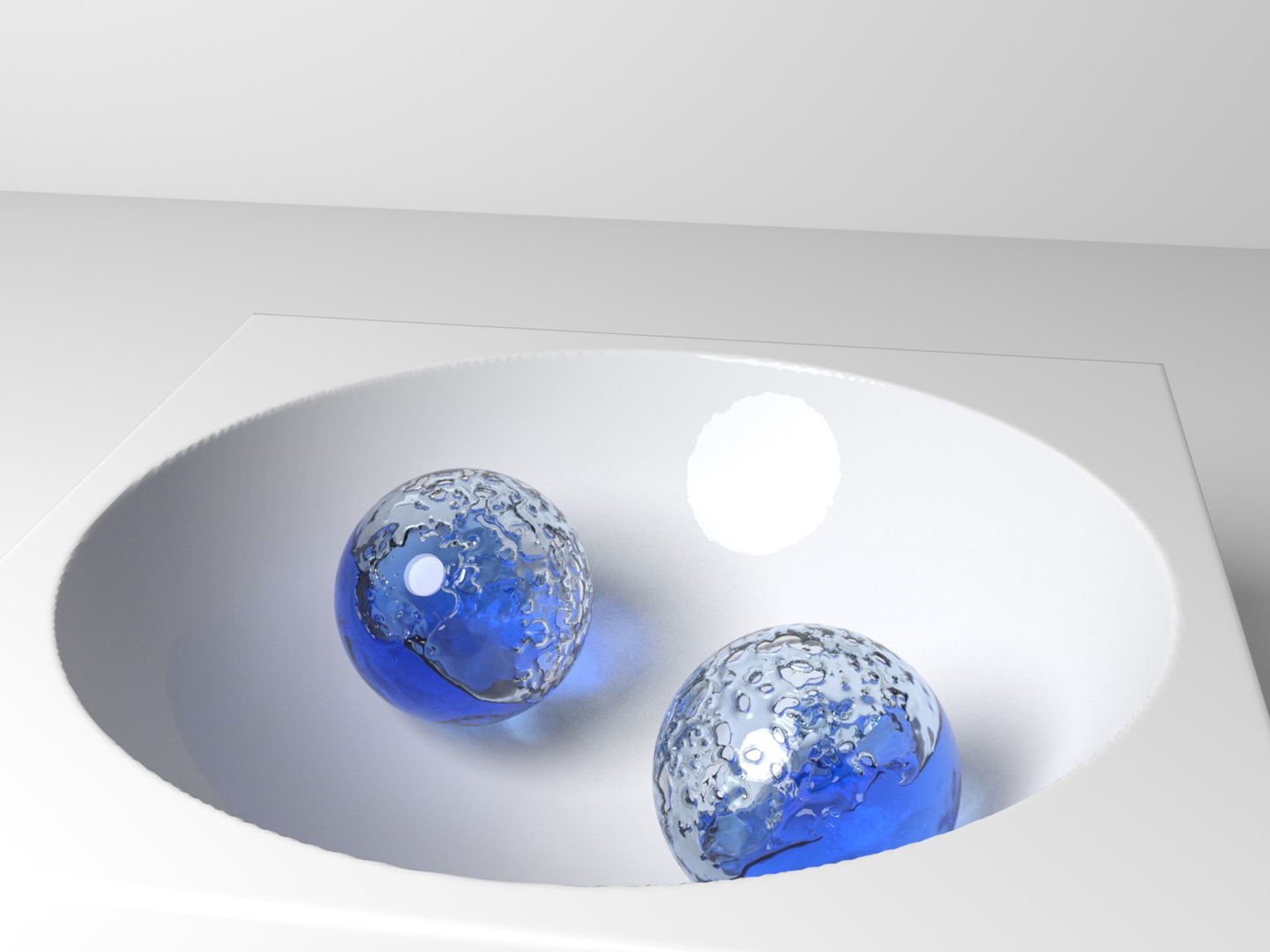
“Monolith: a monolithic pressure-viscosity-contact solver for strong two-way rigid-rigid rigid-fluid coupling” by Takahashi and Batty
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Monolith: a monolithic pressure-viscosity-contact solver for strong two-way rigid-rigid rigid-fluid coupling
Session/Category Title: Animation: Pretty Solid Physics Research
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We propose Monolith, a monolithic pressure-viscosity-contact solver for more accurately, robustly, and efficiently simulating non-trivial two-way interactions of rigid bodies with inviscid, viscous, or non-Newtonian liquids. Our solver simultaneously handles incompressibility and (optionally) implicit viscosity integration for liquids, contact resolution for rigid bodies, and mutual interactions between liquids and rigid bodies by carefully formulating these as a single unified minimization problem. This monolithic approach reduces or eliminates an array of problematic artifacts, including liquid volume loss, solid interpenetrations, simulation instabilities, artificial “melting” of viscous liquid, and incorrect slip at liquid-solid interfaces. In the absence of solid-solid friction, our minimization problem is a Quadratic Program (QP) with a symmetric positive definite (SPD) matrix and can be treated with a single Linear Complementarity Problem (LCP) solve. When friction is present, we decouple the unified minimization problem into two subproblems so that it can be effectively handled via staggered projections with alternating LCP solves. We also propose a complementary approach for non-Newtonian fluids which can be seamlessly integrated and addressed during the staggered projections. We demonstrate the critical importance of a contact-aware, unified treatment of fluid-solid coupling and the effectiveness of our proposed Monolith solver in a wide range of practical scenarios.
