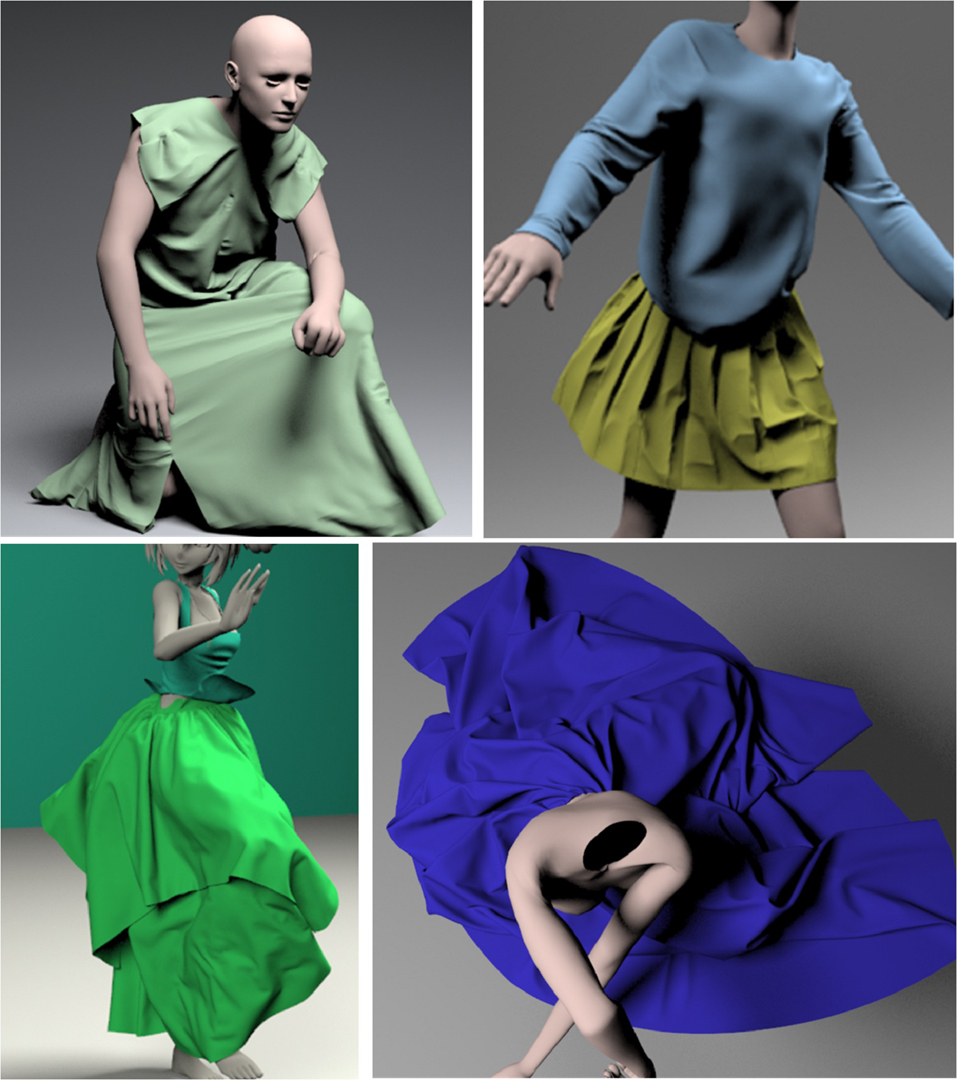
“P-cloth: interactive complex cloth simulation on multi-GPU systems using dynamic matrix assembly and pipelined implicit integrators” by Li, Tang, Tong, Cai, Zhao, et al. …
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- P-cloth: interactive complex cloth simulation on multi-GPU systems using dynamic matrix assembly and pipelined implicit integrators
Session/Category Title: Animation: Pretty Solid Physics Research
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We present a novel parallel algorithm for cloth simulation that exploits multiple GPUs for fast computation and the handling of very high resolution meshes. To accelerate implicit integration, we describe new parallel algorithms for sparse matrix-vector multiplication (SpMV) and for dynamic matrix assembly on a multi-GPU workstation. Our algorithms use a novel work queue generation scheme for a fat-tree GPU interconnect topology. Furthermore, we present a novel collision handling scheme that uses spatial hashing for discrete and continuous collision detection along with a non-linear impact zone solver. Our parallel schemes can distribute the computation and storage overhead among multiple GPUs and enable us to perform almost interactive simulation on complex cloth meshes, which can hardly be handled on a single GPU due to memory limitations. We have evaluated the performance with two multi-GPU workstations (with 4 and 8 GPUs, respectively) on cloth meshes with 0.5 — 1.65M triangles. Our approach can reliably handle the collisions and generate vivid wrinkles and folds at 2 — 5 fps, which is significantly faster than prior cloth simulation systems. We observe almost linear speedups with respect to the number of GPUs.