References:
1. Mridul Aanjaneya. 2018. An Efficient Solver for Two-way Coupling Rigid Bodies with Incompressible Flow. Computer Graphics Forum 37, 8 (2018), 59–68.Google ScholarCross Ref
2. Mridul Aanjaneya, Chengguizi Han, Ryan Goldade, and Christopher Batty. 2019. An Efficient Geometric Multigrid Solver for Viscous Liquids. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2, 2, Article 14 (July 2019), 21 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Muzaffer Akbay, Nicholas Nobles, Victor Zordan, and Tamar Shinar. 2018. An extended partitioned method for conservative solid-fluid coupling. ACM Transactions on Graphics 37 (2018), 1–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Nadir Akinci, Markus Ihmsen, Gizem Akinci, Barbara Solenthaler, and Matthias Teschner. 2012. Versatile Rigid-fluid Coupling for Incompressible SPH. ACM Transactions on Graphics 31, 4, Article 62 (2012), 62:1–62:8 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Ryoichi Ando, Nils Thuerey, and Chris Wojtan. 2015. A stream function solver for liquid simulations. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 1–9.Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Mihai Anitescu and Gary D. Hart. 2004. A constraint-stabilized time-stepping approach for rigid multibody dynamics with joints, contact and friction. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg. 60, 14 (2004), 2335–2371.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Uri M. Ascher and Linda R. Petzold. 1998. Computer Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations and Differential-Algebraic Equations (1st ed.). Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, USA.Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Stefan Band, Christoph Gissler, Markus Ihmsen, Jens Cornelis, Andreas Peer, and Matthias Teschner. 2018a. Pressure Boundaries for Implicit Incompressible SPH. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 2, Article 14 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Stefan Band, Christoph Gissler, Andreas Peer, and Matthias Teschner. 2018b. MLS pressure boundaries for divergence-free and viscous SPH fluids. Computers & Graphics 76 (2018), 37 — 46.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. Adam W. Bargteil, Chris Wojtan, Jessica K. Hodgins, and Greg Turk. 2007. A Finite Element Method for Animating Large Viscoplastic Flow. ACM Transactions on Graphics 26, 3, Article 16 (2007).Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Christopher Batty, Florence Bertails, and Robert Bridson. 2007. A Fast Variational Framework for Accurate Solid-fluid Coupling. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3, Article 100 (2007).Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Christopher Batty and Robert Bridson. 2008. Accurate Viscous Free Surfaces for Buckling, Coiling, and Rotating Liquids. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. 219–228.Google ScholarDigital Library
13. J. Baumgarte. 1972. Stabilization of constraints and integrals of motion in dynamical systems. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 1, 1 (1972), 1 — 16.Google ScholarCross Ref
14. Markus Becker, Hendrik Tessendorf, and Matthias Teschner. 2009. Direct Forcing for Lagrangian Rigid-Fluid Coupling. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 15, 3 (2009), 493–503.Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Stephen Boyd and Lieven Vandenberghe. 2004. Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, USA.Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Christopher Brandt, Leonardo Scandolo, Elmar Eisemann, and Klaus Hildebrandt. 2019. The reduced immersed method for real-time fluid-elastic solid interaction and contact simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 38 (2019).Google Scholar
17. Robert Bridson. 2015. Fluid Simulation for Computer Graphics. A K Peters/CRC Press.Google Scholar
18. Mark Carlson, Peter Mucha, and Greg Turk. 2004. Rigid Fluid: Animating the Interplay Between Rigid Bodies and Fluid. ACM Transactions on Graphics 23 (2004).Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Erin Catto. 2020. Box2D. https://box2d.org/Google Scholar
20. Desai Chen, David I. W. Levin, Wojciech Matusik, and Danny M. Kaufman. 2017. Dynamics-Aware Numerical Coarsening for Fabrication Design. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 84 (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Nuttapong Chentanez, Tolga G. Goktekin, Bryan E. Feldman, and James F. O’Brien. 2006. Simultaneous Coupling of Fluids and Deformable Bodies. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. 83–89.Google Scholar