References:
1. Marco Ament, Gunter Knittel, Daniel Weiskopf, and Wolfgang Strasser. 2010. A Parallel Preconditioned Conjugate Gradient Solver for the Poisson Problem on a Multi-GPU Platform. In 2010 18th Euromicro Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Network-based Processing. 583–592.Google ScholarDigital Library
2. David Baraff and Andrew Witkin. 1998. Large Steps in Cloth Simulation. In Proceedings of the 25th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques (SIGGRAPH ’98). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 43–54.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. David Baraff, Andrew Witkin, and Michael Kass. 2003. Untangling Cloth. In SIGGRAPH ’03. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 862–870.Google Scholar
4. Nathan Bell and Michael Garland. 2008. Efficient Sparse Matrix-vector Multiplication on CUDA. Technical Report. Technical Report NVR-2008-004, Nvidia Corporation.Google Scholar
5. Sofien Bouaziz, Sebastian Martin, Tiantian Liu, Ladislav Kavan, and Mark Pauly. 2014. Projective Dynamics: Fusing Constraint Projections for Fast Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4, Article 154 (July 2014), 11 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Robert Bridson, Ronald Fedkiw, and John Anderson. 2002. Robust Treatment of Collisions, Contact and Friction for Cloth Animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 21, 3 (2002), 594–603.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Tyson Brochu, Essex Edwards, and Robert Bridson. 2012. Efficient Geometrically Exact Continuous Collision Detection. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (2012), 96:1–96:7.Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Juan J. Casafranca, Gabriel Cirio, Alejandro Rodríguez, Eder Miguel, and Miguel A. Otaduy. 2020. Mixing Yarns and Triangles in Cloth Simulation. Computer Graphics Forum 39, 2 (2020), 101–110.Google ScholarCross Ref
9. Ali Cevahir, Akira Nukada, and Satoshi Matsuoka. 2009. Fast Conjugate Gradients with Multiple GPUs. In Inter. Conf. on Computational Science. Springer, 893–903.Google Scholar
10. Jieyu Chu, Nafees Bin Zafar, and Xubo Yang. 2017. A Schur Complement Preconditioner for Scalable Parallel Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 5 (2017), 163.Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Gabriel Cirio, Jorge Lopez-Moreno, David Miraut, and Miguel A. Otaduy. 2014. Yarn-level Simulation of Woven Cloth. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH Asia) 33, 6, Article 207 (Nov. 2014), 11 pages.Google Scholar
12. David Eberle. 2018. Better Collisions and Faster Cloth for Pixar’s Coco. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2018 Talks (SIGGRAPH ’18). Article 8, 2 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Iman Faraji, Seyed H Mirsadeghi, and Ahmad Afsahi. 2016. Topology-aware GPU Selection on Multi-GPU Nodes. In 2016 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW). IEEE, 712–720.Google Scholar
14. Salvatore Filippone, Valeria Cardellini, Davide Barbieri, and Alessandro Fanfarillo. 2017. Sparse Matrix-vector Multiplication on GPGPUs. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS) 43, 4 (2017), 30.Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Jiaquan Gao, Yu Wang, and Jun Wang. 2017. A Novel Multi-graphics Processing Unit Parallel Optimization Framework for the Sparse Matrix-vector Multiplication. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 29, 5 (2017), e3936.Google ScholarCross Ref
16. Serban Georgescu and Hiroshi Okuda. 2010. Conjugate Gradients on Multiple GPUs. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 64, 10–12 (2010), 1254–1273.Google ScholarCross Ref
17. Dominik Göddeke, Robert Strzodka, Jamaludin Mohd-Yusof, Patrick McCormick, Sven HM Buijssen, Matthias Grajewski, and Stefan Turek. 2007. Exploring Weak Scalability for FEM Calculations on a GPU-enhanced Cluster. Parallel Comput. 33, 10–11 (2007), 685–699.Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Naga K. Govindaraju, David Knott, Nitin Jain, Ilknur Kabul, Rasmus Tamstorf, Russell Gayle, Ming C. Lin, and Dinesh Manocha. 2005. Interactive Collision Detection between Deformable Models using Chromatic Decomposition. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 24, 3 (July 2005), 991–999.Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Roger G. Grimes, David R. Kincaid, and David M. Young. 1979. ITPACK 2.0 User’s Guide. Report No. CNA-150. Center for Numerical Analysis, University of Texas at Austin (1979).Google Scholar