22. Kazem Cheshmi, Danny M. Kaufman, Shoaib Kamil, and Maryam Mehri Dehnavi. 2020. NASOQ: Numerically Accurate Sparsity-Oriented QP Solver. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4, Article 96 (2020).Google ScholarDigital Library
23. M. B. Cline and D. K. Pai. 2003. Post-stabilization for rigid body simulation with contact and constraints. In 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.03CH37422), Vol. 3. 3744–3751 vol.3.Google Scholar
24. Erwin Coumans. 2020. Bullet physics library. http://bulletphysics.org/Google Scholar
25. Gilles Daviet and Florence Bertails-Descoubes. 2016. A Semi-implicit Material Point Method for the Continuum Simulation of Granular Materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4, Article 102 (2016), 102:1–102:13 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. O. Ding and C. Schroeder. 2020. Penalty Force for Coupling Materials with Coulomb Friction. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 26, 7 (2020), 2443–2455.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Zdenek Dostal and Joachim Schoberl. 2005. Minimizing Quadratic Functions Subject to Bound Constraints with the Rate of Convergence and Finite Termination. Computational Optimization and Applications 30, 1 (2005), 23–43.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Zdenek Dostl. 2009. Optimal Quadratic Programming Algorithms: With Applications to Variational Inequalities (1st ed.). Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated.Google Scholar
29. Michael Ferris and Todd Munson. 2000. Complementarity Problems in GAMS and the Path Solver. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 24 (2000), 165–188.Google ScholarCross Ref
30. Dan Gerszewski and Adam W. Bargteil. 2013. Physics-based Animation of Large-scale Splashing Liquids. ACM Transactions on Graphics 32, 6, Article 185 (2013), 6 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Frederic Gibou, Ronald P. Fedkiw, Li-Tien Cheng, and Myungjoo Kang. 2002. A Second-Order-Accurate Symmetric Discretization of the Poisson Equation on Irregular Domains. J. Comput. Phys. 176, 1 (2002), 205 — 227.Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Christoph Gissler, Andreas Peer, Stefan Band, Jan Bender, and Matthias Teschner. 2019. Interlinked SPH Pressure Solvers for Strong Fluid-Rigid Coupling. ACM Transactions on Graphics 38 (2019), 1–13.Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Eran Guendelman, Andrew Selle, Frank Losasso, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2005. Coupling water and smoke to thin deformable and rigid shells. ACM Trans. Graph. 24 (2005), 973–981.Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Qi Guo, Xuchen Han, Chuyuan Fu, Theodore Gast, Rasmus Tamstorf, and Joseph Teran. 2018. A Material Point Method for Thin Shells with Frictional Contact. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 147 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Xuchen Han, Theodore F. Gast, Qi Guo, Stephanie Wang, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Joseph Teran. 2019. A Hybrid Material Point Method for Frictional Contact with Diverse Materials. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2, 2, Article 17 (2019).Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Yuanming Hu, Yu Fang, Ziheng Ge, Ziyin Qu, Yixin Zhu, Andre Pradhana, and Chenfanfu Jiang. 2018. A Moving Least Squares Material Point Method with Displacement Discontinuity and Two-Way Rigid Body Coupling. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 150 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
37. David A.B. Hyde and Ronald Fedkiw. 2019. A unified approach to monolithic solid-fluid coupling of sub-grid and more resolved solids. J. Comput. Phys. 390 (2019), 490 — 526.Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Stefan Jeschke, Tomáš Skřivan, Matthias Müller-Fischer, Nuttapong Chentanez, Miles Macklin, and Chris Wojtan. 2018. Water Surface Wavelets. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 94 (2018).Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Chenfanfu Jiang, Craig Schroeder, Andrew Selle, Joseph Teran, and Alexey Stomakhin. 2015. The Affine Particle-in-cell Method. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, Article 51 (2015), 51:1–51:10 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
40. M. Danny Kaufman, Shinjiro Sueda, L. Doug James, and K. Dinesh Pai. 2008. Staggered projections for frictional contact in multibody systems. ACM Trans. Graph. (2008), 164–11.Google Scholar
41. Gergely Klár, Theodore Gast, Andre Pradhana, Chuyuan Fu, Craig Schroeder, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Joseph Teran. 2016. Drucker-prager Elastoplasticity for Sand Animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4, Article 103 (2016), 103:1–103:12 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Bryan Klingner, Bryan Feldman, Nuttapong Chentanez, and James O’Brien. 2006. Fluid animation with dynamic meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 25 (2006), 820–825.Google ScholarDigital Library
43. Dan Koschier and Jan Bender. 2017. Density Maps for Improved SPH Boundary Handling. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH / Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. Article 1, 10 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
44. Dan Koschier, Jan Bender, Barbara Solenthaler, and Matthias Teschner. 2019. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Techniques for the Physics Based Simulation of Fluids and Solids. In Eurographics 2019 – Tutorials.Google Scholar
45. Tassilo Kugelstadt, Andreas Longva, Nils Thurey, and Jan Bender. 2019. Implicit Density Projection for Volume Conserving Liquids. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (2019), 1–1.Google Scholar
46. Junyu Lai, Yangang Chen, Yu Gu, Christopher Batty, and Justin W.L. Wan. 2020. Fast and Scalable Solvers for the Fluid Pressure Equations with Separating Solid Boundary Conditions. Computer Graphics Forum 39, 2 (2020), 23–33.Google ScholarCross Ref
47. Egor Larionov, Christopher Batty, and Robert Bridson. 2017. Variational Stokes: A Unified Pressure-viscosity Solver for Accurate Viscous Liquids. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 101 (July 2017), 101:1–101:11 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
48. Michael Lentine, Jon Gretarsson, Craig Schroeder, Avi Robinson-Mosher, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2011. Creature Control in a Fluid Environment. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 17 (2011), 682 — 693.Google ScholarDigital Library
49. J. E. Lloyd. 2005. Fast Implementation of Lemke’s Algorithm for Rigid Body Contact Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. 4538–4543.Google ScholarCross Ref
50. Libin Lu, Abtin Rahimian, and Denis Zorin. 2017. Contact-aware simulations of particulate Stokesian suspensions. J. Comput. Phys. 347 (2017), 160–182.Google ScholarDigital Library
51. Miles Macklin and Matthias Müller. 2013. Position Based Fluids. ACM Transactions on Graphics 32, 4, Article 104 (2013), 5 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
52. Patrick Mullen, Keenan Crane, Dmitry Pavlov, Yiying Tong, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2009. Energy-preserving integrators for fluid animation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 28, 3 (2009), 1–8.Google ScholarDigital Library
53. Rahul Narain, Abhinav Golas, and Ming C. Lin. 2010. Free-flowing Granular Materials with Two-way Solid Coupling. ACM Transactions on Graphics 29, 6, Article 173 (2010), 10 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
54. Yen Ting Ng, Chohong Min, and Frédéric Gibou. 2009. An efficient fluid-solid coupling algorithm for single-phase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 23 (2009), 8807 — 8829.Google ScholarDigital Library
55. Miguel A Otaduy, Rasmus Tamstorf, Denis Steinemann, and Markus Gross. 2009. Implicit contact handling for deformable objects. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 28. 559–568.Google ScholarCross Ref
56. Saket Patkar, Mridul Aanjaneya, Wenlong Lu, Michael Lentine, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2016. Towards positivity preservation for monolithic two-way solid-fluid coupling. J. Comput. Phys. 312 (2016).Google Scholar
57. Charles Peskin. 2002. Peskin, C.S.: The immersed boundary method. Acta Numerica 11, 479–517. Acta Numerica 11 (01 2002), 479 — 517.Google ScholarCross Ref