20. Ping Guo and Changjiang Zhang. 2016. Performance Optimization for SpMV on Multi-GPU Systems Using Threads and Multiple Streams. In 2016 International Symposium on Computer Architecture and High Performance Computing Workshops (SBAC-PADW). IEEE, 67–72.Google Scholar
21. Qi Guo, Xuchen Han, Chuyuan Fu, Theodore Gast, Rasmus Tamstorf, and Joseph Teran. 2018. A Material Point Method for Thin Shells with Frictional Contact. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4 (2018), 147:1–147:15.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Dongsoo Han. 2015. Interleaved Cloth Simulation. In Workshop on Virtual Reality Interaction and Physical Simulation, Fabrice Jaillet, Florence Zara, and Gabriel Zachmann (Eds.). The Eurographics Association. Google ScholarCross Ref
23. David Harmon, Etienne Vouga, Rasmus Tamstorf, and Eitan Grinspun. 2008. Robust Treatment of Simultaneous Collisions. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (2008), 23:1–23:4.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Marco Hutter, Martin Knuth, and Arjan Kuijper. 2014. Mesh partitioning for parallel garment simulation. In Proceedings of WSCG. 125–133.Google Scholar
25. Chenfanfu Jiang, Theodore Gast, and Joseph Teran. 2017. Anisotropic Elastoplasticity for Cloth, Knit and Hair Frictional Contact. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 152:1–14.Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Ye Juntao, Ma Guanghui, Jiang Liguo, Chen Lan, Li Jituo, Xiong Gang, Zhang Xiaopeng, and Tang Min. 2017. A Unified Cloth Untangling Framework Through Discrete Collision Detection. Computer Graphics Forum 36, 7 (2017), 217–228.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Hyung-Jin Kim. 2011. GPU Performance of Conjugate Gradient Solver with Staggered Fermions. In The XXVIII International Symposium on Lattice Field Theory. SISSA Medialab, 028.Google Scholar
28. Martin Komaritzan and Mario Botsch. 2019. Fast Projective Skinning. In Motion, Interaction and Games. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 22, 10 pages.Google Scholar
29. Aimei Kutt. 2018. Art-directed Costumes at Pixar: Design, Tailoring, and Simulation in Production. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2018 Courses (SA ’18). Article 2, 102 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Yongjoon Lee, Sung-Eui Yoon, Seungwoo Oh, Duksu Kim, and Sunghee Choi. 2010. Multi-Resolution Cloth Simulation. Comp. Graph. Forum 29, 7 (2010), 2225–2232.Google ScholarCross Ref
31. Junbang Liang and Ming C. Lin. 2018. Time-Domain Parallelization for Accelerating Cloth Simulation. Computer Graphics Forum 37, 8 (2018), 21–34.Google ScholarCross Ref
32. Haixiang Liu, Nathan Mitchell, Mridul Aanjaneya, and Eftychios Sifakis. 2016. A Scalable Schur-complement Fluids Solver for Heterogeneous Compute Platforms. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 6, Article 201 (Nov. 2016), 12 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Tiantian Liu, Adam W. Bargteil, James F. O’Brien, and Ladislav Kavan. 2013. Fast Simulation of Mass-Spring Systems. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6 (2013), 209:1–7.Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Tiantian Liu, Sofien Bouaziz, and Ladislav Kavan. 2017. Quasi-Newton Methods for Real-Time Simulation of Hyperelastic Materials. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 3, Article 23 (May 2017), 16 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Nathan Luehr. 2016. Fast Multi-GPU Collectives with NCCL. https://devblogs.nvidia.com/fast-multi-gpu-collectives-nccl/Google Scholar
36. Michael Malahe. 2016. PDE Solvers for Hybrid CPU-GPU Architectures. Ph.D. Dissertation. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.Google Scholar
37. Dinesh Manocha. 1998. Solving Polynomial Equations. Applications of Computational Algebraic Geometry: American Mathematical Society Short Course, January 6–7, 1997, San Diego, California 53 (1998), 41.Google Scholar