58. Avi Robinson-Mosher, R. Elliot English, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2009. Accurate Tangential Velocities for Solid Fluid Coupling. In Proceedings of the 2009 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA ’09). 227–236.Google ScholarDigital Library
59. Avi Robinson-Mosher, Craig Schroeder, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2011. A Symmetric Positive Definite Formulation for Monolithic Fluid Structure Interaction. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 4 (Feb. 2011), 1547–1566.Google ScholarDigital Library
60. Avi Robinson-Mosher, Tamar Shinar, Jon Gretarsson, Jonathan Su, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2008. Two-way Coupling of Fluids to Rigid and Deformable Solids and Shells. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3, Article 46 (2008), 9 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
61. K. C. Sahu, P. Valluri, P. D. M. Spelt, and O. K. Matar. 2007. Linear instability of pressure-driven channel flow of a Newtonian and a Herschel-Bulkley fluid. Physics of Fluids 19, 12 (2007), 122101.Google ScholarCross Ref
62. K. Schittkowski. 2005. QL: A fortran code for convex quadratic programming – user’s guide, version 2.11. Technical Report.Google Scholar
63. Tamar Shinar, Craig Schroeder, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2008. Two-way coupling of rigid and deformable bodies. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. 95–103.Google ScholarDigital Library
64. Russell Smith. 2008. Open Dynamics Engine. http://www.ode.org/Google Scholar
65. David E. Stewart. 2000. Rigid-Body Dynamics with Friction and Impact. SIAM Rev. 42, 1 (2000), 3–39.Google ScholarDigital Library
66. Tetsuya Takahashi and Ming C. Lin. 2019. A Geometrically Consistent Viscous Fluid Solver with Two-Way Fluid-Solid Coupling. Computer Graphics Forum 38, 2 (2019), 49–58.Google ScholarCross Ref
67. Jie Tan, Yuting Gu, Greg Turk, and C. Liu. 2011. Articulated Swimming Creatures. ACM Trans. Graph. 30 (2011), 58.Google ScholarDigital Library
68. Jie Tan, Kristin Siu, and C. Karen Liu. 2012. Contact Handling for Articulated Rigid Bodies Using LCP. Technical Report GIT-GVU-15-01-2. Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Interactive Computing.Google Scholar
69. Yun Teng, David I. W. Levin, and Theodore Kim. 2016. Eulerian Solid-Fluid Coupling. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 6, Article 200 (2016), 8 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
70. Richard Tonge, Feodor Benevolenski, and Andrey Voroshilov. 2012. Mass Splitting for Jitter-Free Parallel Rigid Body Simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics 31 (2012).Google Scholar
71. Jui-Hsien Wang, Rajsekhar Setaluri, Doug L. James, and Dinesh K. Pai. 2017. Bounce Maps: An Improved Restitution Model for Real-Time Rigid-Body Impact. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 150 (2017).Google ScholarDigital Library
72. D. J. A. Welsh and M. B. Powell. 1967. An upper bound for the chromatic number of a graph and its application to timetabling problems. Comput. J. 10, 1 (01 1967), 85–86.Google ScholarCross Ref
73. Yonghao Yue, Breannan Smith, Christopher Batty, Changxi Zheng, and Eitan Grinspun. 2015. Continuum Foam: A Material Point Method for Shear-Dependent Flows. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 5, Article 160 (2015), 160:1–160:20 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
74. Yonghao Yue, Breannan Smith, Peter Yichen Chen, Maytee Chantharayukhonthorn, Ken Kamrin, and Eitan Grinspun. 2018. Hybrid Grains: Adaptive Coupling of Discrete and Continuum Simulations of Granular Media. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 6, Article 283 (2018), 19 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
75. Jae Yun and Yu-Du Han. 2002. Modified incomplete Cholesky factorization preconditioners for a symmetric positive definite matrix. Bulletin of the Korean Mathematical Society 39 (01 2002).Google Scholar
76. Bo Zhu, Minjae Lee, Ed Quigley, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2015. Codimensional non-Newtonian Fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, Article 115 (2015), 9 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
77. Yongning Zhu, Eftychios Sifakis, Joseph Teran, and Achi Brandt. 2010. An Efficient Multigrid Method for the Simulation of High-Resolution Elastic Solids. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 2, Article 16 (2010).Google ScholarDigital Library