38. Dinesh Manocha and James Demmel. 1994. Algorithms for Intersecting Parametric and Algebraic Curves I: Simple Intersections. ACM Trans. Graph. 13, 1 (Jan. 1994), 73–100.Google Scholar
39. Eike Müller, Xu Guo, Robert Scheichl, and Sinan Shi. 2013. Matrix-Free GPU Implementation of a Preconditioned Conjugate Gradient Solver for Anisotropic Elliptic PDEs. Comput. Vis. Sci. 16, 2 (April 2013), 41–58. Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Eike Hermann Müller, Robert Scheichl, and Eero Vainikko. 2014. Petascale Elliptic Solvers for Anisotropic PDEs on GPU Clusters. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1402.3545 (2014).Google Scholar
41. Matthias Müller, Nuttapong Chentanez, Tae-Yong Kim, and Miles Macklin. 2015. Air Meshes for Robust Collision Handling. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, Article 133 (July 2015), 9 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Rahul Narain, Armin Samii, and James F. O’Brien. 2012. Adaptive Anisotropic Remeshing for Cloth Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, Article 152 (Nov. 2012), 10 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
43. Xiang Ni, L.V. Kale, and R. Tamstorf. 2015. Scalable Asynchronous Contact Mechanics Using Charm+ +. In IEEE Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS). 677–686.Google Scholar
44. NVIDIA. 2017. DIGITS DEVBOX User Guide. https://docs.nvidia.com/dgx/pdf/DIGITS_DEVBOX_User_Guide.pdfGoogle Scholar
45. NVIDIA. 2020. NVIDIA DGX-2 System User Guide. https://docs.nvidia.com/dgx/pdf/dgx2-user-guide.pdfGoogle Scholar
46. Miguel A. Otaduy, Rasmus Tamstorf, Denis Steinemann, and Markus Gross. 2009. Implicit Contact Handling for Deformable Objects. Computer Graphics Forum 28, 2 (2009), 559–568.Google ScholarCross Ref
47. Matthew Overby, George E. Brown, Jie Li, and Rahul Narain. 2017. ADMM ⊇ Projective Dynamics: Fast Simulation of Hyperelastic Models with Dynamic Constraints. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 23, 10 (2017), 2222–2234.Google ScholarDigital Library
48. Simon Pabst, Artur Koch, and Wolfgang Straßer. 2010. Fast and Scalable CPU/GPU Collision Detection for Rigid and Deformable Surfaces. Comp. Graph. Forum 29, 5 (2010), 1605–1612.Google ScholarCross Ref
49. Yue Peng, Bailin Deng, Juyong Zhang, Fanyu Geng, Wenjie Qin, and Ligang Liu. 2018. Anderson Acceleration for Geometry Optimization and Physics Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 42 (July 2018), 14 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
50. Bhagyashree C. Prabhune and Krishnan Suresh. 2020. A Fast Matrix-free Elasto-plastic Solver for Predicting Residual Stresses in Additive Manufacturing. Comput. Aided Des. 123 (2020), 102829.Google ScholarCross Ref
51. Xavier Provot. 1995. Deformation Constraints in a Mass-spring Model to Describe Rigid Cloth Behavior. In Proc. of Graphics Interface. 147–154.Google Scholar
52. Xavier Provot. 1997. Collision and Self-collision Handling in Cloth Model Dedicated to Design Garments. In Graphics Interface. 177–189.Google Scholar
53. Andrew Selle, Jonathan Su, Geoffrey Irving, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2009. Robust High-Resolution Cloth Using Parallelism, History-Based Collisions, and Accurate Friction. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comp. Graph. 15, 2 (March 2009), 339–350.Google ScholarDigital Library
54. Wenyi Shao and William McCollough. 2017. Multiple-GPU-based Frequency-dependent Finite-difference Time Domain Formulation using MATLAB Parallel Computing Toolbox. Progress In Electromagnetics Research 60 (2017), 93–100.Google ScholarCross Ref
55. Eftychios Sifakis, Sebastian Marino, and Joseph Teran. 2008. Globally Coupled Collision Handling using Volume Preserving Impulses. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. 147–153.Google ScholarDigital Library
56. Mohammed Sourouri, Johannes Langguth, Filippo Spiga, Scott B Baden, and Xing Cai. 2015. CPU+ GPU programming of Stencil Computations for Resource-Efficient use of GPU Clusters. In 2015 IEEE 18th International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering. IEEE, 17–26.Google ScholarDigital Library
57. Min Tang, Zhongyuan Liu, Ruofeng Tong, and Dinesh Manocha. 2018a. PSCC: Parallel Self-Collision Culling with Spatial Hashing on GPUs. Proceedings of the ACM on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques 1, 1 (2018), 18:1–18.Google ScholarDigital Library
58. Min Tang, Ruofeng Tong, Zhendong Wang, and Dinesh Manocha. 2014. Fast and Exact Continuous Collision Detection with Bernstein Sign Classification. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH Asia) 33 (November 2014), 186:1–186:8. Issue 6.Google ScholarDigital Library
59. Min Tang, Huamin Wang, Le Tang, Ruofeng Tong, and Dinesh Manocha. 2016. CAMA: Contact-Aware Matrix Assembly with Unified Collision Handling for GPU-based Cloth Simulation. Computer Graphics Forum 35, 2 (2016), 511–521.Google ScholarCross Ref
60. Min Tang, Tongtong Wang, Zhongyuan Liu, Ruofeng Tong, and Dinesh Manocha. 2018b. I-Cloth: Incremental Collision Handling for GPU-Based Interactive Cloth Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 6 (November 2018), 204:1–10.Google ScholarDigital Library
61. Mickeal Verschoor and Andrei C Jalba. 2012. Analysis and Performance Estimation of the Conjugate Gradient Method on Multiple GPUs. Parallel Comput. 38, 10–11 (2012), 552–575.Google ScholarDigital Library
62. Etienne Vouga, David Harmon, Rasmus Tamstorf, and Eitan Grinspun. 2011. Asynchronous Variational Contact Mechanics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 200 (June 2011), 2181–2194.Google Scholar
63. Huamin Wang. 2014. Defending Continuous Collision Detection Against Errors. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 33, 4, Article 122 (July 2014), 10 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
64. Huamin Wang. 2018. Rule-Free Sewing Pattern Adjustment with Precision and Efficiency. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 53 (July 2018), 13 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
65. Huamin Wang, James F. O’Brien, and Ravi Ramamoorthi. 2011. Data-Driven Elastic Models for Cloth: Modeling and Measurement. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4, Article Article 71 (July 2011), 12 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
66. Xinlei Wang, Minchen Li, Yu Fang, Xinxin Zhang, Ming Gao, Min Tang, Danny M. Kaufman, and Chenfanfu Jiang. 2020a. Hierarchical Optimization Time Integration for CFL-Rate MPM Stepping. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 3, Article 21 (April 2020), 16 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
67. Xinlei Wang, Yuxing Qiu, Stuart R. Slattery, Yu Fang, Minchen Li, Song-Chun Zhu, Yixin Zhu, Min Tang, Dinesh Manocha, and Chenfanfu Jiang. 2020b. A Massively Parallel and Scalable Multi-GPU Material Point Method. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH 39, 5, Article 1 (Aug. 2020), 12 pages.Google Scholar
68. Zhendong Wang, Longhua Wu, Marco Fratarcangeli, Min Tang, and Huamin Wang. 2018. Parallel Multigrid for Nonlinear Cloth Simulation. Computer Graphics Forum 37, 7 (2018), 131–141.Google ScholarCross Ref
69. Audrey Wong, David Eberle, and Theodore Kim. 2018. Clean Cloth Inputs: Removing Character Self-intersections with Volume Simulation. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2018 Talks (SIGGRAPH ’18). Article 42, 2 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
70. Ichitaro Yamazaki, Stanimire Tomov, and Jack Dongarra. 2015. Mixed-precision Cholesky QR factorization and its case studies on multicore CPU with multiple GPUs. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 37, 3 (2015), C307–C330.Google ScholarCross Ref
71. Florence Zara, François Faure, and Vincent Jean-Marc. 2004. Parallel Simulation of Large Dynamic System on a PCs Cluster: Application to Cloth Simulation. International Journal of Computers and Applications 26, 3 (March 2004).Google Scholar
72. Dongliang Zhang. 2005. Cloth Design and Application. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Courses. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 5–37.Google Scholar
73. Jun Zhou, Yifeng Cui, Efecan Poyraz, Dong Ju Choi, and Clark C Guest. 2013. Multi-GPU Implementation of a 3D Finite Difference Time Domain Earthquake Code on Heterogeneous Supercomputers. Proc. of Computer Science 18 (2013), 1255–1264.Google ScholarCross Ref